
Lowell Observatory Near-Earth-Object Search
Encyclopedia
Lowell Observatory Near-Earth-Object Search (LONEOS) was a project designed to discover asteroids and comets that orbit near the Earth. The project, funded by NASA
, was directed by Dr. Ted Bowell
of Lowell Observatory
in Flagstaff, Arizona
. The LONEOS project began in 1993 and ran until the end of February 2008.
in 1990, and a Lowell-built 16 megapixel CCD
detector. This combination of instruments provided a field of view of 2.88 by 2.88 degrees (8.3 square degrees). It had a maximum nightly scan area of about 1,000 square degrees (covered four times). The instrument could cover the entire accessible dark sky in about a month. The CCD has detected asteroids as faint as visual magnitude 19.8 but its typical limiting visual magnitude was 19.3. The instrument is located at Lowell Observatory's dark sky site, Anderson Mesa Station, near Flagstaff, Arizona, USA.
Four computers were used. Two were used for frame reductions, one for telescope pointing control and one for camera control. The camera control software had scripting capability and could control all the other computers.
All asteroid positions were converted to equatorial coordinates. Various USNO star catalogs http://www.nofs.navy.mil/data/fchpix/ were used for this conversion until 2007. Then the Sloan Digital Sky Survey
catalog was used, along with supplemental information from the Carlsberg Catalog http://www.ast.cam.ac.uk/~dwe/SRF/cmc14.html and the 2MASS
catalog. Asteroid brightness was converted to standard visual magnitude. These data, along with the time of the observations, were sent to the Minor Planet Center
(MPC) from which they were distributed to the scientific community. Potential near-Earth objects were handled expeditiously so that other observers could locate the asteroid on the same night and make further observations.
Telescope operation was automated to the extent that the survey could be run all night without observer intervention. However, the telescope was seldom operated in the automatic mode because an observer was required to reduce data promptly and to correct any malfunctions that might have occurred.
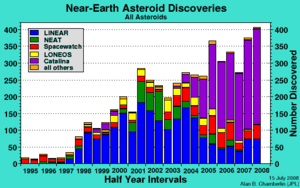 During the period of LONEOS operation, several other NASA funded NEO searches were underway. These projects include LINEAR
During the period of LONEOS operation, several other NASA funded NEO searches were underway. These projects include LINEAR
, Catalina
, Spacewatch
, and NEAT
. Amateur observers made a significant contribution during this time with independent NEO discoveries and by performing follow-up observations of recent discoveries made by the NASA sponsored surveys http://tech.groups.yahoo.com/group/mpml/messages.
. Each asteroid was typically observed four times (once per frame) each night.http://www.minorplanetcenter.org/iau/lists/YearlyBreakdown.html
A complete list of LONEOS NEO observations can be found at the NeoDyshttp://newton.dm.unipi.it/cgi-bin/neodys/neoibo?sites:699;obs;1;200 web site.
Collaborators:
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
, was directed by Dr. Ted Bowell
Edward L. G. Bowell
Edward L. G. Bowell , known as "Ted", is an American astronomer. Bowell was educated at Emanuel School London, University College, London, and the Université de Paris....
of Lowell Observatory
Lowell Observatory
Lowell Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona. Lowell Observatory was established in 1894, placing it among the oldest observatories in the United States, and was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1965....
in Flagstaff, Arizona
Flagstaff, Arizona
Flagstaff is a city located in northern Arizona, in the southwestern United States. In 2010, the city's population was 65,870. The population of the Metropolitan Statistical Area was at 134,421 in 2010. It is the county seat of Coconino County...
. The LONEOS project began in 1993 and ran until the end of February 2008.
Hardware
LONEOS, in its final configuration, used a 0.6-meter f/1.8 Schmidt telescope, acquired from Ohio Wesleyan UniversityOhio Wesleyan University
Ohio Wesleyan University is a private liberal arts college in Delaware, Ohio, United States. It was founded in 1842 by Methodist leaders and Central Ohio residents as a nonsectarian institution, and is a member of the Ohio Five — a consortium of Ohio liberal arts colleges...
in 1990, and a Lowell-built 16 megapixel CCD
Charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time...
detector. This combination of instruments provided a field of view of 2.88 by 2.88 degrees (8.3 square degrees). It had a maximum nightly scan area of about 1,000 square degrees (covered four times). The instrument could cover the entire accessible dark sky in about a month. The CCD has detected asteroids as faint as visual magnitude 19.8 but its typical limiting visual magnitude was 19.3. The instrument is located at Lowell Observatory's dark sky site, Anderson Mesa Station, near Flagstaff, Arizona, USA.
Four computers were used. Two were used for frame reductions, one for telescope pointing control and one for camera control. The camera control software had scripting capability and could control all the other computers.
Technique
Asteroids were found by obtaining four pictures (frames) of the same region of sky, each frame temporally separated by 15 to 30 minutes. The set of four frames were then submitted to reduction software which located all star-like sources on the frame and identified sources that moved with asteroid-like motion. The observer visually examined all asteroid detections that had motion different from a typical main-belt asteroid. Human examination was required because most putative NEO detections were not real but some kind of imaging artifact.All asteroid positions were converted to equatorial coordinates. Various USNO star catalogs http://www.nofs.navy.mil/data/fchpix/ were used for this conversion until 2007. Then the Sloan Digital Sky Survey
Sloan Digital Sky Survey
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey or SDSS is a major multi-filter imaging and spectroscopic redshift survey using a dedicated 2.5-m wide-angle optical telescope at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States. The project was named after the Alfred P...
catalog was used, along with supplemental information from the Carlsberg Catalog http://www.ast.cam.ac.uk/~dwe/SRF/cmc14.html and the 2MASS
2MASS
Observations for the Two Micron All-Sky Survey began in 1997 and were completed in 2001 at two telescopes located one each in the northern and southern hemispheres to ensure coverage of the entire sky...
catalog. Asteroid brightness was converted to standard visual magnitude. These data, along with the time of the observations, were sent to the Minor Planet Center
Minor Planet Center
The Minor Planet Center operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory , which is part of the Center for Astrophysics along with the Harvard College Observatory ....
(MPC) from which they were distributed to the scientific community. Potential near-Earth objects were handled expeditiously so that other observers could locate the asteroid on the same night and make further observations.
Telescope operation was automated to the extent that the survey could be run all night without observer intervention. However, the telescope was seldom operated in the automatic mode because an observer was required to reduce data promptly and to correct any malfunctions that might have occurred.
Other surveys

Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research
The Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research project is a cooperative project between the United States Air Force, NASA, and MIT's Lincoln Laboratory for the systematic discovery and tracking of near-Earth asteroids. LINEAR was responsible for the majority of asteroid detections since 1998 until...
, Catalina
Catalina Sky Survey
Catalina Sky Survey is a project to discover comets and asteroids, and to search for Near-Earth objects. More specifically, to search for potentially hazardous asteroids , that may pose a threat of impact.-Mission:...
, Spacewatch
Spacewatch
Spacewatch is a project at the University of Arizona led by Robert S. McMillan that specializes in the study of minor planets, including various types of asteroids and comets...
, and NEAT
Near Earth Asteroid Tracking
Near-Earth Asteroid Tracking is a program run by NASA and Jet Propulsion Laboratory to discover near-Earth objects. The NEAT project began in December 1995 and ran until April 2007.-History:...
. Amateur observers made a significant contribution during this time with independent NEO discoveries and by performing follow-up observations of recent discoveries made by the NASA sponsored surveys http://tech.groups.yahoo.com/group/mpml/messages.
LONEOS discovery and performance statistics
The table below lists the number of discoveries made by LONEOS each year of operation. Asteroids thought to be larger than one kilometer in diameter were used as benchmarks in assessing survey completeness. Hence, some table elements have two numbers separated by a slash. The second number represents the number of discoveries larger than one kilometer. The column labeled "Asteroid Observations" is the number of observations sent to the MPCMinor Planet Center
The Minor Planet Center operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory , which is part of the Center for Astrophysics along with the Harvard College Observatory ....
. Each asteroid was typically observed four times (once per frame) each night.http://www.minorplanetcenter.org/iau/lists/YearlyBreakdown.html
| Year | Asteroid Observations | NEAs | PHAs | Atens Aten asteroid The Aten asteroids are a group of near-Earth asteroids, named after the first of the group to be discovered . They are defined by having semi-major axes of less than one astronomical unit... |
Apollos Apollo asteroid The Apollo asteroids are a group of near-Earth asteroids named after 1862 Apollo, the first asteroid of this group to be discovered by Karl Wilhelm Reinmuth... |
Amors Amor asteroid The Amor asteroids are a group of near-Earth asteroids named after the asteroid 1221 Amor. They approach the orbit of the Earth from beyond, but do not cross it. Most Amors do cross the orbit of Mars... |
Comet Comet A comet is an icy small Solar System body that, when close enough to the Sun, displays a visible coma and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are both due to the effects of solar radiation and the solar wind upon the nucleus of the comet... s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1998 | 122550 | 7/4 | 0 | 0/0 | 3/2 | 4/2 | 1 |
| 1999 | 128220 | 14/7 | 5 | 2/2 | 6/3 | 6/2 | 6 |
| 2000 | 271237 | 38/10 | 4 | 3/0 | 18/5 | 17/5 | 6 |
| 2001 | 626976 | 42/11 | 9 | 4/0 | 17/4 | 21/7 | 7 |
| 2002 | 407064 | 21/4 | 3 | 3/1 | 9/0 | 9/3 | 3 |
| 2003 | 720528 | 54/10 | 17 | 5/1 | 26/3 | 23/6 | 2 |
| 2004 | 716152 | 39/4 | 9 | 5/0 | 22/4 | 12/0 | 4 |
| 2005 | 820609 | 42/4 | 8 | 6/0 | 15/1 | 21/3 | 8 |
| 2006 | 679927 | 19/1 | 2 | 0/0 | 11/1 | 8/0 | 2 |
| 2007 | 630469 | 12/0 | 2 | 2/0 | 4/0 | 6/0 | 3 |
| 2008 | 88953 | 1/0 | 0 | 0/0 | 1/0 | 0/0 | 0 |
| Total | 5212685 | 289/55 | 59 | 30/4 | 131/23 | 127/28 | 42 |
A complete list of LONEOS NEO observations can be found at the NeoDyshttp://newton.dm.unipi.it/cgi-bin/neodys/neoibo?sites:699;obs;1;200 web site.
Other Science
The LONEOS frame archive provides a data set with wide spatial and temporal sky coverage. Other investigators have used these characteristics to produce the following research papers and presentations.- Investigating the Distinct Components of the Galactic Stellar Halo RR Lyrae from the LONEOS-I Survey, American Astronomical Society, AAS Meeting #211, #163.02, Huber, Mark; Miceli, A.; Cook, K. H.; Rest, A.; Narayan, G.; Stubbs, C. W.
- Evidence for Distinct Components of the Galactic Stellar Halo from 838 RR Lyrae Stars Discovered in the LONEOS-I Survey, eprint arXiv:0706.1583,Miceli, A.; Rest, A.; Stubbs, C. W.; Hawley, S. L.; Cook, K. H.; Magnier, J.Johal, E. A.; Krisciunas, K.; Bowell, E.; Koehn, B.
- Detecting variable objects with the LONEOS photometric database: 15000 square degrees of variability measurements down to 19th magnitude in R, American Astronomical Society, 199th AAS Meeting, #101.10; Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society, Vol. 33, p.1463, Rest, A.; Miceli, A.; Miknaitis, G.; Covarrubias, R.; Stubbs, C.; Magnier, E.; Koehn, B.; Bowell, T.; Cook, K.; Krisciunas, K.
Highlights
- 1999 April 12, Shawn Hermann discovers an Aten, 1999 HF1, more than three kilometers in diameter.http://www.minorplanetcenter.org/mpec/J99/J99H17.html
- 1999 December 2, Bruce Koehn discovers the first Earth-crossing Damacloid, 1999 XS35, (later identified as a comet).http://www.minorplanetcenter.org/mpec/J99/J99X19.html
- 2001 August 14, Mike Van Ness discovers the second Earth-crossing Damacloid, C/2001 OG108 (LONEOS)C/2001 OG108 (LONEOS)C/2001 OG108 is a Halley-type comet with an orbital period of 48.51 years. It was discovered on 28 July 2001 by the LONEOS telescope at Lowell Observatory....
.http://www.minorplanetcenter.org/mpec/K01/K01P40.html
- 2001 November 20, discovers Near-Earth object that will pass 0.00166 AU from the Earth on 2028 June 26.
- 2003 September 27, Bob Cash finds the (then) closest Earth-crossing asteroid, 2003 SQ222.http://www.minorplanetcenter.org/mpec/K03/K03T03.html
- 2003 October 15, Brian A. SkiffBrian A. SkiffBrian A. Skiff is an American astronomer noted for discovering a number of comets including the periodic comets 114P/Wiseman-Skiff and 140P/Bowell-Skiff...
recovers 1937 UB (Hermes), a lost asteroid for 66 years.http://www.minorplanetcenter.org/mpec/K03/K03T74.html
- 2004 May 20, Brian Skiff finds an asteroid, 2004 JG62004 JG6' is an unusual asteroid.It is the second known Apohele asteroid , which means its entire orbit lies within that of the Earth. Its orbital period is less than that of Venus, making it one of the closest known objects to the Sun, after Mercury...
, with the (then) smallest orbit. It is the second asteroid found that has an orbit entirely within Earth's orbit.http://www.minorplanetcenter.org/mpec/K04/K04J60.html
LONEOS staff
Lowell staff:- Dr. Edward Bowell: Principal investigator
- Dr. Bruce Koehn: Computer programming
- Brian Skiff, Bill Ferris, Mike Van Ness, Shawn Hermann:
Professional observers
- Christopher Onken, Jennifer Palguta, Wendy Kelly, Jason Sanborn,
Thomas Grimstad, Lori Levy, Robert Cash, George Bliss, James Ashley:
Volunteer observers
Collaborators:
- Dr. Steve Howell, WIYN/NOAO: CCD performance modeling
- Dr. Karri Muinonen, University of Helsinki: Asteroid detection modeling
External links
- LONEOS
- Planetary Data System (PDS)
See also
- Planetary Data SystemPlanetary Data SystemThe Planetary Data System is a distributed data system that NASA uses to archive data collected by Solar System robotic missions and ground-based support data associated with those missions. PDS is managed by NASA Headquarters' Planetary Sciences Division. The PDS is an active archive that makes...
(PDS) - Minor Planet CenterMinor Planet CenterThe Minor Planet Center operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory , which is part of the Center for Astrophysics along with the Harvard College Observatory ....
- Catalina Sky SurveyCatalina Sky SurveyCatalina Sky Survey is a project to discover comets and asteroids, and to search for Near-Earth objects. More specifically, to search for potentially hazardous asteroids , that may pose a threat of impact.-Mission:...
- Near Earth Asteroid TrackingNear Earth Asteroid TrackingNear-Earth Asteroid Tracking is a program run by NASA and Jet Propulsion Laboratory to discover near-Earth objects. The NEAT project began in December 1995 and ran until April 2007.-History:...
(NEAT) - Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid ResearchLincoln Near-Earth Asteroid ResearchThe Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research project is a cooperative project between the United States Air Force, NASA, and MIT's Lincoln Laboratory for the systematic discovery and tracking of near-Earth asteroids. LINEAR was responsible for the majority of asteroid detections since 1998 until...
(LINEAR) - Pan-STARRSPan-STARRSThe Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System is a planned array of astronomical cameras and telescopes and computing facility that will survey the sky on a continual basis, including accurate astrometry and photometry of detected objects...
- SpaceguardSpaceguardThe term Spaceguard loosely refers to a number of efforts to discover and study near-Earth objects . Asteroids are discovered by telescopes which repeatedly survey large areas of sky. Efforts which concentrate on discovering NEOs are considered part of the "Spaceguard Survey," regardless of which...
- SpacewatchSpacewatchSpacewatch is a project at the University of Arizona led by Robert S. McMillan that specializes in the study of minor planets, including various types of asteroids and comets...

