
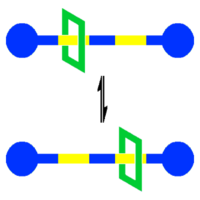
Molecular shuttle
Encyclopedia
Supramolecular chemistry
Supramolecular chemistry refers to the area of chemistry beyond the molecules and focuses on the chemical systems made up of a discrete number of assembled molecular subunits or components...
is a special type of molecular machine
Molecular machine
A molecular machine, or nanomachine, is any discrete number of molecular components that produce quasi-mechanical movements in response to specific stimuli . The expression is often more generally applied to molecules that simply mimic functions that occur at the macroscopic level...
capable of shuttling
Shuttle (weaving)
A shuttle is a tool designed to neatly and compactly store weft yarn while weaving. Shuttles are thrown or passed back and forth through the shed, between the yarn threads of the warp in order to weave in the weft....
molecules or ions from one location to another. This field is of relevance to nanotechnology
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the study of manipulating matter on an atomic and molecular scale. Generally, nanotechnology deals with developing materials, devices, or other structures possessing at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometres...
in its quest for nanoscale electronic components and also to biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
where many biochemical functions are based on molecular shuttles. Academic interest also exists for synthetic molecular shuttles, the first prototype reported in 1991 based on a rotaxane
Rotaxane
A rotaxane is a mechanically-interlocked molecular architecture consisting of a "dumbbell shaped molecule" which is threaded through a "macrocycle" . The name is derived from the Latin for wheel and axle...
.
This device is based on a molecular thread composed of a ethyleneglycol chain interrupted by two arene groups acting as so-called stations. The terminal units (or stoppers) on this wire are bulky triisopropylsilyl groups. The bead is a tetracationic cyclophane
Cyclophane
A cyclophane is a hydrocarbon consisting of an aromatic unit and an aliphatic chain that forms a bridge between two non-adjacent positions of the aromatic ring. More complex derivatives with multiple aromatic units and bridges forming cagelike structures are also known...
based on two bipyridine
Bipyridine
Bipyridines are a family of chemical compounds with the formula 2, which are formed by the coupling of two pyridine rings. Six isomers of bipyridine exist, but two isomers are prominent: 2,2'-bipyridine is a popular ligand in coordination chemistry and 4,4'-bipyridine is a precursor to the...
groups and two para-phenylene
Phenylene
The phenylene group is based on a di-substituted benzene ring . For example, poly is a polymer built up from para-phenylene repeating units....
groups. The bead is locked to one of the stations by pi-pi interactions but since the activation energy
Activation energy
In chemistry, activation energy is a term introduced in 1889 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius that is defined as the energy that must be overcome in order for a chemical reaction to occur. Activation energy may also be defined as the minimum energy required to start a chemical reaction...
for migration from one station to the other station is only 13 kcal
Calorie
The calorie is a pre-SI metric unit of energy. It was first defined by Nicolas Clément in 1824 as a unit of heat, entering French and English dictionaries between 1841 and 1867. In most fields its use is archaic, having been replaced by the SI unit of energy, the joule...
/mol
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
(54 kJ/mol) the bead shuttles between them. The stoppers prevent the bead from slipping from the thread. Chemical synthesis of this device is based on molecular self-assembly
Molecular self-assembly
Molecular self-assembly is the process by which molecules adopt a defined arrangement without guidance or management from an outside source. There are two types of self-assembly, intramolecular self-assembly and intermolecular self-assembly...
from a preformed thread and two bead fragments (32% chemical yield).
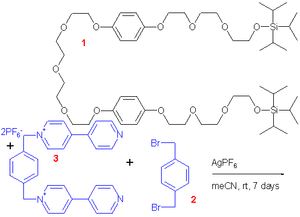 |
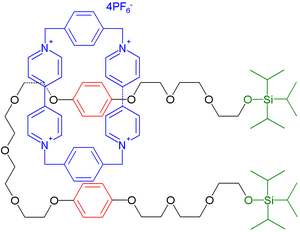 |
|
| molecular shuttle components | Molecular shuttle | |
In certain molecular switch
Molecular switch
A molecular switch is a molecule that can be reversibly shifted between two or more stable states. The molecules may be shifted between the states in response to changes in e.g. pH, light, temperature, an electrical current, microenvironment, or the presence of a ligand. In some cases, a...
es the two stations are non-degenerate.

