
List of armored cruisers of Germany
Encyclopedia

Cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. The term has been in use for several hundreds of years, and has had different meanings throughout this period...
types, including small aviso
Aviso
An aviso , a kind of dispatch boat or advice boat, survives particularly in the French navy, they are considered equivalent to the modern sloop....
s and larger protected cruisers. Due to budget constraints, the navy was unable to build cruisers designed solely for fleet service or for overseas duties. As a result, the naval construction department attempted to design vessels that could fulfill both roles. The protected cruisers, the first of which were the two vessels, were laid down starting in 1886. The protected cruisers evolved into more powerful vessels, culminating in , Germany's first armored cruiser
Armored cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Like other types of cruiser, the armored cruiser was a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship, and fast enough to outrun any battleships it encountered.The first...
. Fürst Bismarck was laid down in 1896, a decade after the first German protected cruiser.
Fürst Bismarck proved to be "ideally suited" to overseas duties and formed the basis for subsequent armored cruiser designs. followed in 1898 and incorporated several alterations, including a reduced primary armament, a thinner but more comprehensive armor system, and a higher top speed. The two vessels, laid down in 1900 and 1901, were designed with incremental improvements over Prinz Heinrich. and , two sister ships laid down in 1902 and 1903, respectively, were similar to the two Prinz Adalbert-class cruisers and incorporated only minor improvements. The two s, laid down in 1904 and 1905, were marked improvements over the previous designs; they carried a much heavier armament and were more than 2 knots (1.1 m/s) faster than the earlier vessels. The last German armored cruiser, , bridged the development of larger, more powerful battlecruiser
Battlecruiser
Battlecruisers were large capital ships built in the first half of the 20th century. They were developed in the first decade of the century as the successor to the armoured cruiser, but their evolution was more closely linked to that of the dreadnought battleship...
s. The ship was significantly larger, better armed, and faster than the Scharnhorst class, though she remained inferior to the new s then being built by the British Royal Navy
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service...
.
German armored cruisers followed the pattern set by the corresponding battleships; as compared to foreign equivalents, German warships mounted smaller main battery guns, but a heavier secondary battery. This armament has been compared unfavorably against their British and other counterparts. Naval historian Hugh Lyon remarked that the armored cruisers built by Germany were the "worst designed and least battle-worthy ships" in the navy. Conversely, the German battlecruisers, into which the armored cruiser evolved, were very highly regarded; naval historian John Campbell stated that was "a considerably better fighting ship than any of the 6 British 12 in gun battlecruisers."
Key
| Armament | The number and type of the primary armament |
| Armor | The maximum thickness of the armored belt |
| Displacement | Ship displacement Displacement (ship) A ship's displacement is its weight at any given time, generally expressed in metric tons or long tons. The term is often used to mean the ship's weight when it is loaded to its maximum capacity. A number of synonymous terms exist for this maximum weight, such as loaded displacement, full load... at full combat load |
| Propulsion | Number of shafts, type of propulsion system, and top speed/horsepower generated |
| Cost | Cost of the ship's construction |
| Service | The dates work began and finished on the ship and its ultimate fate |
| Laid down | The date the keel Keel In boats and ships, keel can refer to either of two parts: a structural element, or a hydrodynamic element. These parts overlap. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in construction of a ship, in British and American shipbuilding traditions the construction is dated from this event... began to be assembled |
| Commissioned | The date the ship was commissioned Ship commissioning Ship commissioning is the act or ceremony of placing a ship in active service, and may be regarded as a particular application of the general concepts and practices of project commissioning. The term is most commonly applied to the placing of a warship in active duty with its country's military... |
SMS Fürst Bismarck

Fürst Bismarck was the first armored cruiser
Armored cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Like other types of cruiser, the armored cruiser was a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship, and fast enough to outrun any battleships it encountered.The first...
constructed for the Imperial Navy. The ship was the only member of its class, and was designed primarily to serve in Germany's colonial fleet. The design for Fürst Bismarck was an improvement over the previous Victoria Louise-class
Victoria Louise class protected cruiser
The Victoria Louise class of protected cruisers was Germany's last class of ships of that type. They were designed for overseas cruiser duties. The class design introduced the clipper bow and blocky sides that typified later German armored cruisers....
protected cruiser
Protected cruiser
The protected cruiser is a type of naval cruiser of the late 19th century, so known because its armoured deck offered protection for vital machine spaces from shrapnel caused by exploding shells above...
—Fürst Bismarck was significantly larger and better armed than her predecessors. She was equipped with four 24 centimetres (9.4 in) guns mounted in twin gun turret
Gun turret
A gun turret is a weapon mount that protects the crew or mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon and at the same time lets the weapon be aimed and fired in many directions.The turret is also a rotating weapon platform...
s fore and aft, and with twelve 15 cm (5.9 in) casemate
Casemate
A casemate, sometimes rendered casement, is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which guns are fired. originally a vaulted chamber in a fortress.-Origin of the term:...
d guns as secondary armament. Fürst Bismarck was fitted with Krupp armor; the ship's main armor belt was up to 20 cm (7.9 in) thick over the vessel's machinery spaces, and the deck was armored to a thickness of 3 to 5 cm (1.2 to 2 in).
Assigned to the German East Asia Squadron
German East Asia Squadron
The German East Asia Squadron was a German Navy cruiser squadron which operated mainly in the Pacific Ocean between the 1870s and 1914...
, Fürst Bismarck assisted in suppressing the Boxer Rebellion
Boxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also called the Boxer Uprising by some historians or the Righteous Harmony Society Movement in northern China, was a proto-nationalist movement by the "Righteous Harmony Society" , or "Righteous Fists of Harmony" or "Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists" , in China between...
before being replaced in 1909 by . Modernized upon arriving in Germany, she acted in a coast-defense role early in World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, but was soon relegated to service as a stationary training ship. Following the war, Fürst Bismarck was scrapped in 1919–1920.
| Ship | Armament | Armor | Displacement | Propulsion | Cost | Service | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laid down | Commissioned | Fate | ||||||
| 4 × 24 cm (9.4 in) SK L/40 10 × 15 cm (5.9 in) SK L/40 guns |
20 cm (7.9 in) | 11461 MT (11,280 LT) | 3 screws, triple expansion engines, 18.7 kn (10.2 m/s), 13,622 ihp | 18,945,000 marks German gold mark The Goldmark was the currency used in the German Empire from 1873 to 1914.-History:Before unification, the different German states issued a variety of different currencies, though most were linked to the Vereinsthaler, a silver coin containing 16⅔ grams of pure silver... |
1896 | 1 April 1900 | Broken up for scrap in 1919–1920 | |
SMS Prinz Heinrich
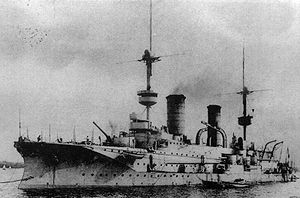
Kaiserliche Werft Kiel
Kaiserliche Werft Kiel was a German shipbuilding company founded in 1867, first as Königliche Werft Kiel but renamed in 1871 with the proclamation of the German Empire...
in Kiel
Kiel
Kiel is the capital and most populous city in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 238,049 .Kiel is approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the north of Germany, the southeast of the Jutland peninsula, and the southwestern shore of the...
. She was laid down in 1898 and completed in March 1902 at a cost of 16,588,000 Marks
German gold mark
The Goldmark was the currency used in the German Empire from 1873 to 1914.-History:Before unification, the different German states issued a variety of different currencies, though most were linked to the Vereinsthaler, a silver coin containing 16⅔ grams of pure silver...
. Prinz Heinrichs design was a modification of Fürst Bismarck, and traded a smaller main battery for higher speed and more comprehensive armor protection. The ship set a precedent for subsequent German armored cruisers by concentrating her secondary armament amidships, as opposed to Fürst Bismarck, which spread the secondary armament along the length of the ship.
Prinz Heinrich served with the German fleet for the majority of her career. After the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, the ship participated in an operation against the British coast in December 1914, after which she was transferred to the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
. Here, she operated against the Russian navy and was involved in the Battle of the Gulf of Riga
Battle of the Gulf of Riga
The Battle of the Gulf of Riga was a World War I naval operation of the German High Seas Fleet against the Russian Baltic Fleet in the Gulf of Riga in the Baltic Sea in August 1915...
in August 1915, where she damaged a Russian destroyer. In 1916, the ship was withdrawn from active duty and was used in several secondary roles in Kiel, including acting as a floating office for naval staff. Prinz Heinrich was ultimately sold in 1920 and broken up for scrap later that year.
| Ship | Armament | Armor | Displacement | Propulsion | Cost | Service | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laid down | Commissioned | Fate | ||||||
| 2 × 24 cm (9.4 in) SK L/40 10 × 15 cm (5.9 in) SK L/40 guns |
10 cm (3.9 in) | 9806 MT (9,651.1 LT) | 3 screws, triple expansion engines, 19.9 kn (10.8 m/s), 15,694 ihp | 16,588,000 marks | 1898 | 11 March 1902 | Broken up for scrap in 1920 | |
Prinz Adalbert class
The Prinz Adalbert class comprised two ships, and . Friedrich Carl was commissioned first, on 12 December 1903, and Prinz Adalbert followed on 12 January 1904. They were an improvement on the design of the previous armored cruiser, Prinz Heinrich. Their armor belts were the same thickness but were more extensive than that of their predecessor. The two ships were armed with four main guns in twin gun turrets, as opposed to the two single gun turrets of Prinz Heinrich.Both ships saw extensive service with the German Navy; Prinz Adalbert was used as a gunnery training ship for the her entire peacetime career, while Friedrich Carl served with the fleet until 1909, when she was withdrawn to act as a torpedo training vessel. At the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, both vessels were mobilized and assigned to the cruiser squadron in the Baltic. Friedrich Carl was sunk by Russian naval mines off Memel
Klaipeda
Klaipėda is a city in Lithuania situated at the mouth of the Nemunas River where it flows into the Baltic Sea. It is the third largest city in Lithuania and the capital of Klaipėda County....
in November 1914, though most of her crew was safely evacuated. Prinz Adalbert was torpedoed twice by British submarines operating in the Baltic; the first, on 1 July 1915, caused serious damage that was ultimately repaired. The second, on 23 October 1915, caused a catastrophic explosion in the ship's ammunition magazines that destroyed the vessel. Six hundred and seventy-two men were killed, the greatest single loss of life for the German Navy in the Baltic during the war.
| Ship | Armament | Armor | Displacement | Propulsion | Cost | Service | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laid down | Commissioned | Fate | ||||||
| 4 × 21 cm (8.3 in) SK L/40 10 × 15 cm (5.9 in) SK L/40 guns |
10 cm (3.9 in) | 9875 MT (9,719 LT) | 3 screws, triple expansion engines, 20.4 kn (11.1 m/s), 17,272 ihp | 16,371,000 marks | 1900 | 12 January 1904 | Sunk on 23 October 1915 by | |
| 4 × 21 cm (8.3 in) SK L/40 10 × 15 cm (5.9 in) SK L/40 guns |
10 cm (3.9 in) | 9875 MT (9,719 LT) | 3 screws, triple expansion engines, 20.5 kn (11.2 m/s), 18,541 ihp | 15,665,000 marks | 1901 | 12 December 1903 | Sunk on 17 November 1914 by Russian mines | |
Roon class
The Roon class comprised and , which closely resembled the earlier Prinz Adalbert class ships, but incorporated incremental improvements. The ships were easily distinguished from their predecessors by the addition of a fourth funnel. Like all of the armored cruisers built by Germany, they were intended to serve as station ships in Germany's overseas possessions. The ships displaced up to 9875 metric tons (9,719 LT) and were armed with a main battery of four 21 cm (8.3 in) guns. Their top speed was 21 kn (11.4 m/s).The two ships served with the High Seas Fleet
High Seas Fleet
The High Seas Fleet was the battle fleet of the German Empire and saw action during World War I. The formation was created in February 1907, when the Home Fleet was renamed as the High Seas Fleet. Admiral Alfred von Tirpitz was the architect of the fleet; he envisioned a force powerful enough to...
in the reconnaissance squadrons after they joined the fleet in 1905–1906. At the outbreak of World War I in 1914, the ships served alongside the more powerful battlecruiser
Battlecruiser
Battlecruisers were large capital ships built in the first half of the 20th century. They were developed in the first decade of the century as the successor to the armoured cruiser, but their evolution was more closely linked to that of the dreadnought battleship...
s of the I Scouting Group
I Scouting Group
The I Scouting Group was a special reconnaissance unit within the German Kaiserliche Marine. The unit was famously commanded by Admiral Franz von Hipper during World War I. The I Scouting Group was one of the most active formations in the High Seas Fleet during the war; the unit took part in every...
. While returning to port after a raid of the English coast
Raid on Yarmouth
The Raid on Yarmouth, which took place on 3 November 1914, was an attack by the German Navy on the British North Sea port and town of Great Yarmouth. Little damage was done to the town since shells only landed on the beach after German ships laying mines offshore were interrupted by British...
on 3–4 November 1914, Yorck struck German mines and sank with heavy loss of life. Roon was disarmed in 1916 and intended to be converted into a seaplane carrier, though this was never carried out. The ship was eventually broken up for scrap in 1921.
| Ship | Armament | Armor | Displacement | Propulsion | Cost | Service | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laid down | Commissioned | Fate | ||||||
| 4 × 21 cm SK L/40 10 × 15 cm (5.9 in) SK L/40 guns |
10 cm (3.9 in) | 10266 MT (10,103.8 LT) | 3 screws, triple expansion engines, 21.1 kn (11.5 m/s), 20,625 ihp | 15,345,000 marks | 1902 | 5 April 1906 | Broken up for scrap in 1921 | |
| 4 × 21 cm SK L/40 10 × 15 cm (5.9 in) SK L/40 guns |
10 cm (3.9 in) | 10266 MT (10,103.8 LT) | 3 screws, triple expansion engines, 21.4 kn (11.7 m/s), 20,031 ihp | 16,241,000 marks | 1903 | 21 November 1905 | Sunk on 4 November 1914 by German mines | |
Scharnhorst class

Built for overseas service, Scharnhorst and Gneisenau were assigned to the East Asia Squadron
German East Asia Squadron
The German East Asia Squadron was a German Navy cruiser squadron which operated mainly in the Pacific Ocean between the 1870s and 1914...
in 1909 and 1910, respectively. Both ships had brief careers; shortly before the outbreak of World War I, the ships departed the German colony at Tsingtao. On 1 November 1914, the ships destroyed a British force at the Battle of Coronel
Battle of Coronel
The First World War naval Battle of Coronel took place on 1 November 1914 off the coast of central Chile near the city of Coronel. German Kaiserliche Marine forces led by Vice-Admiral Graf Maximilian von Spee met and defeated a Royal Navy squadron commanded by Rear-Admiral Sir Christopher...
and inflicted upon the Royal Navy
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service...
its first defeat since the Battle of Plattsburgh
Battle of Plattsburgh
The Battle of Plattsburgh, also known as the Battle of Lake Champlain, ended the final invasion of the northern states during the War of 1812...
in 1814. The East Asia Squadron, including both Scharnhorst-class ships, was subsequently annihilated at the Battle of the Falkland Islands
Battle of the Falkland Islands
The Battle of the Falkland Islands was a British naval victory over the Imperial German Navy on 8 December 1914 during the First World War in the South Atlantic...
on 8 December.
| Ship | Armament | Armor | Displacement | Propulsion | Cost | Service | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laid down | Commissioned | Fate | ||||||
| 8 × 21 cm (8.3 in) SK L/40 6 × 15 cm (5.9 in) SK L/40 guns |
15 cm (5.9 in) | 12985 MT (12,779.9 LT) | 3 screws, triple expansion engines, 23.5 kn (12.8 m/s), 28,783 ihp | 20,319,000 marks | 1905 | 24 October 1907 | Sunk on 8 December 1914 at the Battle of the Falkland Islands Battle of the Falkland Islands The Battle of the Falkland Islands was a British naval victory over the Imperial German Navy on 8 December 1914 during the First World War in the South Atlantic... |
|
| 8 × 21 cm (8.3 in) SK L/40 6 × 15 cm (5.9 in) SK L/40 guns |
15 cm (5.9 in) | 12985 MT (12,779.9 LT) | 3 screws, triple expansion engines, 23.6 kn (12.8 m/s), 30,396 ihp | 19,243,000 marks | 1904 | 6 March 1908 | Sunk on 8 December 1914 at the Battle of the Falkland Islands Battle of the Falkland Islands The Battle of the Falkland Islands was a British naval victory over the Imperial German Navy on 8 December 1914 during the First World War in the South Atlantic... |
|
SMS Blücher

SMS Blücher was the last armored cruiser to be built by the Imperial Navy. She was designed to match what German intelligence incorrectly believed to be the specifications of the British s. Blücher was larger than preceding armored cruisers and carried more heavy guns, but was unable to match the size and armament of the battlecruiser
Battlecruiser
Battlecruisers were large capital ships built in the first half of the 20th century. They were developed in the first decade of the century as the successor to the armoured cruiser, but their evolution was more closely linked to that of the dreadnought battleship...
s which replaced armored cruisers in the British and German navies. Her primary armament of twelve 21 cm (8.3 in) guns was greatly inferior to the eight 12 in (30.5 cm) guns of the British battlecruisers.
The ship initially served as a gunnery training ship, but joined the I Scouting Group after the outbreak of World War I. She took part in the operation to bombard Yarmouth
Raid on Yarmouth
The Raid on Yarmouth, which took place on 3 November 1914, was an attack by the German Navy on the British North Sea port and town of Great Yarmouth. Little damage was done to the town since shells only landed on the beach after German ships laying mines offshore were interrupted by British...
and the raid on Scarborough, Hartlepool and Whitby
Raid on Scarborough, Hartlepool and Whitby
The raid on Scarborough, Hartlepool and Whitby, which took place on 16 December 1914, was an attack by the Imperial German Navy on the British seaport towns of Scarborough, Hartlepool, West Hartlepool, and Whitby. The attack resulted in 137 fatalities and 592 casualties, many of which were civilians...
in 1914. At the Battle of Dogger Bank
Battle of Dogger Bank (1915)
The Battle of Dogger Bank was a naval battle fought near the Dogger Bank in the North Sea on 24 January 1915, during the First World War, between squadrons of the British Grand Fleet and the German High Seas Fleet....
on 24 January 1915, Blücher was slowed significantly after being hit by gunfire from the British battlecruiser squadron under the command of Vice Admiral Sir David Beatty
David Beatty, 1st Earl Beatty
Admiral of the Fleet David Richard Beatty, 1st Earl Beatty, GCB, OM, GCVO, DSO was an admiral in the Royal Navy...
. Rear Admiral Franz von Hipper
Franz von Hipper
Franz Ritter von Hipper was an admiral in the German Imperial Navy . Franz von Hipper joined the German Navy in 1881 as an officer cadet. He commanded several torpedo boat units and served as watch officer aboard several warships, as well as Kaiser Wilhelm II's yacht Hohenzollern...
, the commander of the German squadron, decided to abandon Blücher to the pursuing enemy ships in order to save his more valuable battlecruisers. Under heavy fire from the British ships, she was sunk with heavy loss of life.
| Ship | Armament | Armor | Displacement | Propulsion | Cost | Service | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laid down | Commissioned | Fate | ||||||
| 12 × 21 cm (8.3 in) SK L/40 8 × 15 cm (5.9 in) SK L/40 guns |
18 cm (7.1 in) | 17500 MT (17,223.6 LT) | 3 screws, triple expansion engines, 25.4 kn (13.8 m/s), 38,323 ihp | 28,532,000 marks | 21 February 1907 | 1 October 1909 | Sunk on 24 January 1915 at the Battle of Dogger Bank Battle of Dogger Bank (1915) The Battle of Dogger Bank was a naval battle fought near the Dogger Bank in the North Sea on 24 January 1915, during the First World War, between squadrons of the British Grand Fleet and the German High Seas Fleet.... |
|

