MiniTSFO
Encyclopedia
The Mini TSFO was the first artillery
call-for-fire simulation
designed for a personal computer
. It was started in 1985 as an outgrowth of a Field Artillery
Officer
Advanced Course battlefield research project at the U.S. Army Field Artillery School (USAFAS) to develop a concept for incorporating PCs into artillery training and completed in 1986. It replaced summer artillery live fire training for cadets at West Point in 1986 and 1987.
One of the USAFAS students involved in the battlefield research project, Captain (later Colonel
) Bill Erwin, volunteered to continue to develop the concept into an actual application during his follow-on assignment to the USAFAS Directorate of Training and Doctrine.
Versions:
MINITSFO - Original version using a Digital Message Device (DMD)
, virtual map, and CGA
graphics.
VTSFO - Replaced the DMD
with keyboard interface for use at West Point.
NGFTSFO - Naval Gunfire version using EGA
graphics, actual scenes from San Clemente Island training area, and incorporating effects of dispersion between rounds.
.
The virtual DMD required extensive programming in order to simulate the actual operation of a real DMD and consumed most of the program code space.
The MiniTSFO was originally coded in BASICA, an interpreted
version of BASIC
available on IBM
PC
s. As the design of the program was pushing the limits of BASICA, Microsoft
introduced the QuickBASIC
compiler
. This allowed the MiniTSFO to grow beyond the memory limits of BASICA and structured programming allowed additional complexity.
In its initial design, the MiniTSFO drew all screens from program code. It wasn't long before the limitations of this approach became obvious and so the screens completed to date were captured and imported into PC Paintbrush
to be edited. This allowed the additional of details that would have been too tedious to incorporate through code and also allowed the target screens to be easily edited to add additional types of targets.
To allow the target screens to be easily changed to provide additional challenges, the target locations and descriptions were read in from an initialization fire when the MiniTSFO was started.
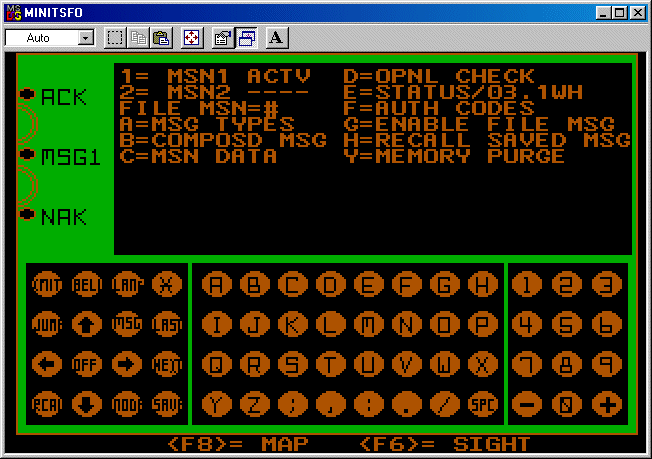 The MiniTSFO used a virtual DMD
The MiniTSFO used a virtual DMD
to control fire missions. Users would be presented with one of five random target screens. The user would then determine how to engage the target by either grid location, polar coordinates, or shifting from a known point by flipping back and forth between the target screen and the map. Once the target was located, the user would go to the virtual DMD and enter a fire mission just as a real FO would do with a real DMD. Messages back and forth between the user and the fire direction center (shot and splash) would precede the depiction of an artillery round bursting where the user had described the target location. The user would then use the virtual DMD to adjust the fire onto the target, fire for effect, and then give end-of-mission details. After the end of the fire mission, the user would be critiqued on several factors such as initial target location, description, how many rounds were needed to fire-for-effect, and overall mission completion.
The best available graphic card for a PC at that time was the CGA
which allowed for 320x200 resolution in only four colors. This meant that the graphics for the MiniTSFO, while state-of-the-art for the time would be considered very crude by today's standards.
training the cadets at West Point decided that teaching the cadets to use a DMD was too time consuming and wanted them to just call the fire mission information to the NCO in charge who would then enter it into the MiniTSFO. This was the only difference from the classic edition.
Efforts to include this effect in the TSFO were deemed too expensive and would take too long. One of the members of the group was familiar with the MiniTSFO and suggested that it be modified. Additionally, since the original MiniTSFO supported the Army call for fire process, it was deemed appropriate to have the new version support the Navel Gunfire (NGF) process.
Work began immediately. By this time, the Extended Graphics Adapter (EGA)
was commonly available for the PC offering 640/350 resolution and a palate of 16 colors. Photographs of San Clemente Island impact area were scanned-in, incorporated into PC Paintbrush for cleanup, and realistic targets added. An actual map of the area was also scanned-in providing additional realism.
The virtual DMD was replaced by a fire mission workup board as was used by Naval Gunfire Liaison Officers. Once the target was located, the user would flip to the workup board, enter the mission information, and submit to the ship.
Communications back and forth were through a scrolling strip of text at the bottom of the screen. The actual transmissions that would be used in a real naval gunfire mission kept the user informed on the progress of the mission.
Besides the enhanced graphics and dispersion, several additional enhancements were made. The ship's location would move during the conduct of the fire mission and the user would see the pattern of rounds on the ground move along with the ship as its direction to the target shifted. The initialization file listed the direction, speed, and weapon type for each available firing platform. Also, the effects on the target would be judged on how close the rounds actually came to the target based on the caliber of the weapon.


and brigade
commanders as well as visiting dignitaries. It also provided some inspiration for the developers of the Guardfist II, a much more capable system. Some Artillerymen used it to keep their skills up (the Directory of the USAFAS Gunnery Department used it before meeting with lieutenants in basic Artillery training so that he could impress them with his skills with a DMD). In retrospect, it was a good introduction to what was to come later.
Artillery
Originally applied to any group of infantry primarily armed with projectile weapons, artillery has over time become limited in meaning to refer only to those engines of war that operate by projection of munitions far beyond the range of effect of personal weapons...
call-for-fire simulation
Simulation
Simulation is the imitation of some real thing available, state of affairs, or process. The act of simulating something generally entails representing certain key characteristics or behaviours of a selected physical or abstract system....
designed for a personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
. It was started in 1985 as an outgrowth of a Field Artillery
Field artillery
Field artillery is a category of mobile artillery used to support armies in the field. These weapons are specialized for mobility, tactical proficiency, long range, short range and extremely long range target engagement....
Officer
Officer (armed forces)
An officer is a member of an armed force or uniformed service who holds a position of authority. Commissioned officers derive authority directly from a sovereign power and, as such, hold a commission charging them with the duties and responsibilities of a specific office or position...
Advanced Course battlefield research project at the U.S. Army Field Artillery School (USAFAS) to develop a concept for incorporating PCs into artillery training and completed in 1986. It replaced summer artillery live fire training for cadets at West Point in 1986 and 1987.
One of the USAFAS students involved in the battlefield research project, Captain (later Colonel
Colonel
Colonel , abbreviated Col or COL, is a military rank of a senior commissioned officer. It or a corresponding rank exists in most armies and in many air forces; the naval equivalent rank is generally "Captain". It is also used in some police forces and other paramilitary rank structures...
) Bill Erwin, volunteered to continue to develop the concept into an actual application during his follow-on assignment to the USAFAS Directorate of Training and Doctrine.
Versions:
MINITSFO - Original version using a Digital Message Device (DMD)
Digital Message Device
The AN/PSG-2 Digital Message Device is a portable data-entry terminal used by artillery forward observers to communicate with artillery batteries to request and control artillery fire missions...
, virtual map, and CGA
Color Graphics Adapter
The Color Graphics Adapter , originally also called the Color/Graphics Adapter or IBM Color/Graphics Monitor Adapter, introduced in 1981, was IBM's first color graphics card, and the first color computer display standard for the IBM PC....
graphics.
VTSFO - Replaced the DMD
Digital Message Device
The AN/PSG-2 Digital Message Device is a portable data-entry terminal used by artillery forward observers to communicate with artillery batteries to request and control artillery fire missions...
with keyboard interface for use at West Point.
NGFTSFO - Naval Gunfire version using EGA
Enhanced Graphics Adapter
The Enhanced Graphics Adapter is the IBM PC computer display standard specification which is between CGA and VGA in terms of color and space resolution. Introduced in October 1984 by IBM shortly after its new PC/AT, EGA produces a display of 16 simultaneous colors from a palette of 64 at a...
graphics, actual scenes from San Clemente Island training area, and incorporating effects of dispersion between rounds.
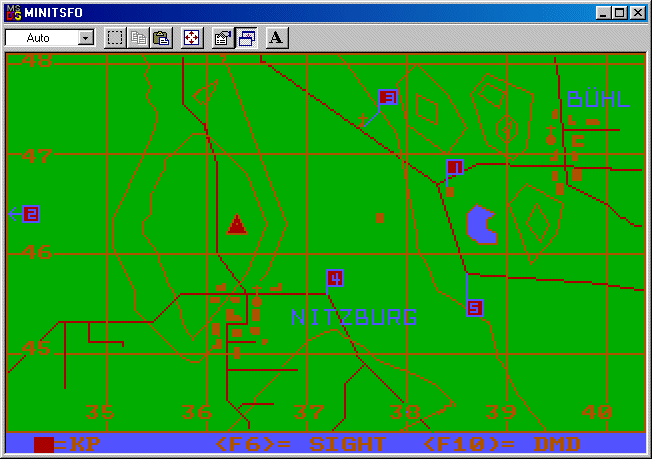
Evolution of a Military Video Game
As originally envisioned, the MiniTSFO would be a complete system that required only a computer to play. This meant that there had to be some way to see targets on-screen, some way to locate the target coordinates such as a map, and some way to call for fire. This resulted in a combination of three screens which the user could flip back-and-forth by using function keys. The first screen showed a simutated view through an AN/GVS-5 laser rangefinder. The map screen was a depiction of the fictional German town of Nitzburg and surrounding area. Lastly, the way to enter firing commands was a virtual AN/PSG-2 Digital Message Device (DMD)Digital Message Device
The AN/PSG-2 Digital Message Device is a portable data-entry terminal used by artillery forward observers to communicate with artillery batteries to request and control artillery fire missions...
.
The virtual DMD required extensive programming in order to simulate the actual operation of a real DMD and consumed most of the program code space.
The MiniTSFO was originally coded in BASICA, an interpreted
Interpreter (computing)
In computer science, an interpreter normally means a computer program that executes, i.e. performs, instructions written in a programming language...
version of BASIC
BASIC
BASIC is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages whose design philosophy emphasizes ease of use - the name is an acronym from Beginner's All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code....
available on IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
PC
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s. As the design of the program was pushing the limits of BASICA, Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
introduced the QuickBASIC
QuickBASIC
Microsoft QuickBASIC is an Integrated Development Environment and compiler for the BASIC programming language that was developed by Microsoft. QuickBASIC runs mainly on DOS, though there was a short-lived version for Mac OS...
compiler
Compiler
A compiler is a computer program that transforms source code written in a programming language into another computer language...
. This allowed the MiniTSFO to grow beyond the memory limits of BASICA and structured programming allowed additional complexity.
In its initial design, the MiniTSFO drew all screens from program code. It wasn't long before the limitations of this approach became obvious and so the screens completed to date were captured and imported into PC Paintbrush
PC Paintbrush
PC Paintbrush was graphics editing software created by the ZSoft Corporation in 1985 for computers running the MS-DOS operating system....
to be edited. This allowed the additional of details that would have been too tedious to incorporate through code and also allowed the target screens to be easily edited to add additional types of targets.
To allow the target screens to be easily changed to provide additional challenges, the target locations and descriptions were read in from an initialization fire when the MiniTSFO was started.
MiniTSFO (Classic Edition)


Digital Message Device
The AN/PSG-2 Digital Message Device is a portable data-entry terminal used by artillery forward observers to communicate with artillery batteries to request and control artillery fire missions...
to control fire missions. Users would be presented with one of five random target screens. The user would then determine how to engage the target by either grid location, polar coordinates, or shifting from a known point by flipping back and forth between the target screen and the map. Once the target was located, the user would go to the virtual DMD and enter a fire mission just as a real FO would do with a real DMD. Messages back and forth between the user and the fire direction center (shot and splash) would precede the depiction of an artillery round bursting where the user had described the target location. The user would then use the virtual DMD to adjust the fire onto the target, fire for effect, and then give end-of-mission details. After the end of the fire mission, the user would be critiqued on several factors such as initial target location, description, how many rounds were needed to fire-for-effect, and overall mission completion.
The best available graphic card for a PC at that time was the CGA
Color Graphics Adapter
The Color Graphics Adapter , originally also called the Color/Graphics Adapter or IBM Color/Graphics Monitor Adapter, introduced in 1981, was IBM's first color graphics card, and the first color computer display standard for the IBM PC....
which allowed for 320x200 resolution in only four colors. This meant that the graphics for the MiniTSFO, while state-of-the-art for the time would be considered very crude by today's standards.
Trainer Edition
This edition was the classic edition with the DMD removed and a keyboard interface used instead. The NCOsNon-commissioned officer
A non-commissioned officer , called a sub-officer in some countries, is a military officer who has not been given a commission...
training the cadets at West Point decided that teaching the cadets to use a DMD was too time consuming and wanted them to just call the fire mission information to the NCO in charge who would then enter it into the MiniTSFO. This was the only difference from the classic edition.
Naval Gunfire Edition
In 1987, the Joint Munitions Effectiveness Group became concerned that existing simulations such as the TSFO gave an unrealistic picture of effects on a target because the effect of dispersion between rounds was not taken into account. In other words, if you fired 10 rounds at a target, not all the rounds would hit in the same spot. Most would hit close to the target and a couple might be quite a distance away in a pattern along the gun-to-target line. This can be computed using a Gaussian Distribution function.Efforts to include this effect in the TSFO were deemed too expensive and would take too long. One of the members of the group was familiar with the MiniTSFO and suggested that it be modified. Additionally, since the original MiniTSFO supported the Army call for fire process, it was deemed appropriate to have the new version support the Navel Gunfire (NGF) process.
Work began immediately. By this time, the Extended Graphics Adapter (EGA)
Enhanced Graphics Adapter
The Enhanced Graphics Adapter is the IBM PC computer display standard specification which is between CGA and VGA in terms of color and space resolution. Introduced in October 1984 by IBM shortly after its new PC/AT, EGA produces a display of 16 simultaneous colors from a palette of 64 at a...
was commonly available for the PC offering 640/350 resolution and a palate of 16 colors. Photographs of San Clemente Island impact area were scanned-in, incorporated into PC Paintbrush for cleanup, and realistic targets added. An actual map of the area was also scanned-in providing additional realism.
The virtual DMD was replaced by a fire mission workup board as was used by Naval Gunfire Liaison Officers. Once the target was located, the user would flip to the workup board, enter the mission information, and submit to the ship.
Communications back and forth were through a scrolling strip of text at the bottom of the screen. The actual transmissions that would be used in a real naval gunfire mission kept the user informed on the progress of the mission.
Besides the enhanced graphics and dispersion, several additional enhancements were made. The ship's location would move during the conduct of the fire mission and the user would see the pattern of rounds on the ground move along with the ship as its direction to the target shifted. The initialization file listed the direction, speed, and weapon type for each available firing platform. Also, the effects on the target would be judged on how close the rounds actually came to the target based on the caliber of the weapon.
Unfinished Work
Development of expansion cards for PCs which allowed communication with the TACFIRE system raised the possibility of using an actual DMD to replace the virtual DMD in the MiniTSFO and also of using the MiniTSFO's virtual DMD to communicate with a real TACFIRE system.

The MiniTSFO's Legacy
For several years, the Field Artillery School used the MiniTSFO as an example of the School's leadership in adopting computer technology. An overview of the MiniTSFO was briefed to all pre-command classes for Field Artillery battalionBattalion
A battalion is a military unit of around 300–1,200 soldiers usually consisting of between two and seven companies and typically commanded by either a Lieutenant Colonel or a Colonel...
and brigade
Brigade
A brigade is a major tactical military formation that is typically composed of two to five battalions, plus supporting elements depending on the era and nationality of a given army and could be perceived as an enlarged/reinforced regiment...
commanders as well as visiting dignitaries. It also provided some inspiration for the developers of the Guardfist II, a much more capable system. Some Artillerymen used it to keep their skills up (the Directory of the USAFAS Gunnery Department used it before meeting with lieutenants in basic Artillery training so that he could impress them with his skills with a DMD). In retrospect, it was a good introduction to what was to come later.
External links
- http://sill-www.army.mil/famag/1989/AUG_1989/AUG_1989_FULL_EDITION.pdf The Field Artillery Journal, August 1989, PP 32

