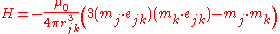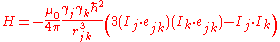Magnetic dipole-dipole interaction
Encyclopedia
Magnetic dipole–dipole interaction, also called dipolar coupling, refers to the direct interaction between two magnetic dipole
s. The potential energy
of the interaction is as follows:
where ejk is a unit vector parallel to the line joining the centers of the two dipoles. rjk is the distance between two dipoles, mk and mj.
For two interacting nuclear spin
s:
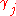 ,
, 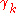 and rjk are gyromagnetic ratios of two spins and spin-spin distance respectively.
and rjk are gyromagnetic ratios of two spins and spin-spin distance respectively.
s (NOEs).
The residual dipolar coupling
(RDC) occur if the molecules in solution exhibit a partial alignment leading to an incomplete averaging of spatially anisotropic magnetic interactions i.e. dipolar couplings. RDC measurement provides information on the global folding
of the protein-long distance structural information. It also provides information about "slow" dynamics in molecules
Magnetic dipole
A magnetic dipole is the limit of either a closed loop of electric current or a pair of poles as the dimensions of the source are reduced to zero while keeping the magnetic moment constant. It is a magnetic analogue of the electric dipole, but the analogy is not complete. In particular, a magnetic...
s. The potential energy
Potential energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy stored in a body or in a system due to its position in a force field or due to its configuration. The SI unit of measure for energy and work is the Joule...
of the interaction is as follows:
where ejk is a unit vector parallel to the line joining the centers of the two dipoles. rjk is the distance between two dipoles, mk and mj.
For two interacting nuclear spin
Spin (physics)
In quantum mechanics and particle physics, spin is a fundamental characteristic property of elementary particles, composite particles , and atomic nuclei.It is worth noting that the intrinsic property of subatomic particles called spin and discussed in this article, is related in some small ways,...
s:
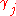 ,
, 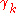 and rjk are gyromagnetic ratios of two spins and spin-spin distance respectively.
and rjk are gyromagnetic ratios of two spins and spin-spin distance respectively.Dipolar coupling and NMR spectroscopy
The direct dipole-dipole coupling is very useful for molecular structural studies, since it depends only on known physical constants and the inverse cube of internuclear distance. Estimation of this coupling provides a direct spectroscopic route to the distance between nuclei and hence the geometrical form of the molecule, or additionally also on intermolecular distances in the solid state leading to NMR crystallography notably in amorphous materials. Although internuclear magnetic dipole couplings contain a great deal of structural information, in isotropic solution, they average to zero as a result of rotational diffusion. However, their effect on nuclear spin relaxation results in measurable nuclear Overhauser effectNuclear Overhauser effect
The Nuclear Overhauser Effect is the transfer of nuclear spin polarization from one nuclear spin population to another via cross-relaxation. It is a common phenomenon observed by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The theoretical basis for the NOE was described and experimentally verified...
s (NOEs).
The residual dipolar coupling
Residual dipolar coupling
The residual dipolar coupling between two spins in a molecule occurs if the molecules in solution exhibit a partial alignment leading to an incomplete averaging of spatially anisotropic dipolar couplings....
(RDC) occur if the molecules in solution exhibit a partial alignment leading to an incomplete averaging of spatially anisotropic magnetic interactions i.e. dipolar couplings. RDC measurement provides information on the global folding
Protein folding
Protein folding is the process by which a protein structure assumes its functional shape or conformation. It is the physical process by which a polypeptide folds into its characteristic and functional three-dimensional structure from random coil....
of the protein-long distance structural information. It also provides information about "slow" dynamics in molecules
See also
- J-couplingJ-couplingJ-coupling is the coupling between two nuclear spins due to the influence of bonding electrons on the magnetic field running between the two nuclei. J-coupling contains information about dihedral angles, which can be estimated using the Karplus equation...
- Magic angleMagic angleThe magic angle is a precisely defined angle, the value of which is approximately 54.7356°. The magic angle is a root of a second-order Legendre polynomial, P_2=0 \,, and so any interaction which depends on this second-order Legendre polynomial vanishes at the magic angle...
- Residual dipolar couplingResidual dipolar couplingThe residual dipolar coupling between two spins in a molecule occurs if the molecules in solution exhibit a partial alignment leading to an incomplete averaging of spatially anisotropic dipolar couplings....
- Nuclear Overhauser effectNuclear Overhauser effectThe Nuclear Overhauser Effect is the transfer of nuclear spin polarization from one nuclear spin population to another via cross-relaxation. It is a common phenomenon observed by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The theoretical basis for the NOE was described and experimentally verified...
- Magnetic momentMagnetic momentThe magnetic moment of a magnet is a quantity that determines the force that the magnet can exert on electric currents and the torque that a magnetic field will exert on it...