
Methanol reformer
Encyclopedia
A methanol refomer is a device used in chemical engineering
, especially in the area of fuel cell
technology, which can produce pure hydrogen
gas and carbon dioxide
by reacting a methanol
and water
(steam) mixture.
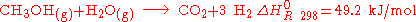
Methanol is transformed into hydrogen and carbon dioxide by pressure and heat and interaction with a catalyst
.
ratio (water:methanol) of 1.0 - 1.5 is pressurized to approximately 20 bar
, vaporized and heated to a temperature of 250 - 360 °C
. The hydrogen that is created is separated through the use of Pressure swing adsorption
or a hydrogen-permeable membrane made of polymer
or a palladium
alloy.
There are two basic methods of conducting this process.
With either design, not all of the hydrogen is removed from the product gases (raffinate). Since the remaining gas mixture still contains a significant amount of chemical energy, it is often mixed with air and burned to provide heat for the endothermic reforming reaction.
, is toxic and (of course) flammable. The cost of the PdAg membrane and its susceptibility to damage by temperature changes provide obstacles to adoption.
Another problem is that although hydrogen power produces energy without CO2, a methanol reformer creates the gas as a byproduct. The high level of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere significantly contributes to global warming
.
Methanol (prepared from natural gas) that is used in an efficient fuel cell, however, releases less CO2 in the atmosphere than gasoline, in a net analysis.
Chemical engineering
Chemical engineering is the branch of engineering that deals with physical science , and life sciences with mathematics and economics, to the process of converting raw materials or chemicals into more useful or valuable forms...
, especially in the area of fuel cell
Fuel cell
A fuel cell is a device that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Hydrogen is the most common fuel, but hydrocarbons such as natural gas and alcohols like methanol are sometimes used...
technology, which can produce pure hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
gas and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
by reacting a methanol
Methanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol...
and water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
(steam) mixture.
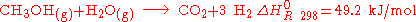
Methanol is transformed into hydrogen and carbon dioxide by pressure and heat and interaction with a catalyst
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
.
Technology
A mixture of water and methanol with a molar concentrationConcentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
ratio (water:methanol) of 1.0 - 1.5 is pressurized to approximately 20 bar
Bar (unit)
The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar...
, vaporized and heated to a temperature of 250 - 360 °C
Celsius
Celsius is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius , who developed a similar temperature scale two years before his death...
. The hydrogen that is created is separated through the use of Pressure swing adsorption
Pressure swing adsorption
Pressure swing adsorption is a technology used to separate some gas species from a mixture of gases under pressure according to the species' molecular characteristics and affinity for an adsorbent material. It operates at near-ambient temperatures and so differs from cryogenic distillation...
or a hydrogen-permeable membrane made of polymer
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
or a palladium
Palladium
Palladium is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pd and an atomic number of 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired...
alloy.
There are two basic methods of conducting this process.
- The water-methanol mixture is introduced into a tube-shaped reactor where it makes contact with the catalyst. Hydrogen is then separated from the other reactantsReagentA reagent is a "substance or compound that is added to a system in order to bring about a chemical reaction, or added to see if a reaction occurs." Although the terms reactant and reagent are often used interchangeably, a reactant is less specifically a "substance that is consumed in the course of...
and products in a later chamber, either by pressure swing adsorption (PSA), or through use of a membrane where the majority of the hydrogen passes through. This method is typically used for larger, non-mobile units. - The other process features an integrated reaction chamber and separation membrane, a membrane reactorMembrane reactorA membrane reactor is a piece of chemical equipment that combines a catalyst-filled reaction chamber with a membrane to add reactants or remove products of the reaction.Chemical reactors making use of membranes are usually referred to as membrane reactors...
. In this, relatively new approach, the reaction chamber is made to contain high-temperature, hydrogen-permeable membranes that can be formed of refractory metalsRefractory metalsRefractory metals are a class of metals that are extraordinarily resistant to heat and wear. The expression is mostly used in the context of materials science, metallurgy and engineering. The definition of which elements belong to this group differs...
, palladium alloys, or a PdAg-coated ceramicCeramicA ceramic is an inorganic, nonmetallic solid prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling. Ceramic materials may have a crystalline or partly crystalline structure, or may be amorphous...
. The hydrogen is thereby separated out of the reaction chamber as the reaction proceeds, This purifies the hydrogen and, as the reaction continues, increases both the reaction rate and the amount of hyrogen extracted.
With either design, not all of the hydrogen is removed from the product gases (raffinate). Since the remaining gas mixture still contains a significant amount of chemical energy, it is often mixed with air and burned to provide heat for the endothermic reforming reaction.
Advantages and disadvantages
Methanol reformers are being considered as a component of a hydrogen fuel cell-powered vehicle. A prototype car, the NECAR 5, was introduced by Daimler-Chrysler in the year 2000. The primary advantage of a vehicle with a reformer is that it does not need a pressurized gas tank to store hydrogen fuel; instead methanol is stored as a liquid. The logistic implications of this are great; pressurized hydrogen is difficult to store and produce. Also, this could help ease the public's concern over the danger of hydrogen and thereby make fuel cell powered vehicles more attractive. However, methanol, like gasolineGasoline
Gasoline , or petrol , is a toxic, translucent, petroleum-derived liquid that is primarily used as a fuel in internal combustion engines. It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. Some gasolines also contain...
, is toxic and (of course) flammable. The cost of the PdAg membrane and its susceptibility to damage by temperature changes provide obstacles to adoption.
Another problem is that although hydrogen power produces energy without CO2, a methanol reformer creates the gas as a byproduct. The high level of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere significantly contributes to global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
.
Methanol (prepared from natural gas) that is used in an efficient fuel cell, however, releases less CO2 in the atmosphere than gasoline, in a net analysis.

