
Method of Fluxions
Encyclopedia
Method of Fluxions is a book by Isaac Newton
. The book was completed in 1671, and published in 1736. Fluxions is Newton's term for differential calculus
(fluents was his term for integral
calculus). He originally developed the method at Woolsthorpe Manor
during the closing of Cambridge
during the Great Plague of London
from 1665 to 1667, but did not choose to make his findings known (similarly, his findings which eventually became the Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica
were developed at this time and hidden from the world in Newton's notes for many years). Gottfried Leibniz
developed his calculus around 1673, and published it in 1684, fifty years before Newton. The calculus notation we use today is mostly that of Leibniz, although Newton's dot notation for differentiation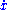 for denoting derivatives with respect to time is still in current use throughout mechanics
for denoting derivatives with respect to time is still in current use throughout mechanics
.
Newton's Method of Fluxions was formally published posthumously, but following Leibniz's publication of the calculus a bitter rivalry
erupted between the two mathematicians over who had developed the calculus first and so Newton no longer hid his knowledge of fluxions.
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton PRS was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian, who has been "considered by many to be the greatest and most influential scientist who ever lived."...
. The book was completed in 1671, and published in 1736. Fluxions is Newton's term for differential calculus
Differential calculus
In mathematics, differential calculus is a subfield of calculus concerned with the study of the rates at which quantities change. It is one of the two traditional divisions of calculus, the other being integral calculus....
(fluents was his term for integral
Integral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
calculus). He originally developed the method at Woolsthorpe Manor
Woolsthorpe Manor
Woolsthorpe Manor in Woolsthorpe-by-Colsterworth, near Grantham, Lincolnshire, England, was the birthplace of Sir Isaac Newton on 25 December 1642...
during the closing of Cambridge
University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public research university located in Cambridge, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest university in both the United Kingdom and the English-speaking world , and the seventh-oldest globally...
during the Great Plague of London
Great Plague of London
The Great Plague was a massive outbreak of disease in the Kingdom of England that killed an estimated 100,000 people, 20% of London's population. The disease is identified as bubonic plague, an infection by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, transmitted through a flea vector...
from 1665 to 1667, but did not choose to make his findings known (similarly, his findings which eventually became the Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica
Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica
Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, Latin for "Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy", often referred to as simply the Principia, is a work in three books by Sir Isaac Newton, first published 5 July 1687. Newton also published two further editions, in 1713 and 1726...
were developed at this time and hidden from the world in Newton's notes for many years). Gottfried Leibniz
Gottfried Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was a German philosopher and mathematician. He wrote in different languages, primarily in Latin , French and German ....
developed his calculus around 1673, and published it in 1684, fifty years before Newton. The calculus notation we use today is mostly that of Leibniz, although Newton's dot notation for differentiation
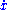 for denoting derivatives with respect to time is still in current use throughout mechanics
for denoting derivatives with respect to time is still in current use throughout mechanicsMechanics
Mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the behavior of physical bodies when subjected to forces or displacements, and the subsequent effects of the bodies on their environment....
.
Newton's Method of Fluxions was formally published posthumously, but following Leibniz's publication of the calculus a bitter rivalry
Newton v. Leibniz calculus controversy
The calculus controversy was an argument between 17th-century mathematicians Isaac Newton and Gottfried Leibniz over who had first invented calculus...
erupted between the two mathematicians over who had developed the calculus first and so Newton no longer hid his knowledge of fluxions.
External links
- Method of Fluxions at the Internet ArchiveInternet ArchiveThe Internet Archive is a non-profit digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It offers permanent storage and access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, music, moving images, and nearly 3 million public domain books. The Internet Archive...

