.gif)
Mistral (wind)
Encyclopedia

Rhône
Rhone can refer to:* Rhone, one of the major rivers of Europe, running through Switzerland and France* Rhône Glacier, the source of the Rhone River and one of the primary contributors to Lake Geneva in the far eastern end of the canton of Valais in Switzerland...
and the Durance
Durance
The Durance is a major river in south-eastern France.Its source is in the south-western Alps, in Montgenèvre ski resort near Briançon and it flows south-west through the following départements and cities:* Hautes-Alpes: Briançon, Embrun.* Alpes-de-Haute-Provence: Sisteron, Manosque.* Vaucluse:...
Rivers to the coast of the Mediterranean around the Camargue
Camargue
The Camargue is the region located south of Arles, France, between the Mediterranean Sea and the two arms of the Rhône River delta. The eastern arm is called the Grand Rhône; the western one is the Petit Rhône....
region. It affects the northeast of the plain of Languedoc
Languedoc
Languedoc is a former province of France, now continued in the modern-day régions of Languedoc-Roussillon and Midi-Pyrénées in the south of France, and whose capital city was Toulouse, now in Midi-Pyrénées. It had an area of approximately 42,700 km² .-Geographical Extent:The traditional...
and Provence
Provence
Provence ; Provençal: Provença in classical norm or Prouvènço in Mistralian norm) is a region of south eastern France on the Mediterranean adjacent to Italy. It is part of the administrative région of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur...
to the east of Toulon
Toulon
Toulon is a town in southern France and a large military harbor on the Mediterranean coast, with a major French naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte-d'Azur region, Toulon is the capital of the Var department in the former province of Provence....
, where it is felt as a strong west wind. It has a major influence all along the Mediterranean coast of France, and often causes sudden storms in the Mediterranean between Corsica
Corsica
Corsica is an island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is located west of Italy, southeast of the French mainland, and north of the island of Sardinia....
and the Balearic Islands
Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands are an archipelago of Spain in the western Mediterranean Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula.The four largest islands are: Majorca, Minorca, Ibiza and Formentera. The archipelago forms an autonomous community and a province of Spain with Palma as the capital...
.
In the south of France the name comes from the Languedoc
Languedoc
Languedoc is a former province of France, now continued in the modern-day régions of Languedoc-Roussillon and Midi-Pyrénées in the south of France, and whose capital city was Toulouse, now in Midi-Pyrénées. It had an area of approximately 42,700 km² .-Geographical Extent:The traditional...
dialect of the provençal language
Provençal language
Provençal is a dialect of Occitan spoken by a minority of people in southern France, mostly in Provence. In the English-speaking world, "Provençal" is often used to refer to all dialects of Occitan, but it actually refers specifically to the dialect spoken in Provence."Provençal" is also the...
and means "masterly". The same wind is called mistrau in the Occitan language, mestral in Catalan
Catalan language
Catalan is a Romance language, the national and only official language of Andorra and a co-official language in the Spanish autonomous communities of Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and Valencian Community, where it is known as Valencian , as well as in the city of Alghero, on the Italian island...
, maestrale in Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
and Corsican
Corsican language
Corsican is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken and written on the islands of Corsica and northern Sardinia . Corsican is the traditional native language of the Corsican people, and was long the vernacular language alongside the Italian, official language in Corsica until 1859, which was...
, maistràle or bentu maestru in Sardinian
Sardinian language
Sardinian is a Romance language spoken and written on most of the island of Sardinia . It is considered the most conservative of the Romance languages in terms of phonology and is noted for its Paleosardinian substratum....
and majjistral in Maltese
Maltese language
Maltese is the national language of Malta, and a co-official language of the country alongside English,while also serving as an official language of the European Union, the only Semitic language so distinguished. Maltese is descended from Siculo-Arabic...
.
The mistral is usually accompanied by clear and fresh weather, and it plays an important role in creating the climate of Provence. It can reach speeds of more than ninety kilometers an hour, particularly in the Rhone Valley. Its average speed during the day can reach about fifty kilometers an hour, calming noticeably at night. The mistral is a regional wind, which usually blows during the winter and spring, though it occurs in all seasons. It sometimes lasts only one or two days, frequently lasts several days, and sometimes lasts more than a week.
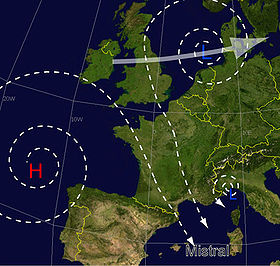
The cause of the mistral
The mistral takes place each time there is an anticyclone, or area of high pressure, in the Atlantic between Spain and the southeast of France, and an area of low pressure around the Gulf of GenoaGulf of Genoa
The Gulf of Genoa is the northernmost part of the Ligurian Sea. The width of the gulf is about 125 km, from the city of Imperia in the west to La Spezia in the east. The largest city on the its coast is Genoa, which has an important port....
. When this happens, the flow of air between the high and low pressure areas draws in a current of cold air from the north which accelerates through the lower elevations between the foothills of the Alps
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
and the Cevennes
Cévennes
The Cévennes are a range of mountains in south-central France, covering parts of the départements of Gard, Lozère, Ardèche, and Haute-Loire.The word Cévennes comes from the Gaulish Cebenna, which was Latinized by Julius Caesar to Cevenna...
. The conditions for a mistral are even more favorable when a cold rainy front has crossed France from the northwest to the southeast as far as the Mediterranean. This cold, dry wind usually causes a period of cloudless skies and luminous sunshine, which gives the mistral its reputation for making the sky especially clear. There is also, however, the mistral noir, which brings clouds and rain. The mistral noir occurs when the Azores High
Azores High
The Azores High is a large subtropical semi-permanent centre of high atmospheric pressure found near the Azores in the Atlantic Ocean, at the Horse latitudes...
is extended and draws in unusually moist air from the northeast.
The long and enclosed shape of the Rhone Valley, and the Venturi effect
Venturi effect
The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section of pipe. The Venturi effect is named after Giovanni Battista Venturi , an Italian physicist.-Background:...
of funnelng the air through a narrowing space, is frequently cited as the reason for the speed and force of the mistral, but the reasons are apparently more complex. The mistral reaches its maximum speed not at the narrowest part of the Rhone Valley, south of Valence, but much farther south, where the Valley has widened. Also, the wind occurs not just in the Valley, but high above in the atmosphere, up to the troposphere, three kilometers above the earth. The mistral is very strong at the summit of Mont Ventoux, 1900 meters in elevation, though the plain below is very wide. Other contributing factors to the strength of the mistral are the accumulation of masses of cold air, whose volume is greater, pouring down the mountains and valleys to the lower elevations. This is similar to a foehn wind, but unlike a foehn wind the descent in altitude does not significantly warm the mistral. The causes and characteristics of the mistral are very similar to those of the Tramontane
Tramontane
Tramontane is a classical name for a northern wind. The exact form of the name and precise direction varies from country to country. The word came to English from Italian tramontana, which developed from Latin trānsmontānus , "beyond the mountains/across the mountains", referring to the alps in...
, another wind of the French Mediterranean region.

Provence
Provence ; Provençal: Provença in classical norm or Prouvènço in Mistralian norm) is a region of south eastern France on the Mediterranean adjacent to Italy. It is part of the administrative région of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur...
, Languedoc
Languedoc
Languedoc is a former province of France, now continued in the modern-day régions of Languedoc-Roussillon and Midi-Pyrénées in the south of France, and whose capital city was Toulouse, now in Midi-Pyrénées. It had an area of approximately 42,700 km² .-Geographical Extent:The traditional...
east of Montpellier
Montpellier
-Neighbourhoods:Since 2001, Montpellier has been divided into seven official neighbourhoods, themselves divided into sub-neighbourhoods. Each of them possesses a neighbourhood council....
, as well as all of the Rhone Valley from Lyon
Lyon
Lyon , is a city in east-central France in the Rhône-Alpes region, situated between Paris and Marseille. Lyon is located at from Paris, from Marseille, from Geneva, from Turin, and from Barcelona. The residents of the city are called Lyonnais....
to Marseille
Marseille
Marseille , known in antiquity as Massalia , is the second largest city in France, after Paris, with a population of 852,395 within its administrative limits on a land area of . The urban area of Marseille extends beyond the city limits with a population of over 1,420,000 on an area of...
, and as far southeast as Corsica and Sardinia. The mistral usually blows from the north or northwest, but in certain pre-alpine valleys and along the Côte d'Azur, the wind is channelled by the mountains so that it blows from east to west. Sometimes it also blows from the north-north-east toward the east of Languedoc as far as Cap Béar. Frequently the mistral will affect only one part of the region.
In the Languedoc area, where the tramontane is the strongest wind, the mistral and the tramontane blow together onto the Gulf of Lion and the northwest of the western Mediterranean, and can be felt to the east of the Balearic Islands
Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands are an archipelago of Spain in the western Mediterranean Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula.The four largest islands are: Majorca, Minorca, Ibiza and Formentera. The archipelago forms an autonomous community and a province of Spain with Palma as the capital...
, in Sardinia
Sardinia
Sardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
, and sometimes as far as the coast of Africa.
When the mistral blows from the west, the mass of air is not so cold and the wind only affects the plain of the Rhone delta and the Côte d'Azur. The good weather is confined to the coast of the Mediterranean, while it can rain in the interior. The Côte d'Azur generally has a clear sky and warmer temperatures. This type of mistral usually blows for no more than one to three days.
The mistral originating from the northeast has a very different character; it is felt only in the west of Provence and as far as Montpellier, with the wind coming from either a northerly or north-northeasterly direction. In the winter this is by far the coldest form of the mistral. The wind can blow for more than a week. This kind of mistral is often connected with a low pressure area in the Gulf of Genoa, and it can bring unstable weather to the Côte d'Azur and the east of Provence, sometimes bringing heavy snow to low altitudes in winter.
When the flow of air comes from the northeast due to a widespread low pressure area over the Atlantic and atmospheric disturbances over France, the air is even colder at both high altitudes and ground level, and the mistral is even stronger, and the weather worse, with the creation of cumulus clouds bringing weak storms. This kind of mistral is weaker in the east of Provence and the Côte d'Azur.
The mistral is not always synonymous with clear skies. When a low pressure front over the Mediterranean approaches the coast from the southeast, the weather can change quickly for the worse, and the mistral and its clear sky changes rapidly to an east wind bringing humid air and threatening clouds. The position of the low-pressure front creates a flow of air from the northwest or the northeast, channeled through the Rhone Valley. If this low-pressure area moves back toward the southeast, the mistral will quickly clear the air and the good weather will return; but if the cold-weather front continues to approach the land, bad weather will continue for several days in the entire Mediterranean basin, sometimes transforming into what French meteorologists call an épisode cévenol, a succession of torrential rains and floods, particularly in the areas west of the Rhone Valley: the Ardèche
Ardèche
Ardèche is a department in south-central France named after the Ardèche River.- History :The area has been inhabited by humans at least since the Upper Paleolithic, as attested by the famous cave paintings at Chauvet Pont d'Arc. The plateau of the Ardeche River has extensive standing stones ,...
, the Gard
Gard
Gard is a département located in southern France in the Languedoc-Roussillon region.The department is named after the River Gard, although the formerly Occitan name of the River Gard, Gardon, has been replacing the traditional French name in recent decades, even among French speakers.- History...
, Hérault
Hérault
Hérault is a department in the south of France named after the Hérault river.-History:Hérault is one of the original 83 departments created during the French Revolution on 4 March 1790...
and Lozère
Lozère
Lozère , is a department in southeast France near the Massif Central, named after Mont Lozère.- History :Lozère is one of the original 83 departments created during the French Revolution on March 4, 1790...
.
The summer mistral, unlike the others, is created by purely local conditions. It usually happens in July, and only in the valley of the Rhone and on the coast of Provence. It is caused by a thermal depression over the interior of Provence (The Var and Alpes de Haute-Provence), created when the land is overheated. This creates a flow of air from the north toward the east of Provence. This wind is frequently cancelled out close to the coast by the breezes from the sea. It does not blow for more than a single day, but it is feared in Provence, because it dries the vegetation and it can spread forest fires
The effects of the mistral
The mistral has the reputation of bringing good health, since the dry air dries stagnant water and the mud, giving the mistral the local name mange-fange (Eng. "mud-eater"). It also blows away pollution from the skies over the large cities and industrial areas.
The sunshine and dryness brought by the mistral have an important effect on the local vegetation. The vegetation in Provence, which is already dry because of the small amount of rainfall, is made even drier by the wind, which makes it particularly susceptible to fires, which the wind spreads very rapidly, sometimes devastating vast expanses of mountainside before being extinguished. During the summer, thousands of hectares can burn when the mistral is blowing.
In the Rhone Valley and on the plain of la Crau, the regularity and force of the mistral causes the trees to grow leaning to the south. Once the forest has been razed by fire, the strong wind makes it difficult for new trees to grow. The farmers of the Rhone Valley have long planted rows of cypress trees to shelter their crops from the dry force of the mistral. The mistral can also have beneficial effects—the moving air can save crops from the spring frost, which can last until the end of April.
As summer visitors to the beach in Provence learn, the summer mistral can quickly lower the temperature of the sea, as the wind pushes the warm water near the surface out to sea and it is replaced by colder water from greater depths.
The effects of the mistral beyond France

Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
and Malta
Malta
Malta , officially known as the Republic of Malta , is a Southern European country consisting of an archipelago situated in the centre of the Mediterranean, south of Sicily, east of Tunisia and north of Libya, with Gibraltar to the west and Alexandria to the east.Malta covers just over in...
or throughout the Mediterranean, particularly when low pressure area
Low pressure area
A low-pressure area, or "low", is a region where the atmospheric pressure at sea level is below that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence which occur in upper levels of the troposphere. The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as...
s form in the Gulf of Genoa
Gulf of Genoa
The Gulf of Genoa is the northernmost part of the Ligurian Sea. The width of the gulf is about 125 km, from the city of Imperia in the west to La Spezia in the east. The largest city on the its coast is Genoa, which has an important port....
.
Similar names—maestral or maestro—are used for (although also mostly northwestern) a quite different wind in the Adriatic Sea
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan peninsula, and the system of the Apennine Mountains from that of the Dinaric Alps and adjacent ranges...
. It is an anabatic sea-breeze
Sea breeze
A sea-breeze is a wind from the sea that develops over land near coasts. It is formed by increasing temperature differences between the land and water; these create a pressure minimum over the land due to its relative warmth, and forces higher pressure, cooler air from the sea to move inland...
wind which blows in the summer when the east Adriatic coast gets warmer than the sea. It is thus a mild sea-to-coast wind, unlike the mistral. The strong katabatic wind there is the northeastern bora
Bora (wind)
Bora or Bura is a northern to north-eastern katabatic wind in the Adriatic, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Montenegro, Italy, Greece, Slovenia, and Turkey....
.
In Greece it is also known as maïstros or maïstráli and south-western Crete it is considered the most beneficial wind, said to blow only in daytime.
The mistral in Provençal culture


Terra Amata
Terra Amata is an archeological site in open air located on the slopes of Mount Boron in Nice, at a level 26 meters above the current sea level of the Mediterranean. It was discovered and excavated in 1966 by Henry de Lumley...
, at the foot of Mount Boron in Nice
Nice
Nice is the fifth most populous city in France, after Paris, Marseille, Lyon and Toulouse, with a population of 348,721 within its administrative limits on a land area of . The urban area of Nice extends beyond the administrative city limits with a population of more than 955,000 on an area of...
, showed that in about 400,000 B.C. the inhabitants had built a low wall of rocks and beach stones to the northwest of their fireplace to protect their fire from the power of the mistral.
The mas
Mas (Provencal Farmhouse)
A mas is a traditional farmhouse in the Provence region of France as well as in Catalonia, where is also named masia or masía ....
(farmhouse) traditionally faces south, with its back to the mistral. The bell towers of villages in Provence are often open iron frameworks, which allow the wind to pass through. The traditional Provençal Christmas crib often includes a figure
Santon (figurine)
Santons are small hand-painted, terracotta nativity scene figurines produced in the Provence region of southeastern France...
of a shepherd holding his hat, with his cloak blowing in the mistral.
Pop Culture Reference
'Mistral Wind' is a song written by Ann WilsonAnn Wilson
Ann Dustin Wilson is an American musician, best known as the lead singer, flute player, songwriter, and occasional guitar player of the rock band Heart.-Personal life:...
, Nancy Wilson
Nancy Wilson
Nancy Wilson may refer to:* Nancy Wilson , American jazz singer and actress* Nancy Wilson , American singer and guitar player, member of the band Heart...
, Sue Ennis and Roger Fisher of the rock group Heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
that appeared on the Dog and Butterfly album in 1979.
See also
- Bora (wind)Bora (wind)Bora or Bura is a northern to north-eastern katabatic wind in the Adriatic, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Montenegro, Italy, Greece, Slovenia, and Turkey....
- Cers (wind)Cers (wind)The Cers, also called the Narbonnais by those who live southeast of Narbonne, is a very dry wind that is colder during the winter and warmer during the summer. Originating from moist Atlantic air-masses flowing across the Toulouse area, Cers become intensified through the Lauragais gap. They are...
- EtesianEtesianThe etesians ', sometimes found in the Latin form etesiae), meltemi μελτέμι , or meltem are the strong, dry north windsof the Aegean Sea, which blow from about mid-May to mid-September...
- GregaleGregaleThe Gregale is a Mediterranean wind that can occur during times when a low pressure area moves through the area to the south of Malta and causes a strong, cool, northeasterly wind to affect the island...
- Khamaseen
- Levant (wind)Levant (wind)The levant is an easterly wind that blows in the western Mediterranean Sea and southern France, an example of mountain-gap wind. In Roussillon it is called "llevant" and in Corsica "levante"...
- LevantadesLevantadesGales from between north-north-east and east-north-east are the most important gales of the east coast of Spain. They are known locally as llevantades and are an intense form of the llevante or levanter, i.e., north-easterly winds of long fetch, as opposed to diurnal coastal breezes...
- LevecheLevecheLebeche is the Spanish name for a warm southwest wind in parts of coastal Mediterranean Spain, either a foehn wind or a hot southerly wind in advance of a low pressure area moving from the Sahara Desert...
- Marin (wind)Marin (wind)The Marin is a warm, moist wind in the Gulf of Lion of France, blowing from the southeast or south-southeast onto the coast of Languedoc and Roussillon. It brings rain to this region which it has picked up crossing the Mediterranean, and also can bring coastal fog...
- Santa Ana winds
- SiroccoSiroccoSirocco, scirocco, , jugo or, rarely, siroc is a Mediterranean wind that comes from the Sahara and reaches hurricane speeds in North Africa and Southern Europe. It is known in North Africa by the Arabic word qibli or ghibli Sirocco, scirocco, , jugo or, rarely, siroc is a Mediterranean wind...
- TramontaneTramontaneTramontane is a classical name for a northern wind. The exact form of the name and precise direction varies from country to country. The word came to English from Italian tramontana, which developed from Latin trānsmontānus , "beyond the mountains/across the mountains", referring to the alps in...
- Winds of ProvenceWinds of ProvenceThe Winds of Provence, the region of southeast France along the Mediterranean from the Alps to the mouth of the Rhone River, are an important feature of Provençal life, and each one has a traditional local name, in the Provençal language....
External links
- Meteo-France French-language on meteorology
- Local Mediterranean winds
- Name of Winds
- US Navy Marine Meteorology - Mediterranean Mistral Tutorial

