
List of Fedora versions
Encyclopedia
This page lists and links to information on the various versions of Fedora
, a popular Linux distribution
developed by the community-supported Fedora Project
and sponsored by Red Hat
.
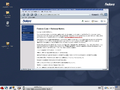
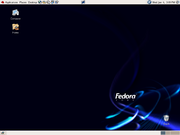 Fedora Core 1 was the first version of Fedora and was released on November 6, 2003. It was codenamed Yarrow. Fedora Core 1 was based on Red Hat Linux 9 and shipped with version 2.4.19 of the Linux kernel, version 2.4 of the GNOME
Fedora Core 1 was the first version of Fedora and was released on November 6, 2003. It was codenamed Yarrow. Fedora Core 1 was based on Red Hat Linux 9 and shipped with version 2.4.19 of the Linux kernel, version 2.4 of the GNOME
desktop environment, and K Desktop Environment 3.1.
Fedora Core 2 was released on May 18, 2004, codenamed Tettnang. It shipped with Linux 2.6, GNOME 2.6, KDE 3.2, and SELinux
(SELinux was disabled by default due to concerns that it radically altered the way that Fedora Core ran). XFree86 was replaced by the newer X.org, a merger of the previous official X11R6 release, which additionally included a number of updates to Xrender, Xft
, Xcursor, fontconfig libraries, and other significant improvements.
Fedora Core 3 was released on November 8, 2004, codenamed Heidelberg. This was the first release of Fedora Core to include the Mozilla Firefox
web browser
, as well as support for the Indic languages. This release also saw the LILO boot loader
deprecated in favour of GRUB
. SELinux
was also enabled by default, but with a new targeted policy, which was less strict than the policy used in Fedora Core 2. Fedora Core 3 shipped with GNOME 2.8 and KDE 3.3. It was the first release to include the new Fedora Extras repository.
Fedora Core 4 was released on June 13, 2005, with the codename Stentz. It shipped with Linux 2.6.11, KDE 3.4 and GNOME 2.10. This version introduced the new Clearlooks theme, which was inspired by the Red Hat
Bluecurve theme. It also shipped with the OpenOffice.org
2.0 office suite, as well as Xen
, a high performance and secure open source virtualization framework. It also introduced support for the PowerPC
CPU architecture, and over 80 new policies for SELinux
.
 The last two Core releases introduced specific artwork that defined them. This is a trend that has continued in later Fedora versions.
The last two Core releases introduced specific artwork that defined them. This is a trend that has continued in later Fedora versions.
Fedora Core 5 was released on March 20, 2006, with the codename Bordeaux, and introduced the Fedora Bubbles artwork. It was the first Fedora release to include Mono
and tools built with it such as Beagle
, F-Spot
and Tomboy
. It also introduced new package management tools such as pup and pirut (see Yellowdog Updater, Modified). It also was the first Fedora release not to include the long deprecated (but kept for compatibility) LinuxThreads
, replaced by the Native POSIX Thread Library
.
Fedora Core 6 was released on October 24, 2006, codenamed Zod. This release introduced the Fedora DNA artwork, replacing the Fedora Bubbles artwork used in Fedora Core 5. The codename is derived from the infamous villain, General Zod
, from the Superman DC Comic Books. This version introduced support for the Compiz
compositing window manager
and AIGLX
(a technology that enables GL-accelerated effects on a standard desktop). It shipped with Firefox
1.5 as the default web browser, and Smolt
, a tool that allows users to inform developers about the hardware they use.
 Fedora 7, codenamed Moonshine, was released on May 31, 2007. The biggest difference between Fedora Core 6 and Fedora 7 was the merging of the Red Hat "Core" and Community "Extras" repositories, dropping "Core" from the name "Fedora Core," and the new build system put in place to manage those packages. This release used entirely new build and compose tools that enabled the user to create fully customized Fedora distributions that could also include packages from any third party provider.
Fedora 7, codenamed Moonshine, was released on May 31, 2007. The biggest difference between Fedora Core 6 and Fedora 7 was the merging of the Red Hat "Core" and Community "Extras" repositories, dropping "Core" from the name "Fedora Core," and the new build system put in place to manage those packages. This release used entirely new build and compose tools that enabled the user to create fully customized Fedora distributions that could also include packages from any third party provider.
There were three official spins available for Fedora 7:
Fedora 7 featured GNOME 2.18 and KDE 3.5, a new theme entitled Flying High, OpenOffice.org
2.2 and Firefox
2.0. Fast user switching
was fully integrated and enabled by default. Also, there were a number of updates to SELinux
, including a new setroubleshoot tool for debugging SELinux security notifications, and a new, comprehensive system-config-selinux tool for fine-tuning the SELinux setup.
 Fedora 8, codenamed Werewolf, was released on November 8, 2007.
Fedora 8, codenamed Werewolf, was released on November 8, 2007.
Some of the new features and updates in Fedora 8 included:
Fedora 8 also included a new desktop artwork entitled Infinity, and a new desktop theme called Nodoka. A unique feature of Infinity is that the wallpaper can change during the day to reflect the time of day.
In February 2008, a new Xfce
Live CD "spin" was announced for the x86 and x86-64
architectures. This Live CD
version uses the Xfce desktop environment, which aims to be fast and lightweight, while still being visually appealing and easy to use. Like the GNOME and KDE spins, the Xfce spin can be installed to the hard disk.
 Fedora 9, codenamed Sulphur, was released on May 13, 2008.
Fedora 9, codenamed Sulphur, was released on May 13, 2008.
Some of the new features of Fedora 9 included:
Fedora 9 featured a new artwork entitled Waves which, like Infinity in Fedora 8, changes the wallpaper to reflect the time of day.
 Fedora 10, codenamed Cambridge, was released on November 25, 2008. It flaunts the new Solar artwork. Its features include:
Fedora 10, codenamed Cambridge, was released on November 25, 2008. It flaunts the new Solar artwork. Its features include:
 Fedora 11, codenamed Leonidas, was released on June 9, 2009. This was the first release whose artwork is determined by the name instead of by users voting on themes.
Fedora 11, codenamed Leonidas, was released on June 9, 2009. This was the first release whose artwork is determined by the name instead of by users voting on themes.
Some of the features in Fedora 11 are:
Some of the features in Fedora 12 are:
, was released on May 25, 2010. During early development, Fedora project-leader Paul Frields anticipated "looking at the fit and finish issues. We have tended to build a really tight ship with Fedora, but now we want to make the décor in the cabins a little more sumptuous and to polish the deck chairs and railings."
Features of Fedora 13 include:
, was released on November 2, 2010.
Features of Fedora 14 include:
Features of Fedora 15 include:
, who died about a month before the release.
Some of the features of Fedora 16 include:
Fedora (operating system)
Fedora is a RPM-based, general purpose collection of software, including an operating system based on the Linux kernel, developed by the community-supported Fedora Project and sponsored by Red Hat...
, a popular Linux distribution
Linux distribution
A Linux distribution is a member of the family of Unix-like operating systems built on top of the Linux kernel. Such distributions are operating systems including a large collection of software applications such as word processors, spreadsheets, media players, and database applications...
developed by the community-supported Fedora Project
Fedora Project
The Fedora Project is an endeavor sponsored by Red Hat to co-ordinate the development of the Fedora operating system. Founded on September 2003 as a result of a merger between the Red Hat Linux and old Fedora Linux projects...
and sponsored by Red Hat
Red Hat
Red Hat, Inc. is an S&P 500 company in the free and open source software sector, and a major Linux distribution vendor. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North Carolina with satellite offices worldwide....
.
Fedora Core 1–4


GNOME
GNOME is a desktop environment and graphical user interface that runs on top of a computer operating system. It is composed entirely of free and open source software...
desktop environment, and K Desktop Environment 3.1.
Fedora Core 2 was released on May 18, 2004, codenamed Tettnang. It shipped with Linux 2.6, GNOME 2.6, KDE 3.2, and SELinux
Security-Enhanced Linux
Security-Enhanced Linux is a Linux feature that provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies, including United States Department of Defense-style mandatory access controls, through the use of Linux Security Modules in the Linux kernel...
(SELinux was disabled by default due to concerns that it radically altered the way that Fedora Core ran). XFree86 was replaced by the newer X.org, a merger of the previous official X11R6 release, which additionally included a number of updates to Xrender, Xft
Xft
Xft, the X FreeType interface library, is a free computer program library written by Keith Packard. As of version 2.1, it is licensed under a quasi-BSD license....
, Xcursor, fontconfig libraries, and other significant improvements.
Fedora Core 3 was released on November 8, 2004, codenamed Heidelberg. This was the first release of Fedora Core to include the Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox is a free and open source web browser descended from the Mozilla Application Suite and managed by Mozilla Corporation. , Firefox is the second most widely used browser, with approximately 25% of worldwide usage share of web browsers...
web browser
Web browser
A web browser is a software application for retrieving, presenting, and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. An information resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier and may be a web page, image, video, or other piece of content...
, as well as support for the Indic languages. This release also saw the LILO boot loader
LILO (boot loader)
LILO is a generic boot loader for Linux.-Overview:LILO does not depend on a specific file system, and can boot an operating system from floppy disks and hard disks. One of up to sixteen different images can be selected at boot time. Various parameters, such as the root device, can be set...
deprecated in favour of GRUB
GNU GRUB
GNU GRUB is a boot loader package from the GNU Project. GRUB is the reference implementation of the Multiboot Specification, which provides a user the choice to boot one of multiple operating systems installed on a computer or select a specific kernel configuration available on a particular...
. SELinux
Security-Enhanced Linux
Security-Enhanced Linux is a Linux feature that provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies, including United States Department of Defense-style mandatory access controls, through the use of Linux Security Modules in the Linux kernel...
was also enabled by default, but with a new targeted policy, which was less strict than the policy used in Fedora Core 2. Fedora Core 3 shipped with GNOME 2.8 and KDE 3.3. It was the first release to include the new Fedora Extras repository.
Fedora Core 4 was released on June 13, 2005, with the codename Stentz. It shipped with Linux 2.6.11, KDE 3.4 and GNOME 2.10. This version introduced the new Clearlooks theme, which was inspired by the Red Hat
Red Hat
Red Hat, Inc. is an S&P 500 company in the free and open source software sector, and a major Linux distribution vendor. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North Carolina with satellite offices worldwide....
Bluecurve theme. It also shipped with the OpenOffice.org
OpenOffice.org
OpenOffice.org, commonly known as OOo or OpenOffice, is an open-source application suite whose main components are for word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, graphics, and databases. OpenOffice is available for a number of different computer operating systems, is distributed as free software...
2.0 office suite, as well as Xen
Xen
Xen is a virtual-machine monitor providing services that allow multiple computer operating systems to execute on the same computer hardware concurrently....
, a high performance and secure open source virtualization framework. It also introduced support for the PowerPC
PowerPC
PowerPC is a RISC architecture created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM...
CPU architecture, and over 80 new policies for SELinux
Security-Enhanced Linux
Security-Enhanced Linux is a Linux feature that provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies, including United States Department of Defense-style mandatory access controls, through the use of Linux Security Modules in the Linux kernel...
.
Fedora Core 5–6

Fedora Core 5 was released on March 20, 2006, with the codename Bordeaux, and introduced the Fedora Bubbles artwork. It was the first Fedora release to include Mono
Mono (software)
Mono, pronounced , is a free and open source project led by Xamarin to create an Ecma standard compliant .NET-compatible set of tools including, among others, a C# compiler and a Common Language Runtime....
and tools built with it such as Beagle
Beagle (software)
Beagle is a search system for Linux and other such modern Unix-like systems, enabling the user to search documents, chat logs, email and contact lists in a similar way to Spotlight in Mac OS X, and Windows Search or Google Desktop under Linux or Microsoft Windows...
, F-Spot
F-Spot
F-Spot is an image organizer, designed to provide personal photo management for the GNOME desktop environment. The name is a play on the words F-Stop and G-Spot.-Features:...
and Tomboy
Tomboy (software)
Tomboy is a free and open-source desktop notetaking application written for Unix-like and Microsoft Windows operating systems, written in C# using Gtk#. Tomboy is part of the GNOME desktop environment, often for personal information management. Its interface is a notepad with a wiki-like linking...
. It also introduced new package management tools such as pup and pirut (see Yellowdog Updater, Modified). It also was the first Fedora release not to include the long deprecated (but kept for compatibility) LinuxThreads
LinuxThreads
In the Linux operating system, LinuxThreads was a partial implementation of POSIX Threads that has since been superseded by the Native POSIX Thread Library ....
, replaced by the Native POSIX Thread Library
Native POSIX Thread Library
The Native POSIX Thread Library is a software feature that enables the Linux kernel to run programs written to use POSIX Threads efficiently.-History:...
.
Fedora Core 6 was released on October 24, 2006, codenamed Zod. This release introduced the Fedora DNA artwork, replacing the Fedora Bubbles artwork used in Fedora Core 5. The codename is derived from the infamous villain, General Zod
General Zod
General Zod is a fictional character who appears in comic books published by DC Comics, a supervillain who is one of Superman's more-prominent enemies. The character first appeared in Adventure Comics #283 , and was created by Robert Bernstein and George Papp...
, from the Superman DC Comic Books. This version introduced support for the Compiz
Compiz
Compiz is one of the first compositing window managers for the X Window System that uses 3D graphics hardware to create fast compositing desktop effects for window management. The effects, such as a minimization effect and a cube workspace are implemented as loadable plugins...
compositing window manager
Compositing window manager
A compositing window manager is a type of window manager. A window manager is software that draws a graphical user interface on a computer display – it positions windows, draws additional elements on windows , and controls how windows interact with each other, and with the rest of the desktop...
and AIGLX
AIGLX
Accelerated Indirect GLX is an open source project founded by Red Hat and the Fedora community, led by Kristian Høgsberg, to allow accelerated indirect GLX rendering capabilities to the X.Org Server and DRI drivers...
(a technology that enables GL-accelerated effects on a standard desktop). It shipped with Firefox
Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox is a free and open source web browser descended from the Mozilla Application Suite and managed by Mozilla Corporation. , Firefox is the second most widely used browser, with approximately 25% of worldwide usage share of web browsers...
1.5 as the default web browser, and Smolt
Smolt (Linux)
Smolt is a computer software that gathers hardware information from computers running Linux, and submits them to a central server for statistical purposes, quality assurance and support. It was initiated by Fedora, with the release of Fedora 7, and is now a combined effort of various Linux...
, a tool that allows users to inform developers about the hardware they use.
Fedora 7

There were three official spins available for Fedora 7:
- Live – two Live CDs (one for GNOME and one for KDE);
- Fedora – a DVD that includes all the major packages available at shipping;
- Everything – simply an installation tree for use by yum and Internet installations.
Fedora 7 featured GNOME 2.18 and KDE 3.5, a new theme entitled Flying High, OpenOffice.org
OpenOffice.org
OpenOffice.org, commonly known as OOo or OpenOffice, is an open-source application suite whose main components are for word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, graphics, and databases. OpenOffice is available for a number of different computer operating systems, is distributed as free software...
2.2 and Firefox
Mozilla Firefox
Mozilla Firefox is a free and open source web browser descended from the Mozilla Application Suite and managed by Mozilla Corporation. , Firefox is the second most widely used browser, with approximately 25% of worldwide usage share of web browsers...
2.0. Fast user switching
Fast user switching
Fast user switching is a feature on some modern multi-user operating systems such as Windows XP and newer, Mac OS X, Linux. It allows users to switch between user accounts on a single PC without quitting applications and logging out. Analogous functionality was first developed on consumer level...
was fully integrated and enabled by default. Also, there were a number of updates to SELinux
Security-Enhanced Linux
Security-Enhanced Linux is a Linux feature that provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies, including United States Department of Defense-style mandatory access controls, through the use of Linux Security Modules in the Linux kernel...
, including a new setroubleshoot tool for debugging SELinux security notifications, and a new, comprehensive system-config-selinux tool for fine-tuning the SELinux setup.
Fedora 8

Some of the new features and updates in Fedora 8 included:
- PulseAudioPulseAudioPulseAudio is a cross-platform, networked sound server commonly used on the Linux-based and FreeBSD operating systems.PulseAudio runs under Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, and POSIX-compliant platforms, such as Linux and FreeBSD...
– a sound daemon that allows different applications to control the audio. Fedora was the first distribution to enable it by default. - system-config-firewall – a new firewall configuration tool that replaces system-config-securitylevel from previous releases.
- Codeina – a tool that guides users using content under proprietary or patent-encumbered formats to purchase codecs from fluendoFluendoFluendo DVD Player is one of the first products that can be bought that allows legal/licensed DVD playback for Unix/Linux users...
; it is an optional component that may be uninstalled in favor of GStreamerGStreamerGStreamer is a pipeline-based multimedia framework written in the C programming language with the type system based on GObject.GStreamer allows a programmer to create a variety of media-handling components, including simple audio playback, audio and video playback, recording, streaming and editing...
codec plug-ins from Livna which are free of charge. - IcedTeaIcedTeaIcedTea is a build and integration project for OpenJDK launched by Red Hat in June 2007. The initial goal was to make the Java OpenJDK software which Sun Microsystems released as free software in 2007 usable without requiring any other software that is not free software and hence make it possible...
– a project that attempts to bring OpenJDKOpenJDKOpenJDK is a free and open source implementation of the Java programming language. It is the result of an effort Sun Microsystems began in 2006...
to Fedora by replacing encumbered code. - NetworkManagerNetworkManagerNetwork Manager is a software utility aimed at simplifying the use of computer networks on Linux-based and other Unix-like operating systems.- Overview :...
– faster, more reliable connections; better security (through the use of the keyringGNOME KeyringGNOME Keyring is a daemon application designed to take care of the user's security credentials, such as user names and passwords. The sensitive data is encrypted and stored in a keyring file in the user's home folder...
); clearer display of wireless networks; better D-BusD-BusIn computing, D-Bus is a simple inter-process communication open-source system for software applications to communicate with one another. Heavily influenced by KDE2–3's DCOP system, D-Bus has replaced DCOP in the KDE 4 release. An implementation of D-Bus supports most POSIX operating...
integration. - Better laptop support – enhancements to the kernel to reduce battery load, disabling of background cron jobs when running on the battery, and additional wireless drivers.
Fedora 8 also included a new desktop artwork entitled Infinity, and a new desktop theme called Nodoka. A unique feature of Infinity is that the wallpaper can change during the day to reflect the time of day.
In February 2008, a new Xfce
Xfce
Xfce is a free software desktop environment for Unix and other Unix-like platforms, such as Linux, Solaris, and BSD – though recent compatibility issues have arisen with regard to BSD Unix platforms...
Live CD "spin" was announced for the x86 and x86-64
X86-64
x86-64 is an extension of the x86 instruction set. It supports vastly larger virtual and physical address spaces than are possible on x86, thereby allowing programmers to conveniently work with much larger data sets. x86-64 also provides 64-bit general purpose registers and numerous other...
architectures. This Live CD
Live CD
A live CD, live DVD, or live disc is a CD or DVD containing a bootable computer operating system. Live CDs are unique in that they have the ability to run a complete, modern operating system on a computer lacking mutable secondary storage, such as a hard disk drive...
version uses the Xfce desktop environment, which aims to be fast and lightweight, while still being visually appealing and easy to use. Like the GNOME and KDE spins, the Xfce spin can be installed to the hard disk.
Fedora 9

Some of the new features of Fedora 9 included:
- GNOME 2.22GNOMEGNOME is a desktop environment and graphical user interface that runs on top of a computer operating system. It is composed entirely of free and open source software...
. - KDE 4.0, which is the default interface as part of the KDE spin.
- OpenJDK 6OpenJDKOpenJDK is a free and open source implementation of the Java programming language. It is the result of an effort Sun Microsystems began in 2006...
has replaced IcedTeaIcedTeaIcedTea is a build and integration project for OpenJDK launched by Red Hat in June 2007. The initial goal was to make the Java OpenJDK software which Sun Microsystems released as free software in 2007 usable without requiring any other software that is not free software and hence make it possible...
.
- PackageKitPackageKitPackageKit is an open source and free suite of software applications designed to provide a consistent and high-level front end for a number of different package management systems...
is included as a front-end to yum, and as the default package manager. - One Second X allows the X Window SystemX Window SystemThe X window system is a computer software system and network protocol that provides a basis for graphical user interfaces and rich input device capability for networked computers...
to perform a cold start from the command line in nearly one second; similarly, shutdown of X should be as quick. - UpstartUpstartUpstart is an event-based replacement for the traditional init daemon — the method by which several Unix-like computer operating systems perform tasks when the computer is started. It was written by Scott James Remnant, a former employee of Canonical Ltd....
introduced - Many improvements to the Anaconda installer; among these features, it now supports resizing ext2, ext3 and NTFS file systems, and can create and install Fedora to encrypted file systems.
- FirefoxMozilla FirefoxMozilla Firefox is a free and open source web browser descended from the Mozilla Application Suite and managed by Mozilla Corporation. , Firefox is the second most widely used browser, with approximately 25% of worldwide usage share of web browsers...
3.0 beta 5 is included in this release, and the 3.0 package was released as an update the same day as the general release. - Perl 5.10, which features a smaller memory footprint and other improvements.
- Data Persistence in USB images.
Fedora 9 featured a new artwork entitled Waves which, like Infinity in Fedora 8, changes the wallpaper to reflect the time of day.
Fedora 10

- Faster startup using PlymouthPlymouth (software)Plymouth is a bootsplash for Linux. It supports animations. It makes use of Direct Rendering Manager and kernel-based mode-setting . It gets packed into the initrd.Besides eye-candy, Plymouth also handles user interaction during boot....
(instead of Red Hat Graphical Boot used in previous versions) - Support for ext4Ext4The ext4 or fourth extended filesystem is a journaling file system for Linux, developed as the successor to ext3.It was born as a series of backward compatible extensions to ext3, many of them originally developed by Cluster File Systems for the Lustre file system between 2003 and 2006, meant to...
filesystem - SugarSugar (GUI)Sugar is an open source desktop environment designed with the goal of being used by children for learning.Developed as part of the One Laptop per Child project, it is the default interface on OLPC XO-1 family of laptop computers....
Desktop Environment - LXDELXDELXDE is a free and open source desktop environment for Unix and other POSIX compliant platforms, such as Linux or BSD. The goal of the project is to provide a desktop environment that is fast and energy efficient...
Desktop Environment (LXDE Spin) - GNOME 2.24
- KDE 4.1 (KDE Spin)
- OpenOffice.orgOpenOffice.orgOpenOffice.org, commonly known as OOo or OpenOffice, is an open-source application suite whose main components are for word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, graphics, and databases. OpenOffice is available for a number of different computer operating systems, is distributed as free software...
3.0
Fedora 11

Some of the features in Fedora 11 are:
- ext4Ext4The ext4 or fourth extended filesystem is a journaling file system for Linux, developed as the successor to ext3.It was born as a series of backward compatible extensions to ext3, many of them originally developed by Cluster File Systems for the Lustre file system between 2003 and 2006, meant to...
as the default file systemFile systemA file system is a means to organize data expected to be retained after a program terminates by providing procedures to store, retrieve and update data, as well as manage the available space on the device which contain it. A file system organizes data in an efficient manner and is tuned to the... - experimental BtrfsBtrfsBtrfs is a GPL-licensed copy-on-write file system for Linux.Development began at Oracle Corporation in 2007....
activated by IcantbelieveitsnotBTR command line option at bootup - Faster Bootup aimed at 20 seconds.
- GCC 4.4
- GNOME 2.26
- KDE 4.2 (KDE Spin)
- 2.6.29 Linux kernelLinux kernelThe Linux kernel is an operating system kernel used by the Linux family of Unix-like operating systems. It is one of the most prominent examples of free and open source software....
- EclipseEclipse (software)Eclipse is a multi-language software development environment comprising an integrated development environment and an extensible plug-in system...
3.4.2
- NetbeansNetBeansNetBeans refers to both a platform framework for Java desktop applications, and an integrated development environment for developing with Java, JavaScript, PHP, Python, Groovy, C, C++, Scala, Clojure, and others...
6.5 - nVidiaNVIDIANvidia is an American global technology company based in Santa Clara, California. Nvidia is best known for its graphics processors . Nvidia and chief rival AMD Graphics Techonologies have dominated the high performance GPU market, pushing other manufacturers to smaller, niche roles...
kernel modesetting through the open source nouveau (graphics)Nouveau (graphics)In computing, nouveau is a software project aiming to develop free software drivers for Nvidia graphics cards, by reverse engineering Nvidia's current proprietary drivers for Linux. This project by X.Org Foundation and freedesktop.org was initially based on the obfuscated 2D-only free and...
driver. - OpenOffice 3.1
- PythonPython (programming language)Python is a general-purpose, high-level programming language whose design philosophy emphasizes code readability. Python claims to "[combine] remarkable power with very clear syntax", and its standard library is large and comprehensive...
2.6 - Xfce to 4.6 (Xfce Spin)
- X server 1.6
- fprintFprintfprint is an open source project to develop a library for the consumer fingerprint reader devices.It aims to provide a single API to Software developers for several devices.Currently supports following hardware:...
- support for systems with fingerprint readers
Fedora 12
Fedora 12, codenamed Constantine, was released on November 17, 2009.Some of the features in Fedora 12 are:
- Optimized performance. All software packages on 32-bit (x86_32) architecture have been compiled for i686 systems
- Improved Webcam support (CheeseCheese (software)Cheese is a GNOME webcam application, similar to Apple's Photo Booth. It was developed as a Google Summer of Code 2007 project by Daniel G. Siegel. It uses GStreamer to apply effects to photos and videos...
) - Better video codec with a newer version of OggOggOgg is a free, open container format maintained by the Xiph.Org Foundation. The creators of the Ogg format state that it is unrestricted by software patents and is designed to provide for efficient streaming and manipulation of high quality digital multimedia.The Ogg container format can multiplex...
TheoraTheoraTheora is a free lossy video compression format. It is developed by the Xiph.Org Foundation and distributed without licensing fees alongside their other free and open media projects, including the Vorbis audio format and the Ogg container.... - Audio improvements
- Automatic bug reporting tool (abrt)
- Bluetooth on demand
- Enhanced NetworkManager to manage broadband
- Many virtualization enhancements (KVMKernel-based Virtual MachineKernel-based Virtual Machine is a virtualization infrastructure for the Linux kernel. KVM supports native virtualization on processors with hardware virtualization extensions....
, libvirtLibvirtlibvirt is an open source API, daemon and management tool for managing platform virtualization. It can be used to manage Linux KVM, Xen, VMware ESX and other virtualization technologies...
, libguestfsLibguestfslibguestfs is an open source API for modifying the virtual disk images used in virtualization of operating systems. libguestfs provides multiple editing tools for Fedora-based hosts modelled after ordinary Unix commands, such as "virt-cat" and "virt-tar", and can edit virtual machines managed by...
) - ext4Ext4The ext4 or fourth extended filesystem is a journaling file system for Linux, developed as the successor to ext3.It was born as a series of backward compatible extensions to ext3, many of them originally developed by Cluster File Systems for the Lustre file system between 2003 and 2006, meant to...
used even for the boot partition - Moblin interface
- Yum-presto plugin providing Delta RPMs for updates by default
- New compression algorithm (XZXzxz is a lossless data compression file format incorporating the LZMA2 compression algorithm. Like gzip and bzip2, concatenation is supported to compress multiple files, but the convention is to bundle a file that is an archive itself, such as those created by the tar or cpio Unix...
, the new LZMA format) in RPMRPM Package ManagerRPM Package Manager is a package management system. The name RPM variously refers to the .rpm file format, files in this format, software packaged in such files, and the package manager itself...
packages for smaller and faster updates - Experimental 3D support for ATI R600Radeon R600The graphics processing unit codenamed the Radeon R600 is the foundation of the Radeon HD 2000/3000 series and the FireGL 2007 series video cards developed by ATI Technologies...
/R700Radeon R700The Radeon R700 is the engineering codename for a graphics processing unit series developed by Advanced Micro Devices under the ATI brand name. The foundation chip, codenamed RV770, was announced and demonstrated on June 16, 2008 as part of the FireStream 9250 and Cinema 2.0 initiative launch media...
cards - GCC 4.4
- SystemTapSystemTapIn computing, SystemTap is the primary scripting language and tool for dynamically instrumenting running production Linux operating systems...
1.0 with EclipseEclipse (software)Eclipse is a multi-language software development environment comprising an integrated development environment and an extensible plug-in system...
integration - GNOME 2.28
- GNOME Shell preview
- KDE 4.3, KDE 4.4 was pushed to updates repository on 27 February 2010 (KDE Spin)
- 2.6.31 Linux kernelLinux kernelThe Linux kernel is an operating system kernel used by the Linux family of Unix-like operating systems. It is one of the most prominent examples of free and open source software....
, Kernel 2.6.32 was pushed to updates repository on 27 February 2010 - X server 1.7 with Multi-Pointer X (MPX) support
- NetBeans 6.7
- PHP 5.3
- Rakudo PerlRakudo PerlRakudo Perl is a compiler that implements the Perl 6 specification and runs on the Parrot virtual machine. Rakudo Perl is currently in development....
(Perl 6)
Fedora 13
Fedora 13, codenamed GoddardGoddard
-Places:In the United States:* Goddard, Alaska* Goddard, Kansas* Goddard, Maryland* Goddard Memorial State Park, Warwick, Rhode Island* Goddard College, a private college in Plainfield, Vermont* Maurice K...
, was released on May 25, 2010. During early development, Fedora project-leader Paul Frields anticipated "looking at the fit and finish issues. We have tended to build a really tight ship with Fedora, but now we want to make the décor in the cabins a little more sumptuous and to polish the deck chairs and railings."
Features of Fedora 13 include:
- Automatic printer-driver installation
- Automatic language pack installation
- Redesigned user-account tool
- Color management to calibrate monitors and scanners
- Experimental 3D support for NVIDIANVIDIANvidia is an American global technology company based in Santa Clara, California. Nvidia is best known for its graphics processors . Nvidia and chief rival AMD Graphics Techonologies have dominated the high performance GPU market, pushing other manufacturers to smaller, niche roles...
video cards - A new way to install Fedora over the Internet
- SSSD authentication for users
- Updates to NFS
- Inclusion of Zarafa Open Source editionZarafa (software)Zarafa is the name of an European open source collaborative software, developed in Delft, the Netherlands. The company that develops Zarafa, previously known as Connectux, is also called Zarafa. The Zarafa groupware provides email storage on the server side and brings its own Ajax-based mail client...
- System rollback for the Btrfs file systemBtrfsBtrfs is a GPL-licensed copy-on-write file system for Linux.Development began at Oracle Corporation in 2007....
- Better SystemTapSystemTapIn computing, SystemTap is the primary scripting language and tool for dynamically instrumenting running production Linux operating systems...
probes - Support for the entire Java EE 6 spec in NetbeansNetBeansNetBeans refers to both a platform framework for Java desktop applications, and an integrated development environment for developing with Java, JavaScript, PHP, Python, Groovy, C, C++, Scala, Clojure, and others...
6.8 - KDEKDEKDE is an international free software community producing an integrated set of cross-platform applications designed to run on Linux, FreeBSD, Microsoft Windows, Solaris and Mac OS X systems...
PulseAudioPulseAudioPulseAudio is a cross-platform, networked sound server commonly used on the Linux-based and FreeBSD operating systems.PulseAudio runs under Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, and POSIX-compliant platforms, such as Linux and FreeBSD...
Integration - New command-line interface for NetworkManagerNetworkManagerNetwork Manager is a software utility aimed at simplifying the use of computer networks on Linux-based and other Unix-like operating systems.- Overview :...
Fedora 14
Fedora 14, codenamed LaughlinRobert B. Laughlin
Robert Betts Laughlin is a professor of Physics and Applied Physics at Stanford University. Along with Horst L. Störmer of Columbia University and Daniel C. Tsui of Princeton University, he was awarded a share of the 1998 Nobel Prize in physics for their explanation of the fractional quantum Hall...
, was released on November 2, 2010.
Features of Fedora 14 include:
- Updated Boost to the upstream 1.44 release
- Addition of the D compilerD (programming language)The D programming language is an object-oriented, imperative, multi-paradigm, system programming language created by Walter Bright of Digital Mars. It originated as a re-engineering of C++, but even though it is mainly influenced by that language, it is not a variant of C++...
(LDC) and D standard runtime libraryD (programming language)The D programming language is an object-oriented, imperative, multi-paradigm, system programming language created by Walter Bright of Digital Mars. It originated as a re-engineering of C++, but even though it is mainly influenced by that language, it is not a variant of C++...
(Tango) - Concurrent release of Fedora 14 on the Amazon EC2 cloud
- Updated Fedora's EclipseEclipse (software)Eclipse is a multi-language software development environment comprising an integrated development environment and an extensible plug-in system...
stack to Helios releases - Updated Erlang to the upstream R14 release
- Replacement of libjpegLibjpeglibjpeg is a library written entirely in C which contains a widely-used implementation of a JPEG decoder, JPEG encoder and other JPEG utilities...
with libjpeg-turbo - Inclusion of virt-v2v tool
- Inclusion of Spice framework for VDI deployment
- Updates to Rakudo Star implementation of Perl 6Perl 6Perl 6 is a major revision to the Perl programming language. It is still in development, as a specification from which several interpreter and compiler implementations are being written. It is introducing elements of many modern and historical languages. Perl 6 is intended to have many...
- NetBeansNetBeansNetBeans refers to both a platform framework for Java desktop applications, and an integrated development environment for developing with Java, JavaScript, PHP, Python, Groovy, C, C++, Scala, Clojure, and others...
IDE updated to the 6.9 release - Inclusion of ipmiutil system management tool
- Inclusion of a tech preview of the GNOME Shell environment
Fedora 15
Fedora 15, codenamed Lovelock, was released on May 24, 2011.Features of Fedora 15 include:
- Inclusion of GNOME 3 desktop
- LibreOfficeLibreOfficeLibreOffice is a free and open source office suite developed by The Document Foundation as a fork of OpenOffice.org. It is largely compatible with other major office suites, including Microsoft Office, and available on a variety of platforms...
replaced OpenOffice.orgOpenOffice.orgOpenOffice.org, commonly known as OOo or OpenOffice, is an open-source application suite whose main components are for word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, graphics, and databases. OpenOffice is available for a number of different computer operating systems, is distributed as free software... - Inclusion of GNU Compiler CollectionGNU Compiler CollectionThe GNU Compiler Collection is a compiler system produced by the GNU Project supporting various programming languages. GCC is a key component of the GNU toolchain...
4.6 - Responsibility for booting is taken up by SystemdSystemdsystemd is a replacement for the System V init daemon for Linux. It is intended to provide a better framework for expressing services' dependencies, allow more work to be done in parallel at system startup, and to reduce shell overhead....
- LLVMpipe replacing Mesa software rasterizer
- Inclusion of BoxGrinder software
- Support for dynamic firewalls with firewalld
- Inclusion of PowerTOPPowerTOPPowerTOP is a software utility designed to measure, explain and minimise a computer's electrical power consumption. It was released by Intel in 2007 under the GPLv2 license...
2.x - Adoption of Consistent Network Device NamingConsistent Network Device NamingConsistent Network Device Naming is a standard for naming ethernet adapters in Linux created to replace the old standard ethX which caused problems on multihomed machines whereby the network adapters would get renamed based on which was polled first during bootup.The new naming scheme is as...
- Better support for encrypted Home directories
Fedora 16
The current release of the operating system is Fedora 16 and it was codenamed "Verne" and released on November 8, 2011. Fedora 16 is also dedicated to the memory of Dennis RitchieDennis Ritchie
Dennis MacAlistair Ritchie , was an American computer scientist who "helped shape the digital era." He created the C programming language and, with long-time colleague Ken Thompson, the UNIX operating system...
, who died about a month before the release.
Some of the features of Fedora 16 include:
- Inclusion of Gnome 3.2.1 desktop
- Updated to latest KDE Software CompilationKDE Software CompilationThe KDE Software Compilation is a desktop environment and an associated range of KDE Applications produced by KDE. Prior to version 4.4, released in February 2010, the Software Compilation was known as KDE, which used to stand for K Desktop Environment until November 2009...
4.7.2 - GRUB2 is now the boot-loader by default
- Ext4Ext4The ext4 or fourth extended filesystem is a journaling file system for Linux, developed as the successor to ext3.It was born as a series of backward compatible extensions to ext3, many of them originally developed by Cluster File Systems for the Lustre file system between 2003 and 2006, meant to...
driver is now used for Ext3Ext3The ext3 or third extended filesystem is a journaled file system that is commonly used by the Linux kernel. It is the default file system for many popular Linux distributions, including Debian...
and Ext2Ext2The ext2 or second extended filesystem is a file system for the Linux kernel. It was initially designed by Rémy Card as a replacement for the extended file system ....
file systems - HAL daemon now removed in favour of udisks, upower, and libudev
- Unification of the user interfaces for all problem reporting programs and mechanisms
- Virtualization improvements including OpenStack and Aeolus Conductor
- Fedora will now use UID/GIDs of up to 1000 for system accounts
- Enhanced cloud support including Condor Cloud, HekaFS, and pacemaker-cloud
Version history
| Color | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Red | Release no longer supported |
| Green | Release still supported |
| Blue | Future release |
| Project Name | Version | Code name | Release date | Kernel version |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fedora Core | 1 | Yarrow | 2003–11–05 | 2.4.19 |
| 2 | Tettnang | 2004–05–18 | 2.6.5 | |
| 3 | Heidelberg | 2004–11–08 | 2.6.9 | |
| 4 | Stentz | 2005–06–13 | 2.6.11 | |
| 5 | Bordeaux | 2006–03–20 | 2.6.15 | |
| 6 | Zod | 2006–10–24 | 2.6.18 | |
| Fedora | 7 | Moonshine | 2007–05–31 | 2.6.21 |
| 8 | Werewolf | 2007–11–08 | 2.6.23 | |
| 9 | Sulphur | 2008–05–13 | 2.6.25 | |
| 10 | Cambridge | 2008–11–25 | 2.6.27 | |
| 11 | Leonidas | 2009–06–09 | 2.6.29 | |
| 12 | Constantine | 2009–11–17 | 2.6.31 | |
| 13 | Goddard | 2010–05–25 | 2.6.33 | |
| 14 | Laughlin | 2010–11-02 | 2.6.35 | |
| 15 | Lovelock | 2011–05-24 | 2.6.38 | |
| 16 | Verne | 2011-11-08 | 3.1 | |
| 17 | Beefy Miracle | 2012-05-08 | ||

