
Local Outlier Factor
Encyclopedia
Local outlier factor is an anomaly detection
algorithm presented as "LOF: Identifying Density-based Local Outliers" by Markus M. Breunig, Hans-Peter Kriegel
, Raymond T. Ng and Jörg Sander. The key idea of LOF is comparing the local density of a point's neighborhood with the local density of its neighbors.
LOF shares some concepts with DBSCAN
and OPTICS
such as the concepts of "core distance" and "reachability distance", which are used for local density estimation.
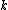 nearest neighbors, whose distance is used to estimate the density. By comparing the local density of an object to the local densities of its neighbors, one can identify regions of similar density, and points that have a substantially lower density than their neighbors. These are considered to be outlier
nearest neighbors, whose distance is used to estimate the density. By comparing the local density of an object to the local densities of its neighbors, one can identify regions of similar density, and points that have a substantially lower density than their neighbors. These are considered to be outlier
s.
The local density is estimated by the typical distance at which a point can be "reached" from its neighbors. The definition of "reachability distance" used in LOF is an additional measure to produce more stable results within clusters.
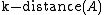 be the distance of the object
be the distance of the object 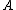 to the k nearest neighbor. Note that the set of the k nearest neighbors includes all objects at this distance, which can in the case of a "tie" be more than k objects. We denote the set of k nearest neighbors as
to the k nearest neighbor. Note that the set of the k nearest neighbors includes all objects at this distance, which can in the case of a "tie" be more than k objects. We denote the set of k nearest neighbors as 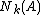 .
.
This distance is used to define what is called reachability distance:
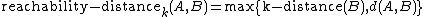
In words, the reachability distance of an object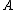 from
from 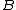 is the true distance of the two objects, but at least the
is the true distance of the two objects, but at least the 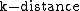 of
of 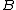 . Objects that belong to the k nearest neighbors of
. Objects that belong to the k nearest neighbors of 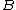 (the "core" of
(the "core" of 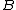 , see DBSCAN cluster analysis
, see DBSCAN cluster analysis
) are considered to be equally distant. The reason for this distance is to get more stable results. Note that this is not a distance
in the mathematical definition, since it is not symmetric.
The local reachability density of an object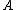 is defined by
is defined by
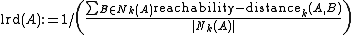
Which is the quotient of the average reachability distance of the object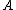 from its neighbors. Note that it is not the average reachability of the neighbors from
from its neighbors. Note that it is not the average reachability of the neighbors from 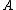 (which by definition would be the
(which by definition would be the 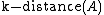 ), but the distance at which it can be "reached" from its neighbors.
), but the distance at which it can be "reached" from its neighbors.
The local reachability densities are then compared with those of the neighbors using
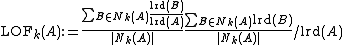
Which is the average local reachability density of the neighbors divided by the objects own local reachability density. A value of approximately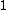 indicates that the object is comparable to its neighbors (and thus not an outlier). A value below
indicates that the object is comparable to its neighbors (and thus not an outlier). A value below 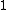 indicates a denser region (which would be an inlier), while values significantly larger than
indicates a denser region (which would be an inlier), while values significantly larger than 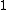 indicate outliers.
indicate outliers.
While the geometric intuition of LOF is only applicable to low dimensional vector spaces, the algorithm can be applied in any context a dissimilarity function can be defined. It has experimentally been shown to work very well in numerous setups, often outperforming the competitors, for example in network intrusion detection
.
-values and hard to interpret. A value of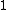 or even less indicates a clear inlier, but there is no clear rule for when a point is an outlier. In one data set, a value of
or even less indicates a clear inlier, but there is no clear rule for when a point is an outlier. In one data set, a value of 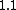 may already be an outlier, in another dataset and parameterization (with strong local fluctuations) a value of
may already be an outlier, in another dataset and parameterization (with strong local fluctuations) a value of 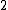 could still be an inlier. These differences can also occur within a dataset due to the locality of the method.
could still be an inlier. These differences can also occur within a dataset due to the locality of the method.
Anomaly detection
Anomaly detection, also referred to as outlier detection refers to detecting patterns in a given data set that do not conform to an established normal behavior....
algorithm presented as "LOF: Identifying Density-based Local Outliers" by Markus M. Breunig, Hans-Peter Kriegel
Hans-Peter Kriegel
Hans-Peter Kriegel is a German computer scientist and professor at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich and leading the Database Systems Group in the Department of Computer Science....
, Raymond T. Ng and Jörg Sander. The key idea of LOF is comparing the local density of a point's neighborhood with the local density of its neighbors.
LOF shares some concepts with DBSCAN
DBSCAN
DBSCAN is a data clustering algorithm proposed by Martin Ester, Hans-Peter Kriegel, Jörg Sander and Xiaowei Xu in 1996....
and OPTICS
OPTICS algorithm
OPTICS is an algorithm for finding density-based clusters in spatial data. It was presented by Mihael Ankerst, Markus M. Breunig, Hans-Peter Kriegel and Jörg Sander....
such as the concepts of "core distance" and "reachability distance", which are used for local density estimation.
Basic idea
As indicated by the title, the local outlier factor is based on a concept of a local density, where locality is given by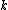 nearest neighbors, whose distance is used to estimate the density. By comparing the local density of an object to the local densities of its neighbors, one can identify regions of similar density, and points that have a substantially lower density than their neighbors. These are considered to be outlier
nearest neighbors, whose distance is used to estimate the density. By comparing the local density of an object to the local densities of its neighbors, one can identify regions of similar density, and points that have a substantially lower density than their neighbors. These are considered to be outlierOutlier
In statistics, an outlier is an observation that is numerically distant from the rest of the data. Grubbs defined an outlier as: An outlying observation, or outlier, is one that appears to deviate markedly from other members of the sample in which it occurs....
s.
The local density is estimated by the typical distance at which a point can be "reached" from its neighbors. The definition of "reachability distance" used in LOF is an additional measure to produce more stable results within clusters.
Formal
Let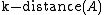 be the distance of the object
be the distance of the object 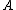 to the k nearest neighbor. Note that the set of the k nearest neighbors includes all objects at this distance, which can in the case of a "tie" be more than k objects. We denote the set of k nearest neighbors as
to the k nearest neighbor. Note that the set of the k nearest neighbors includes all objects at this distance, which can in the case of a "tie" be more than k objects. We denote the set of k nearest neighbors as 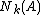 .
.This distance is used to define what is called reachability distance:
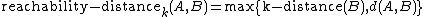
In words, the reachability distance of an object
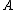 from
from 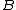 is the true distance of the two objects, but at least the
is the true distance of the two objects, but at least the 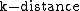 of
of 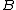 . Objects that belong to the k nearest neighbors of
. Objects that belong to the k nearest neighbors of 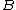 (the "core" of
(the "core" of 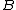 , see DBSCAN cluster analysis
, see DBSCAN cluster analysisDBSCAN
DBSCAN is a data clustering algorithm proposed by Martin Ester, Hans-Peter Kriegel, Jörg Sander and Xiaowei Xu in 1996....
) are considered to be equally distant. The reason for this distance is to get more stable results. Note that this is not a distance
Distance
Distance is a numerical description of how far apart objects are. In physics or everyday discussion, distance may refer to a physical length, or an estimation based on other criteria . In mathematics, a distance function or metric is a generalization of the concept of physical distance...
in the mathematical definition, since it is not symmetric.
The local reachability density of an object
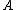 is defined by
is defined by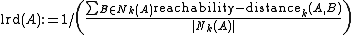
Which is the quotient of the average reachability distance of the object
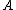 from its neighbors. Note that it is not the average reachability of the neighbors from
from its neighbors. Note that it is not the average reachability of the neighbors from 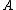 (which by definition would be the
(which by definition would be the 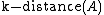 ), but the distance at which it can be "reached" from its neighbors.
), but the distance at which it can be "reached" from its neighbors.The local reachability densities are then compared with those of the neighbors using
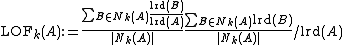
Which is the average local reachability density of the neighbors divided by the objects own local reachability density. A value of approximately
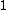 indicates that the object is comparable to its neighbors (and thus not an outlier). A value below
indicates that the object is comparable to its neighbors (and thus not an outlier). A value below 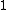 indicates a denser region (which would be an inlier), while values significantly larger than
indicates a denser region (which would be an inlier), while values significantly larger than 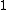 indicate outliers.
indicate outliers.Advantages
Due to the local approach, LOF is able to identify outliers in a data set that would not be outliers in another area of the data set. For example, a point at a "small" distance to a very dense cluster is an outlier, while a point within a sparse cluster might exhibit similar distances to its neighbors.While the geometric intuition of LOF is only applicable to low dimensional vector spaces, the algorithm can be applied in any context a dissimilarity function can be defined. It has experimentally been shown to work very well in numerous setups, often outperforming the competitors, for example in network intrusion detection
Network intrusion detection system
A Network Intrusion Detection System is an intrusion detection system that tries to detect malicious activity such as denial of service attacks, port scans or even attempts to crack into computers by Network Security Monitoring of network traffic.A NIDS reads all the incoming packets and tries to...
.
Disadvantages
The resulting values are quotientQuotient
In mathematics, a quotient is the result of division. For example, when dividing 6 by 3, the quotient is 2, while 6 is called the dividend, and 3 the divisor. The quotient further is expressed as the number of times the divisor divides into the dividend e.g. The quotient of 6 and 2 is also 3.A...
-values and hard to interpret. A value of
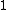 or even less indicates a clear inlier, but there is no clear rule for when a point is an outlier. In one data set, a value of
or even less indicates a clear inlier, but there is no clear rule for when a point is an outlier. In one data set, a value of 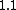 may already be an outlier, in another dataset and parameterization (with strong local fluctuations) a value of
may already be an outlier, in another dataset and parameterization (with strong local fluctuations) a value of 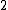 could still be an inlier. These differences can also occur within a dataset due to the locality of the method.
could still be an inlier. These differences can also occur within a dataset due to the locality of the method.Extensions
- Feature Bagging for Outlier Detection runs LOF on multiple projections and combines the results for improved detection qualities in high dimensions.
- Local Outlier Probability (LoOP) is a method derived from LOF but using inexpensive local statistics to become less sensitive to the choice of the parameter k. In addition, the resulting values are scaled to a value range of
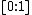 .
. - Interpreting and Unifying Outlier Scores proposes a normalization of the LOF outlier scores to the interval
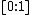 using statistical scaling to increase usabilityUsabilityUsability is the ease of use and learnability of a human-made object. The object of use can be a software application, website, book, tool, machine, process, or anything a human interacts with. A usability study may be conducted as a primary job function by a usability analyst or as a secondary job...
using statistical scaling to increase usabilityUsabilityUsability is the ease of use and learnability of a human-made object. The object of use can be a software application, website, book, tool, machine, process, or anything a human interacts with. A usability study may be conducted as a primary job function by a usability analyst or as a secondary job...
.

