Molluscum contagiosum virus
Encyclopedia
The Molluscum contagiosum virus or MCV is a species of virus in the poxvirus family, which causes the disease Molluscum contagiosum
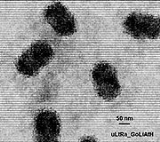
in humans. Virions have a complex structure and is consistent with the structure of the poxvirus family: an envelope, surface membrane, core, and lateral bodies. Virus may be contained within inclusion bodies and mature by budding through the membrane of the host cell giving rise to a large amount of viral shedding
in a short period of time. Approximate measurements of the virus are 200 nm in diameter, 320 nm in length and 100 nm in height.
 Diagnosis is made on the clinical appearance; the virus cannot routinely be cultured.
Diagnosis is made on the clinical appearance; the virus cannot routinely be cultured.
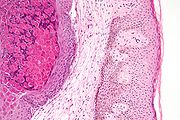
The diagnosis can be confirmed by excisional biopsy
.
There are 4 types of MCV, MCV-1 to -4. MCV-1 is the most prevalent in human infections, and MCV-2 seen usually in adults and often sexually transmitted. Polymerase chain reaction
techniques are being developed to help confirm lesions as being caused by MCV, and distinguish between strains.
of 180000–200000 nucleotides. It is covalently
linked at both ends and contain redundant, repeating sequences at both ends. 160 putative genes have been identified.
Molluscum contagiosum
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral infection of the skin or occasionally of the mucous membranes. It is caused by a DNA poxvirus called the molluscum contagiosum virus . MCV has no animal reservoir, infecting only humans. There are four types of MCV, MCV-1 to -4; MCV-1 is the most prevalent and...
in humans. Virions have a complex structure and is consistent with the structure of the poxvirus family: an envelope, surface membrane, core, and lateral bodies. Virus may be contained within inclusion bodies and mature by budding through the membrane of the host cell giving rise to a large amount of viral shedding
Viral shedding
Viral shedding refers to the successful reproduction, expulsion, and host-cell infection caused by virus progeny. Once replication has been completed and the host cell is exhausted of all resources in making viral progeny, the viruses may begin to leave the cell by several methods.The term is used...
in a short period of time. Approximate measurements of the virus are 200 nm in diameter, 320 nm in length and 100 nm in height.

The diagnosis can be confirmed by excisional biopsy
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test involving sampling of cells or tissues for examination. It is the medical removal of tissue from a living subject to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist, and can also be analyzed chemically...
.
There are 4 types of MCV, MCV-1 to -4. MCV-1 is the most prevalent in human infections, and MCV-2 seen usually in adults and often sexually transmitted. Polymerase chain reaction
Polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction is a scientific technique in molecular biology to amplify a single or a few copies of a piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence....
techniques are being developed to help confirm lesions as being caused by MCV, and distinguish between strains.
Genome
The genome is a non-segmented single molecule of linear, double-stranded DNADNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
of 180000–200000 nucleotides. It is covalently
Covalent bond
A covalent bond is a form of chemical bonding that is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons is known as covalent bonding....
linked at both ends and contain redundant, repeating sequences at both ends. 160 putative genes have been identified.

