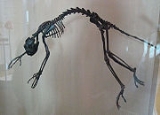
Notharctus
Encyclopedia
Notharctus was an early primate
that inhabited Europe
and North America
50 million years ago. Modern lemur
s evolved from primates similar to this genus.
The body form of Notharctus is similar to that of modern lemurs. Unlike lemurs, however, Notharctus had a shorter face and forward-facing eyes surrounded by an enclosed circle of bone. Its fingers were elongated for clamping onto branches, including the development of a thumb
. Its spine is flexible, like the living lemurs, and the animal was about 40 centimetres (15.7 in) in length, excluding the long tail. It probably ate fruits and insects.
The lineage that includes Notharctus, the Adapiformes
, is extinct; the last representative, Sivaladapis, died out during the late Miocene
.
There were at least five different Notharctus species. Fossils from at least seven other potential species have also been discovered.
Primate
A primate is a mammal of the order Primates , which contains prosimians and simians. Primates arose from ancestors that lived in the trees of tropical forests; many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging three-dimensional environment...
that inhabited Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
and North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
50 million years ago. Modern lemur
Lemur
Lemurs are a clade of strepsirrhine primates endemic to the island of Madagascar. They are named after the lemures of Roman mythology due to the ghostly vocalizations, reflective eyes, and the nocturnal habits of some species...
s evolved from primates similar to this genus.
The body form of Notharctus is similar to that of modern lemurs. Unlike lemurs, however, Notharctus had a shorter face and forward-facing eyes surrounded by an enclosed circle of bone. Its fingers were elongated for clamping onto branches, including the development of a thumb
Thumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position , the thumb is the lateral-most digit...
. Its spine is flexible, like the living lemurs, and the animal was about 40 centimetres (15.7 in) in length, excluding the long tail. It probably ate fruits and insects.
The lineage that includes Notharctus, the Adapiformes
Adapiformes
Adapiformes are an extinct group of primitive primates.The adapiformes radiated throughout much of the northern continental mass, reaching as far south as northern Africa and tropical Asia. The adapiformes existed from the Eocene to the Miocene epoch...
, is extinct; the last representative, Sivaladapis, died out during the late Miocene
Miocene
The Miocene is a geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about . The Miocene was named by Sir Charles Lyell. Its name comes from the Greek words and and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern sea invertebrates than the Pliocene. The Miocene follows the Oligocene...
.
There were at least five different Notharctus species. Fossils from at least seven other potential species have also been discovered.

