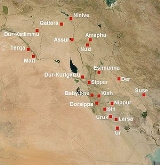
Nuzi
Encyclopedia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
n city southwest of Kirkuk
Kirkuk
Kirkuk is a city in Iraq and the capital of Kirkuk Governorate.It is located in the Iraqi governorate of Kirkuk, north of the capital, Baghdad...
in modern Al Ta'amim Governorate of Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
, located near the Tigris
Tigris
The Tigris River is the eastern member of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of southeastern Turkey through Iraq.-Geography:...
river. The site consists of
one medium sized multiperiod tell and two small single period mounds.
History
The town of Gasur was apparently founded during the Akkadian Empire in thelate third millennium. In the middle second millennium Hurrians
Hurrians
The Hurrians were a people of the Ancient Near East who lived in Northern Mesopotamia and adjacent regions during the Bronze Age.The largest and most influential Hurrian nation was the kingdom of Mitanni. The population of the Hittite Empire in Anatolia to a large part consisted of Hurrians, and...
absorbed
the town and renamed it Nuzi. The history of the site during the intervening period
is unclear, though the presence of a few cuneiform tables from Old Assyria
indicates that trade with nearby Assur
Assur
Assur , was one of the capitals of ancient Assyria. The remains of the city are situated on the western bank of river Tigris, north of the confluence with the tributary Little Zab river, in modern day Iraq, more precisely in the Al-Shirqat District .Assur is also...
was taking place. After the fall
of the Hurrian kingdom of Mitanni
Mitanni
Mitanni or Hanigalbat was a loosely organized Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria and south-east Anatolia from ca. 1500 BC–1300 BC...
to the Hittites
Hittites
The Hittites were a Bronze Age people of Anatolia.They established a kingdom centered at Hattusa in north-central Anatolia c. the 18th century BC. The Hittite empire reached its height c...
, Nuzi fell to the
Assyrians and went into decline. Note that while Hurrian period is well
known because those levels of the site were fully excavated, the earlier
history is less firm because of only scanty digging. The history of Nuzi is closely
interrelated with that of the nearby towns of Eshnunna
Eshnunna
Eshnunna was an ancient Sumerian city and city-state in central Mesopotamia. Although situated in the Diyala Valley north-east of Sumer proper, the city nonetheless belonged securely within the Sumerian cultural milieu.The tutelary deity of the city was Tishpak .- History :Occupied from the Jemdet...
and Khafajah
Khafajah
Khafajah or Khafaje was the ancient town of Tutub in the city-state of Eshnunna...
.
Archaeology
While tablets from Yorghan Tepe began appearing back as far as 1896, the first serious archaeological efforts began in 1925 after Gertrude BellGertrude Bell
Gertrude Margaret Lowthian Bell, CBE was an English writer, traveller, political officer, administrator, and archaeologist who explored, mapped, and became highly influential to British imperial policy-making due to her extensive travels in Greater Syria, Mesopotamia, Asia Minor, and Arabia. Along...
noticed tablets appearing in the markets of Baghdad. The dig was mainly worked by Edward Chiera, Robert Pfeiffer, and Richard Starr under the auspices of the Iraqi Museum and the Baghdad School of the American Schools of Oriental Research
American Schools of Oriental Research
The American Schools of Oriental Research, founded in 1900, supports and encourages the study of the peoples and cultures of the Near East, from the earliest times to the present. It is apolitical and has no religious affiliation...
and later the Harvard University
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States, established in 1636 by the Massachusetts legislature. Harvard is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and the first corporation chartered in the country...
and Fogg Art Museum
Fogg Art Museum
The Fogg Museum, opened to the public in 1896, is the oldest of Harvard University's art museums. The Fogg joins the Busch-Reisinger Museum and the Arthur M. Sackler Museum as part of the Harvard Art Museums....
.
Excavations continued through 1931. The site has 15 occupation levels. The hundreds of tablets and other finds recovered were published in a series of volumes. More finds continue to be published to this day.
To date, around 5000 tablets are known, mostly held at the Oriental Institute
Oriental Institute
Oriental Institute may refer to a number of institutes of Oriental studies:United States* Oriental Institute, Chicago, part of the University of ChicagoEngland* Oriental Institute, Oxford, part of the University of Oxford...
, the Harvard Semitic Museum and the Iraq Museum in Baghdad
Baghdad
Baghdad is the capital of Iraq, as well as the coterminous Baghdad Governorate. The population of Baghdad in 2011 is approximately 7,216,040...
. Many are routine legal and business documents and about one quarter concern the business transactions
of a single family. The vast majority of finds are from the Hurrian period during the second millennium BC with the remainder dating back to the towns founding during the Akkadian Empire. Perhaps the most famous item found is a map of the local region dated to the Akkadian period. An archive contemporary to the Hurrian archive at Nuzi has been excavated from the "Green Palace" at the site of Tell al-Fakhar
Tell al-Fakhar
Tell al-Fakhar is a tell, or archaeological settlement mound, in Kirkuk Governorate, northeastern Iraq. Excavations were carried out at the site between 1967 and 1969 by the Directorate-General of Antiquities of Iraq. The site measures and is high...
, 35 kilometres (21.7 mi) southwest of Nuzi.
See also
- Cities of the ancient Near EastCities of the ancient Near EastThe largest cities in the Bronze Age ancient Near East housed several tens of thousands. Memphis in the Early Bronze Age with some 30,000 inhabitants was the largest city of the time by far...
- Short chronology timelineShort chronology timelineThe short chronology is one chronology of the Near Eastern Bronze and Early Iron Age, which fixes the reign of Hammurabi to 1728 BC – 1686 BC and the sack of Babylon to 1531 BC....

