
List of supernova remnants
Encyclopedia
This is a list of observed supernova remnants.
| Image | Name | Date of Arrival of Supernova's Light at Earth | Apparent Magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... | Distance (ly) | Type | Remnant Supernova remnant A supernova remnant is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar material it sweeps up and shocks along the way.There are two... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sagittarius A East Sagittarius A Sagittarius A is a complex radio source at the center of our galaxy, the Milky Way. It is located in the sky in the Sagittarius constellation... |
? | ? | 26,000 | ? | Sagittarius A East Sagittarius A Sagittarius A is a complex radio source at the center of our galaxy, the Milky Way. It is located in the sky in the Sagittarius constellation... |
|
| Simeis 147 Simeis 147 Simeis 147 is a supernova remnant in the constellations of Taurus and Auriga.The nebulous area is fairly large, with an apparent size covering around 3 degrees, and is approximately 3000 light years away, and covers an area of around 41.9 parsecs , and is approximately 40 000 years old .-References:... |
>100,000 BC | ? | 3,000 | ? | Simeis 147 or Sharpless 2-240 Simeis 147 Simeis 147 is a supernova remnant in the constellations of Taurus and Auriga.The nebulous area is fairly large, with an apparent size covering around 3 degrees, and is approximately 3000 light years away, and covers an area of around 41.9 parsecs , and is approximately 40 000 years old .-References:... |
|
 |
W49B W49B W49B or SNR G043.3-00.2 or 3C 398 is a nebula and is thought to be a remnant of a gamma-ray burster. If so, it is the first one found.W49B is barrel-shaped and located roughly 35,000 light-years from Earth... |
? | ? | 35,000 | ? | GRB Gamma ray burst Gamma-ray bursts are flashes of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the most luminous electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several minutes, although a typical... remnant? |
| W50 W50 (nebula) W50 or SNR G039.7-02.0 is a Supernova remnant located in the Aquila constellation, about 18,000 light years away. In its centre lies the micro-quasar SS 433, whose jets are distorting the remnant's shell. Most likely W50 and SS443 are related objects, remnants from a supernova which occurred about... |
? | ? | 16,000 | ? | SS 433 SS 433 SS 433 is one of the most exotic star systems observed. It is an eclipsing X-ray binary system, with the primary most likely a black hole, or possibly a neutron star., pp. 23–24. The spectrum of the secondary companion star suggests that it is a late A-type star... |
|
| Vela Supernova Vela Supernova Remnant The Vela supernova remnant is a supernova remnant in the southern constellation Vela. Its source supernova exploded approximately 11,000-12,300 years ago... |
11th–9th millennium BC 9th millennium BC The 9th millennium BC marks the beginning of the Neolithic period.Agriculture spread throughout the Fertile Crescent and use of pottery became more widespread. Larger settlements like Jericho arose along salt and flint trade routes. Northern Eurasia was resettled as the glaciers of the last glacial... |
? | 800 | ? | Vela Supernova Remnant Vela Supernova Remnant The Vela supernova remnant is a supernova remnant in the southern constellation Vela. Its source supernova exploded approximately 11,000-12,300 years ago... |
|
| Veil Nebula Veil Nebula The Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and ionized gas and dust in the constellation Cygnus. It constitutes the visible portions of the Cygnus Loop , a large but relatively faint supernova remnant... |
>3600 BC | ? | 1,400–2,600 | ? | NGC 6960, 6974, 6979, 6992, and 6995 |
|
| Puppis A Puppis A Puppis A is a supernova remnant about 10 light-years in diameter. The supernova 'occurred' approximately 3700 years ago... |
~1700 BC | ? | 7,000 approx | ? | ||
| SN 185 SN 185 SN 185 was a supernova which appeared in the year 185 AD, near the direction of Alpha Centauri, between the constellations Circinus and Centaurus, centered at RA Dec , in Circinus. This "guest star" was observed by Chinese astronomers in the Book of Later Han, and may have been recorded in Roman... |
December 7, 185 | ? | 8,200? | Ia Type Ia supernova A Type Ia supernova is a sub-category of supernovae, which in turn are a sub-category of cataclysmic variable stars, that results from the violent explosion of a white dwarf star. A white dwarf is the remnant of a star that has completed its normal life cycle and has ceased nuclear fusion... ? |
Possibly RCW RCW Catalogue The RCW Catalogue is an Astronomical catalogue of Hα-emission regions in the southern Milky Way, described in . It has 180 objects and includes many of the earlier Gum Catalog objects, and the later Caldwell catalogue included some RCW... 86 |
|
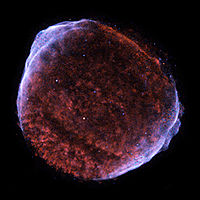 |
SN 1006 SN 1006 SN 1006 was a supernova, widely seen on Earth beginning in the year 1006 AD; Earth was about 7,200 light-years away from the supernova. It was the brightest apparent magnitude stellar event in recorded history reaching an estimated -7.5 visual magnitude... |
May 1, 1006 | −7.5 | 7,200 | Ia Type Ia supernova A Type Ia supernova is a sub-category of supernovae, which in turn are a sub-category of cataclysmic variable stars, that results from the violent explosion of a white dwarf star. A white dwarf is the remnant of a star that has completed its normal life cycle and has ceased nuclear fusion... |
SNR 1006 SN 1006 SN 1006 was a supernova, widely seen on Earth beginning in the year 1006 AD; Earth was about 7,200 light-years away from the supernova. It was the brightest apparent magnitude stellar event in recorded history reaching an estimated -7.5 visual magnitude... |
| SN 1054 SN 1054 SN 1054 is a supernova that was first observed as a new "star" in the sky on July 4, 1054 AD, hence its name, and that lasted for a period of around two years. The event was recorded in multiple Chinese and Japanese documents and in one document from the Arab world... |
1054 | −6 | 6,300 | II | Crab Nebula Crab Nebula The Crab Nebula is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus... |
|
| G350.1-0.3 G350.1-0.3 G350.1-0.3 is a supernova remnant in the Milky Way, possibly associated with a neutron star formed in the same supernova explosion... |
about 1100 | ? | 15,000 approx. | ? | G350.1-0.3 G350.1-0.3 G350.1-0.3 is a supernova remnant in the Milky Way, possibly associated with a neutron star formed in the same supernova explosion... |
|
 |
SN 1181 SN 1181 First observed between August 4 and August 6, 1181, Chinese and Japanese astronomers recorded the supernova now known as SN 1181 in eight separate texts.... |
1181 | −1 | 26,000 at least | ? | Possibly 3C58 3C58 3C58 or 3C 58 is a pulsar and surrounding synchrotron nebula within the Milky Way that is possibly associated with the supernova SN 1181. There are, however, signs that indicate that it could be several thousand years old, and thus not associated with that supernova... |
| RX J0852.0-4622 RX J0852.0-4622 RX J0852.0-4622 is a recently discovered supernova remnant. The remnant is located in the southern sky in the constellation Vela , and sits inside the much larger and older Vela Supernova Remnant... |
about 1250 | ? | 700 | ? | G266.2−1.2 | |
 |
SN 1572 SN 1572 SN 1572 , "B Cassiopeiae" , or 3C 10 was a supernova of Type Ia in the constellation Cassiopeia, one of about eight supernovae visible to the naked eye in historical records... |
November 11, 1572 | −4 | 7,500 | Ia Type Ia supernova A Type Ia supernova is a sub-category of supernovae, which in turn are a sub-category of cataclysmic variable stars, that results from the violent explosion of a white dwarf star. A white dwarf is the remnant of a star that has completed its normal life cycle and has ceased nuclear fusion... |
Tycho's Supernova Remnant SN 1572 SN 1572 , "B Cassiopeiae" , or 3C 10 was a supernova of Type Ia in the constellation Cassiopeia, one of about eight supernovae visible to the naked eye in historical records... |
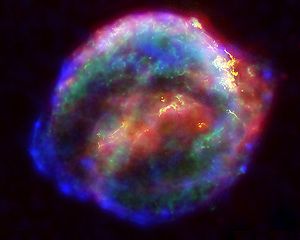 |
SN 1604 SN 1604 Supernova 1604, also known as Kepler's Supernova, Kepler's Nova or Kepler's Star, was a supernova that occurred in the Milky Way, in the constellation Ophiuchus. , it is the last supernova to have been unquestionably observed in our own galaxy, occurring no farther than 6 kiloparsecs or about... |
October 8, 1604 | −2.5 | 20,000 | Ia Type Ia supernova A Type Ia supernova is a sub-category of supernovae, which in turn are a sub-category of cataclysmic variable stars, that results from the violent explosion of a white dwarf star. A white dwarf is the remnant of a star that has completed its normal life cycle and has ceased nuclear fusion... |
Kepler's Supernova Remnant SN 1604 Supernova 1604, also known as Kepler's Supernova, Kepler's Nova or Kepler's Star, was a supernova that occurred in the Milky Way, in the constellation Ophiuchus. , it is the last supernova to have been unquestionably observed in our own galaxy, occurring no farther than 6 kiloparsecs or about... |
 |
Cassiopeia A Cassiopeia A Cassiopeia A is a supernova remnant in the constellation Cassiopeia and the brightest astronomical radio source in the sky, with a flux density of 2720 Jy at 1 GHz. The supernova occurred approximately away in the Milky Way. The expanding cloud of material left over from the supernova is now... |
mid 17th century | +6 | 10,000 | IIb | Cassiopeia A Supernova Remnant Cassiopeia A Cassiopeia A is a supernova remnant in the constellation Cassiopeia and the brightest astronomical radio source in the sky, with a flux density of 2720 Jy at 1 GHz. The supernova occurred approximately away in the Milky Way. The expanding cloud of material left over from the supernova is now... |
| G1.9+0.3 Supernova remnant G1.9+0.3 Supernova remnant G1.9+0.3 is the youngest known supernova remnant in the Milky Way Galaxy. The remnant's young age was established by combining data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and the VLA radio observatory, and is believed to have exploded about 25,000 years ago, and the signal began... |
about 1868 | ? | 25,000 approx. | ? | Supernova remnant G1.9+0.3 Supernova remnant G1.9+0.3 Supernova remnant G1.9+0.3 is the youngest known supernova remnant in the Milky Way Galaxy. The remnant's young age was established by combining data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and the VLA radio observatory, and is believed to have exploded about 25,000 years ago, and the signal began... |
|
| SN 1885A S Andromedae |- style="background-color: #A0B0FF;" colspan="3"| Database References|- bgcolor="#FFFAFA"| Simbad || |- bgcolor="#FFFAFA"| ||... |
August 20, 1885 | +6 | 2,500,000 | ? | SNR 1885A S Andromedae |- style="background-color: #A0B0FF;" colspan="3"| Database References|- bgcolor="#FFFAFA"| Simbad || |- bgcolor="#FFFAFA"| ||... |
|
 |
SN 1987A SN 1987A SN 1987A was a supernova in the outskirts of the Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a nearby dwarf galaxy. It occurred approximately 51.4 kiloparsecs from Earth, approximately 168,000 light-years, close enough that it was visible to the naked eye. It could be seen from the Southern... |
February 24, 1987 | +3 | 168,000 | II-P | SNR 1987A SN 1987A SN 1987A was a supernova in the outskirts of the Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a nearby dwarf galaxy. It occurred approximately 51.4 kiloparsecs from Earth, approximately 168,000 light-years, close enough that it was visible to the naked eye. It could be seen from the Southern... |
| EO102 EO102 E0102 is the remnant of a supernova that exploded in the neighbouring galaxy known as the Small Magellanic Cloud. The supernova was caused when a star much more massive than the Sun collapsed under its own gravity. The explosion would have been visible from the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth over... |
? | ? | 190,000 | ? | EO102 EO102 E0102 is the remnant of a supernova that exploded in the neighbouring galaxy known as the Small Magellanic Cloud. The supernova was caused when a star much more massive than the Sun collapsed under its own gravity. The explosion would have been visible from the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth over... |

