
Meta- (chemistry)
Encyclopedia
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, meta is a prefix
Prefix
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the root of a word. Particularly in the study of languages,a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the words to which it is affixed.Examples of prefixes:...
, used for systematic names in IUPAC nomenclature
IUPAC nomenclature
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry ....
. It has several meanings.
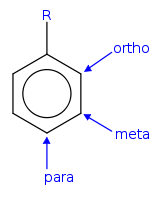
- In organic chemistry, meta indicates the positions of substituentsArene substitution patternsArene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.- Ortho, meta, and para substitution :...
in aromatic cyclic compoundCyclic compoundIn chemistry, a cyclic compound is a compound in which a series of atoms is connected to form a loop or ring.While the vast majority of cyclic compounds are organic, a few inorganic substances form cyclic compounds as well, including sulfur, silanes, phosphanes, phosphoric acid, and triboric acid. ...
s. The substituents have the 1,3-positions, for example in resorcinolResorcinolResorcinol is a dihydroxy benzene. It is the 1,3-isomer of benzenediol with the formula C6H42.-Nomenclature:Benzene-1,3-diol is the name recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry in its 1993 Recommendations for the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry.-Production:It is...
.
- Meta may also denote the dehydrated form of an acid, salt or organic derivative in a series.
- For example metabisulfiteMetabisulfiteA disulfite, commonly known as metabisulfite, is a chemical compound containing the disulfite ion [S2O52−].-Production of the disulfite ion:The disulfite ion is a dimer of the bisulfite ion...
: - 2 bisulfiteBisulfiteBisulfite ion is the ion HSO3−. Salts containing the HSO3− ion are termed bisulfites also known as sulfite lyes...
(HSO3−) → 1 metabisulfite S2O52− + H2O - and metaphosphoric acid:
- 3 orthophosphoric acid H3PO4 → 1 trimetaphosphoric acid (H3P3O9) + 3 H2O.
- Meta-antimonic acid, the dehydrated form of antimonic acid (H3SbO4), is HSbO3.

