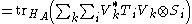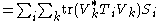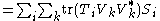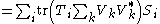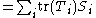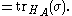No-communication theorem
Encyclopedia
In quantum information theory, a no-communication theorem is a result which gives conditions under which instantaneous transfer of information between two observers is impossible. These results can be applied to understand the so-called paradoxes in quantum mechanics
such as the EPR paradox
or violations of local realism obtained in tests of Bell's theorem
. In these experiments, the no-communication theorem shows that failure of local realism does not lead to what could be referred to as "spooky communication at a distance" (in analogy with Einstein's labeling of quantum entanglement
as "spooky action at a distance").
perform local observations on a common bipartite system, and uses the statistical machinery of quantum mechanics, namely density states and quantum operation
s.
Alice and Bob perform measurements on system S whose underlying Hilbert space
is

It is also assumed that everything is finite dimensional to avoid convergence issues. The state of the composite system is given by a density operator on H. Any density operator σ on H is a sum of the form:

where Ti and Si are operators on HA and HB which however need not be states on the subsystems (that is non-negative of trace 1). In fact, the claim holds trivially for separable states. If the shared state σ is separable, it is clear that any local operation by Alice will leave Bob's system intact. Thus the point of the theorem is no communication can be achieved via a shared entangled state.
Alice performs a local measurement on her subsystem. In general, this is described by a quantum operation, on the system state, of the following kind

where Vk are called Kraus matrices which satisfy
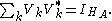
The term
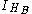
from the expression
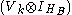
means that Alice's measurement apparatus does not interact with Bob's subsystem.
Supposing the combined system is prepared in state σ and assuming for purposes of argument a non-relativistic situation, immediately (with no time delay) after Alice performs her measurement, the relative state of Bob's system is given by the partial trace
of the overall state with respect to Alice's system. In symbols, the relative state of Bob's system after Alice's operation is

where is the partial trace mapping with respect to Alice's system.
is the partial trace mapping with respect to Alice's system.
One can directly calculate this state:

From this it is argued that, statistically, Bob cannot tell the difference between what Alice did and a random measurement (or whether she did anything at all).
Others have questioned if the no-communication theorem holds for signalling methods using ensembles of entangled particle pairs. As the no-communication theorem is a mathematical derivation on the Hilbert space of a single particle, its implications are not as clear for an ensemble of particles; where one is not attempting to transmit a single bit through a single particle, but instead a single bit through many particles (partial information through each particle). In this case the binary basis state would be over the state of the ensemble, not a property of the Hilbert state of any particular particle. Thus only a measurement on the ensemble as a whole would resolve a bit. However, typically these kind of quantum eraser experiment
s also require a subluminal classical channel for coincidence detection. Physicist John G. Cramer
at the University of Washington
is attempting to replicate one of these experiments and demonstrate whether or not it can produce superluminal communication.
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
such as the EPR paradox
EPR paradox
The EPR paradox is a topic in quantum physics and the philosophy of science concerning the measurement and description of microscopic systems by the methods of quantum physics...
or violations of local realism obtained in tests of Bell's theorem
Bell's theorem
In theoretical physics, Bell's theorem is a no-go theorem, loosely stating that:The theorem has great importance for physics and the philosophy of science, as it implies that quantum physics must necessarily violate either the principle of locality or counterfactual definiteness...
. In these experiments, the no-communication theorem shows that failure of local realism does not lead to what could be referred to as "spooky communication at a distance" (in analogy with Einstein's labeling of quantum entanglement
Quantum entanglement
Quantum entanglement occurs when electrons, molecules even as large as "buckyballs", photons, etc., interact physically and then become separated; the type of interaction is such that each resulting member of a pair is properly described by the same quantum mechanical description , which is...
as "spooky action at a distance").
Formulation
The proof of the theorem is commonly illustrated for the setup of Bell tests in which two observers Alice and BobAlice and Bob
The names Alice and Bob are commonly used placeholder names for archetypal characters in fields such as cryptography and physics. The names are used for convenience; for example, "Alice sends a message to Bob encrypted with his public key" is easier to follow than "Party A sends a message to Party...
perform local observations on a common bipartite system, and uses the statistical machinery of quantum mechanics, namely density states and quantum operation
Quantum operation
In quantum mechanics, a quantum operation is a mathematical formalism used to describe a broad class of transformations that a quantum mechanical system can undergo. This was first discussed as a general stochastic transformation for a density matrix by George Sudarshan...
s.
Alice and Bob perform measurements on system S whose underlying Hilbert space
Hilbert space
The mathematical concept of a Hilbert space, named after David Hilbert, generalizes the notion of Euclidean space. It extends the methods of vector algebra and calculus from the two-dimensional Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space to spaces with any finite or infinite number of dimensions...
is

It is also assumed that everything is finite dimensional to avoid convergence issues. The state of the composite system is given by a density operator on H. Any density operator σ on H is a sum of the form:

where Ti and Si are operators on HA and HB which however need not be states on the subsystems (that is non-negative of trace 1). In fact, the claim holds trivially for separable states. If the shared state σ is separable, it is clear that any local operation by Alice will leave Bob's system intact. Thus the point of the theorem is no communication can be achieved via a shared entangled state.
Alice performs a local measurement on her subsystem. In general, this is described by a quantum operation, on the system state, of the following kind

where Vk are called Kraus matrices which satisfy
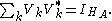
The term
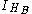
from the expression
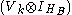
means that Alice's measurement apparatus does not interact with Bob's subsystem.
Supposing the combined system is prepared in state σ and assuming for purposes of argument a non-relativistic situation, immediately (with no time delay) after Alice performs her measurement, the relative state of Bob's system is given by the partial trace
Partial trace
In linear algebra and functional analysis, the partial trace is a generalization of the trace. Whereas the trace is a scalar valued function on operators, the partial trace is an operator-valued function...
of the overall state with respect to Alice's system. In symbols, the relative state of Bob's system after Alice's operation is

where
 is the partial trace mapping with respect to Alice's system.
is the partial trace mapping with respect to Alice's system.One can directly calculate this state:

From this it is argued that, statistically, Bob cannot tell the difference between what Alice did and a random measurement (or whether she did anything at all).
Some comments
- Notice that once time evolutionTime evolutionTime evolution is the change of state brought about by the passage of time, applicable to systems with internal state . In this formulation, time is not required to be a continuous parameter, but may be discrete or even finite. In classical physics, time evolution of a collection of rigid bodies...
operates on the density state, then the calculation in the proof fails. In the case of the (non-relativistic) Schrödinger equationSchrödinger equationThe Schrödinger equation was formulated in 1926 by Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger. Used in physics , it is an equation that describes how the quantum state of a physical system changes in time....
which has infinite propagation speed, then of course the above analysis will fail for positive times. Clearly, the importance of the no-communication theorem for positive times is for relativistic systems.
- The no-communication theorem thus says shared entanglement alone can not be used to transmit quantum information. Compare this with the no teleportation theoremNo teleportation theoremIn quantum information theory, the no-teleportation theorem states that quantum information cannot be measured with complete accuracy.-Formulation:The term quantum information refers to information stored in the state of a quantum system...
, which states a classical information channelClassical information channelIn quantum information science, classical information channel is a communication channel that can be used to transmit classical information...
can not transmit quantum information. (By transmit, we mean transmission with full fidelity.) However, quantum teleportationQuantum teleportationQuantum teleportation, or entanglement-assisted teleportation, is a process by which a qubit can be transmitted exactly from one location to another, without the qubit being transmitted through the intervening space...
schemes utilize both resources to achieve what is impossible for either alone.
Opposing viewpoint
Some authors have argued that most of the proofs of the no-communication theorem are actual circular. In their view, a no-signalling condition is built into the assumptions of the bipartite Hilbert space (the tensor product of the two individual Hilbert spaces) and the locally restricted operators. Therefore, proofs like the one above do not forbid superluminal communication, but show that the formalism of quantum mechanics is consistent in that no superluminal causal interactions appear when the base assumptions do not include them.Others have questioned if the no-communication theorem holds for signalling methods using ensembles of entangled particle pairs. As the no-communication theorem is a mathematical derivation on the Hilbert space of a single particle, its implications are not as clear for an ensemble of particles; where one is not attempting to transmit a single bit through a single particle, but instead a single bit through many particles (partial information through each particle). In this case the binary basis state would be over the state of the ensemble, not a property of the Hilbert state of any particular particle. Thus only a measurement on the ensemble as a whole would resolve a bit. However, typically these kind of quantum eraser experiment
Quantum eraser experiment
In quantum mechanics, the quantum eraser experiment is a double-slit experiment that demonstrates several fundamental aspects of the quantum theory, including quantum entanglement and complementarity....
s also require a subluminal classical channel for coincidence detection. Physicist John G. Cramer
John G. Cramer
John G. Cramer is a professor of physics at the University of Washington in Seattle, the United States. When not teaching, he works with the STAR detector at the new Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider at Brookhaven National Laboratory, and the particle accelerator at CERN in Geneva, Switzerland...
at the University of Washington
University of Washington
University of Washington is a public research university, founded in 1861 in Seattle, Washington, United States. The UW is the largest university in the Northwest and the oldest public university on the West Coast. The university has three campuses, with its largest campus in the University...
is attempting to replicate one of these experiments and demonstrate whether or not it can produce superluminal communication.