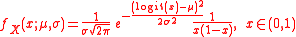Logit-normal distribution
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
, a logit-normal distribution is a probability distribution
of a random variable
whose logit
has a normal distribution. If Y is a random variable with a normal distribution, and P is the logistic function
, then X = P(Y) has a logit-normal distribution; likewise, if X is logit-normally distributed, then Y = logit
(X) is normally distributed.
A variable might be modeled as logit-normal if it is a proportion, which is bounded by zero and one, and where values of zero and one never occur.
of a log-normal distribution is:
where μ and σ are the mean
and standard deviation
of the variable’s logit
(by definition, the variable’s logit is normally distributed).
The density obtained by changing the sign of μ is symmetrical, in that it is equal to f(1-x;-μ,σ), shifting the mode to the other side of 0.5 (the mid-point of the (0,1) interval).
estimated by numerical integration
.
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
, a logit-normal distribution is a probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
of a random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
whose logit
Logit
The logit function is the inverse of the sigmoidal "logistic" function used in mathematics, especially in statistics.Log-odds and logit are synonyms.-Definition:The logit of a number p between 0 and 1 is given by the formula:...
has a normal distribution. If Y is a random variable with a normal distribution, and P is the logistic function
Logistic function
A logistic function or logistic curve is a common sigmoid curve, given its name in 1844 or 1845 by Pierre François Verhulst who studied it in relation to population growth. It can model the "S-shaped" curve of growth of some population P...
, then X = P(Y) has a logit-normal distribution; likewise, if X is logit-normally distributed, then Y = logit
Logit
The logit function is the inverse of the sigmoidal "logistic" function used in mathematics, especially in statistics.Log-odds and logit are synonyms.-Definition:The logit of a number p between 0 and 1 is given by the formula:...
(X) is normally distributed.
A variable might be modeled as logit-normal if it is a proportion, which is bounded by zero and one, and where values of zero and one never occur.
Probability density function
The probability density functionProbability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
of a log-normal distribution is:
where μ and σ are the mean
Mean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
and standard deviation
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
of the variable’s logit
Logit
The logit function is the inverse of the sigmoidal "logistic" function used in mathematics, especially in statistics.Log-odds and logit are synonyms.-Definition:The logit of a number p between 0 and 1 is given by the formula:...
(by definition, the variable’s logit is normally distributed).
The density obtained by changing the sign of μ is symmetrical, in that it is equal to f(1-x;-μ,σ), shifting the mode to the other side of 0.5 (the mid-point of the (0,1) interval).
Moments
The moments of the logit-normal distribution have no analytic solution. However, they can beestimated by numerical integration
Numerical integration
In numerical analysis, numerical integration constitutes a broad family of algorithms for calculating the numerical value of a definite integral, and by extension, the term is also sometimes used to describe the numerical solution of differential equations. This article focuses on calculation of...
.
Mode
When the derivative of the density equals 0 then the location of the mode x satisfies the following equation: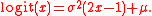
See also
- Normal distribution
- Beta distribution and Kumaraswamy distributionKumaraswamy distributionIn probability and statistics, the Kumaraswamy's double bounded distribution is a family of continuous probability distributions defined on the interval [0,1] differing in the values of their two non-negative shape parameters, a and b....
, other two-parameter distributions on a bounded interval with similar shapes
Further reading
- Frederic, P. & Lad, F. (2008) Two Moments of the Logitnormal Distribution. Communications in Statistics-Simulation and Computation. 37: 1263-1269
External links
- logitnorm package for RR (programming language)R is a programming language and software environment for statistical computing and graphics. The R language is widely used among statisticians for developing statistical software, and R is widely used for statistical software development and data analysis....