
Modern valence bond theory
Encyclopedia
Modern valence bond theory is the term used to describe applications of valence bond theory
with computer programs that are competitive in accuracy and economy with programs for the Hartree-Fock
method and other molecular orbital
based methods. The latter methods dominated quantum chemistry
from the advent of digital computers because they were easier to program. The early popularity of valence bond methods thus declined. It is only recently that the programming of valence bond methods has improved. These developments are due to and described by Gerratt, Cooper, Karadakov and Raimondi (1997); Li and McWeeny (2002); Song, Mo, Zhang and Wu (2005); and Shaik and Hiberty (2004).
In its simplest form the overlapping atomic orbitals are replaced by orbitals which are expanded as linear combination
s of the atom-based basis functions
, forming linear combinations of atomic orbitals (LCAO). This expansion is optimized to give the lowest energy. This procedure gives good energies without including ionic structures.
For example, in the hydrogen molecule, classic valence bond theory
uses two 1s atomic orbital
s (a and b) on the two hydrogen
atoms respectively and then constructs a covalent structure:-
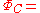 ((a(1)b(2) + b(1)a(2)) ((α(1)β(2) - β(1)α(2))
((a(1)b(2) + b(1)a(2)) ((α(1)β(2) - β(1)α(2))
and then an ion
ic structure:-
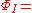 ((a(1)a(2) + b(1)b(2)) ((α(1)β(2) - β(1)α(2))
((a(1)a(2) + b(1)b(2)) ((α(1)β(2) - β(1)α(2))
The final wave function is a linear combination
of these two functions. Coulson
and Fischer
pointed out that a completely equivalent function is:-
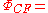 ((a+kb)(1)(b+ka)(2) + (b+ka)(1)(a+kb)(2)) ((α(1)β(2) - β(1)α(2))
((a+kb)(1)(b+ka)(2) + (b+ka)(1)(a+kb)(2)) ((α(1)β(2) - β(1)α(2))
as expanding this out gives a linear combination
of the covalent and ionic structures. Modern valence bond theory replaces the simple linear combination
of the two atomic orbitals with a linear combination of all orbitals in a larger basis set
. The two resulting valence bond orbitals look like an atomic orbital on one hydrogen
atom slightly distorted towards the other hydrogen atom. Modern valence bond theory is thus an extension of this Coulson-Fischer method
.
There are a large number of different valence bond methods. Most use n valence bond orbitals for n electrons. If a single set of these orbitals is combined with all linear independent combinations of the spin functions, we have spin-coupled valence bond theory. The total wave function is optimized using the variation principle by varying the coefficients of the basis functions
in the valence bond orbitals and the coefficients of the different spin functions. In other cases only a sub-set of all possible spin functions is used. Many valence bond methods use several sets of the valence bond orbitals. Be warned that different authors use different names for these different valence bond methods.
for modern valence bond calculations that are freely available.
Valence bond theory
In chemistry, valence bond theory is one of two basic theories, along with molecular orbital theory, that were developed to use the methods of quantum mechanics to explain chemical bonding. It focuses on how the atomic orbitals of the dissociated atoms combine to give individual chemical bonds...
with computer programs that are competitive in accuracy and economy with programs for the Hartree-Fock
Hartree-Fock
In computational physics and chemistry, the Hartree–Fock method is an approximate method for the determination of the ground-state wave function and ground-state energy of a quantum many-body system....
method and other molecular orbital
Molecular orbital
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The term "orbital" was first...
based methods. The latter methods dominated quantum chemistry
Quantum chemistry
Quantum chemistry is a branch of chemistry whose primary focus is the application of quantum mechanics in physical models and experiments of chemical systems...
from the advent of digital computers because they were easier to program. The early popularity of valence bond methods thus declined. It is only recently that the programming of valence bond methods has improved. These developments are due to and described by Gerratt, Cooper, Karadakov and Raimondi (1997); Li and McWeeny (2002); Song, Mo, Zhang and Wu (2005); and Shaik and Hiberty (2004).
In its simplest form the overlapping atomic orbitals are replaced by orbitals which are expanded as linear combination
Linear combination
In mathematics, a linear combination is an expression constructed from a set of terms by multiplying each term by a constant and adding the results...
s of the atom-based basis functions
Basis set (chemistry)
A basis set in chemistry is a set of functions used to create the molecular orbitals, which are expanded as a linear combination of such functions with the weights or coefficients to be determined. Usually these functions are atomic orbitals, in that they are centered on atoms. Otherwise, the...
, forming linear combinations of atomic orbitals (LCAO). This expansion is optimized to give the lowest energy. This procedure gives good energies without including ionic structures.
For example, in the hydrogen molecule, classic valence bond theory
Valence bond theory
In chemistry, valence bond theory is one of two basic theories, along with molecular orbital theory, that were developed to use the methods of quantum mechanics to explain chemical bonding. It focuses on how the atomic orbitals of the dissociated atoms combine to give individual chemical bonds...
uses two 1s atomic orbital
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus...
s (a and b) on the two hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atoms respectively and then constructs a covalent structure:-
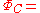 ((a(1)b(2) + b(1)a(2)) ((α(1)β(2) - β(1)α(2))
((a(1)b(2) + b(1)a(2)) ((α(1)β(2) - β(1)α(2))and then an ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
ic structure:-
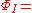 ((a(1)a(2) + b(1)b(2)) ((α(1)β(2) - β(1)α(2))
((a(1)a(2) + b(1)b(2)) ((α(1)β(2) - β(1)α(2))The final wave function is a linear combination
Linear combination
In mathematics, a linear combination is an expression constructed from a set of terms by multiplying each term by a constant and adding the results...
of these two functions. Coulson
Charles Coulson
Charles Alfred Coulson FRS was an applied mathematician, theoretical chemist and religious author.His major scientific work was as a pioneer of the application of the quantum theory of valency to problems of molecular structure, dynamics and reactivity...
and Fischer
pointed out that a completely equivalent function is:-
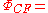 ((a+kb)(1)(b+ka)(2) + (b+ka)(1)(a+kb)(2)) ((α(1)β(2) - β(1)α(2))
((a+kb)(1)(b+ka)(2) + (b+ka)(1)(a+kb)(2)) ((α(1)β(2) - β(1)α(2))as expanding this out gives a linear combination
Linear combination
In mathematics, a linear combination is an expression constructed from a set of terms by multiplying each term by a constant and adding the results...
of the covalent and ionic structures. Modern valence bond theory replaces the simple linear combination
Linear combination
In mathematics, a linear combination is an expression constructed from a set of terms by multiplying each term by a constant and adding the results...
of the two atomic orbitals with a linear combination of all orbitals in a larger basis set
Basis set (chemistry)
A basis set in chemistry is a set of functions used to create the molecular orbitals, which are expanded as a linear combination of such functions with the weights or coefficients to be determined. Usually these functions are atomic orbitals, in that they are centered on atoms. Otherwise, the...
. The two resulting valence bond orbitals look like an atomic orbital on one hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
atom slightly distorted towards the other hydrogen atom. Modern valence bond theory is thus an extension of this Coulson-Fischer method
Coulson-Fischer theory
In theoretical chemistry and molecular physics, Coulson-Fischer theory provides a quantum mechanical description of the electronic structure of molecules...
.
There are a large number of different valence bond methods. Most use n valence bond orbitals for n electrons. If a single set of these orbitals is combined with all linear independent combinations of the spin functions, we have spin-coupled valence bond theory. The total wave function is optimized using the variation principle by varying the coefficients of the basis functions
Basis set (chemistry)
A basis set in chemistry is a set of functions used to create the molecular orbitals, which are expanded as a linear combination of such functions with the weights or coefficients to be determined. Usually these functions are atomic orbitals, in that they are centered on atoms. Otherwise, the...
in the valence bond orbitals and the coefficients of the different spin functions. In other cases only a sub-set of all possible spin functions is used. Many valence bond methods use several sets of the valence bond orbitals. Be warned that different authors use different names for these different valence bond methods.
Valence bond programs
Several groups have produced computer programsValence bond codes
VB computer programs for modern valence bond calculations:-* CRUNCH is by Gordon A. Gallup and his group.* GAMESS includes calculation of VB wave functions by the TURTLE code, due to J.H. van Lenthe....
for modern valence bond calculations that are freely available.
Further reading
- J. Gerratt, D. L. Cooper, P. B. Karadakov and M. Raimondi, "Modern Valence Bond Theory", Chemical Society Reviews, 26, 87, 1997, and several others by the same authors.
- J. Li and R. McWeeny, "VB2000: Pushing Valence Bond Theory to new limits", International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 89, 208, 2002.
- L. Song, Y. Mo, Q. Zhang and W. Wu, "XMVB: A program for ab initio nonorthogonal valence bond computations", Journal of Computational Chemistry, 26, 514, 2005.
- S. Shaik and P. C. Hiberty, "Valence Bond theory, its History, Fundamentals and Applications. A Primer", Reviews of Computational Chemistry, 20, 1 2004. A recent review that covers, not only their own contributions, but the whole of modern valence bond theory.

