List of 16-bit computer hardware palettes
Encyclopedia
This is a list of color palettes
of some of the most popular 16-bit
personal computer
s, roughly those manufactured from 1985 to 1995. All of them are based on RGB palettes; although some output in composite video
, the internal logic to produce colors is always RGB. Also, the list does not include obscure palettes, such as those available only through special adjustment and/or CPU assisted techniques (flickering, palette swapping, etc.), except where noted.
For color palettes of early 8-bit
personal computer
s, see the List of 8-bit computer hardware palettes article.
For current RGB display systems for 32-bit
and better PCs
(Super VGA, etc.), see the 16-bit RGB for HighColor (thousands) and 24-bit RGB for TrueColor (millions of colors) modes.
This n-bit distinction is not intended as a true strict categorization of such machines, due to mixed architectures also existing (16-bit processors
with 8-bit data bus or 32-bit processors with 16-bit data bus, among others). The distinction is more related with a broad 16-bit computer age or generation (around 1985-1995) and its associated state of the art
in color display capabilities.
For various software arrangements and sorts of colors, see the List of software palettes article.
For video game console
s, see the List of videogame consoles palettes article.
For a more complete and technical description of the computer's hardware video capabilities, see the List of home computers by video hardware.
They are listed the original model of every system, which implies that enhanced versions, clones and compatibles also supports the original's one palette.
For every model, their main different graphical color modes are listed based exclusively in the way they handle colors on screen, not all their possible different screen modes (text modes or resolution modes that shares the same color schemes).
Every palette has technical details about how the colors are produced and/or used by the computer's display video subsystem.
Due to all palettes being RGB based, color charts already exist in other articles, and they are not shown here. Links to their corresponding RGB palette color charts are available.
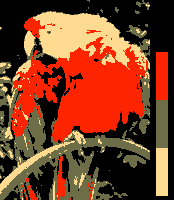
Simulations of how the parrot sample image would render in different graphic modes are provided. These simulations are always up to the maximum vertical resolution of the given graphic mode or up to 200 scan lines, if vertical resolution is greater. So any of them could be properly padded, transcoded and dumped into the original hardware and/or software emulators without any other changes. See the summary of every simulated image to obtain technical details about conversion to the original machine's format.
The simulated images only try to show how a certain system is able to handle to an image in terms of color without improvements nor additional clever tricks of design like anti-aliasing
or dithering. Doubtlessly a human artist is able to improve enormously the look of the simulated images to approximate them to the original one, but that is not the goal of this article.
Note: please do not change the compression scheme of every image by a lossy compression scheme (i.e. JPEG
) in order to improve their file size, nor change the thumbnail size of the images, nor gamma-correct them. They are didactical material AS IS, and they have been already optimized for this purpose.
series has a Digital-to-Analog Converter
of 3-bits, eight levels per RGB channel, featuring a 9-bit RGB palette (512 colors).
The STE series has a Digital-to-Analog Converter
of 4-bits, sixteen levels per RGB channel, featuring a 12-bit RGB palette (4096 colors).
Depending on the (proprietary) monitor type attached, it displays one of the 320×200, 16-colors and 640×200, 4-colors modes with the color monitor, or the high resolution 640×400 black and white mode with the monochrome monitor.
The output of the sample image with the 16-, 4-colors and the monochrome modes with the Atari ST video hardware looks like:
The graphic surface is divided in a series of bit planes
, from 1 up to 6, no matter how many horizontal (320 or 640) or vertical resolution (200 NTSC
compatible, 256 PAL
compatible, both interlaced or not) it has in a given graphic mode. The color lookup table
has up to 32 entries. So the different indexed color modes are from 1 to 5 bits pixel depth, 2-, 4-, 8-, 16- or 32-color out of 4,096.
When the sixth bit-plane is used, two extra color modes can be set: Extra Half-Brite (EHB) and Hold-And-Modify
(HAM). The EHB mode 6-bits pixel points to one of the 32 colors in the palette with their lower 5-bits, and if the 6th bit is on, the bright of the color is halved (hence the name of this mode). So there are a total of 64 visible colors: the user chooses light versions of the first 32 colors and the system already provides their darker versions.
In the HAM mode, the two higher bits of the 6-bits pixels are used as a four state command. Three of the states changes only the red, green or blue component of the pixel respect of the precedent in the scan line, and hold the other two RGB components. The new value for the modified color component is in the four lower bits. The remaining command state forces the pixel value to be one of the 16 first values of the palette, whose indice is in the four lower bits of the pixel. So it is very important to have a well selected palette, or the color will spread easily among consecutive pixels in the scan line of the image. This mode can display all of the 4,096 colors simultaneously.
Here are the simulated images for the EHB and the HAM modes:
, along with full compatible graphic modes with the Apple II
, features a custom Video Graphics Chip (VGC) which supports a 12-bit RGB, 4,096-color palette. It has an extended set of 320×200 and 640×200 graphic modes (called Super High-Res modes by Apple), with different (and a bit complex) color modes:
Also, along with the one of 16 palettes, to each scan line the Apple IIgs VGC is able to assign individual 320 or 640 horizontal resolution independently.
(EGA) supports all CGA modes and add three more: two 320×200 and 640×200 graphic modes, both with the full CGA 16-color palette (intended to be used with the same "digital RGB" CGA color monitor of 200 scan lines) and an extra 640×350 graphic mode with 16 colors chosen from a 6-bit RGB (64 colors) palette for what IBM then called an "analog RGB" type monitor.
The word analog
means here that the RGB signals can have more than the bare two possible levels 0 and 1 (as the so called —by IBM— "digital RGB" CGA monitor type has); despite of its name, colors are produced digitally, so there exists binary (quantized) steps for every primary RGB signal (two bits, four levels per primary, in this case). Thus, the EGA signal from the computer to this kind of monitor had two wires for each primary red, green and blue. Later, true analog connectors were developed by IBM for the more advanced MCGA and VGA display adapters and monitors (see the next section), which are unrelated to (and incompatible with) the EGA "analog" monitors.
Some early EGA cards shipped only 64 KiB of video memory (the nominal was 128KiB, up to a maximum of 256 KiB to allow more screen pages in memory), so the 640×350 graphic mode provides only four colors. This was never a proper mode by itself, and therefore was not popular.
The output of the sample image with 16 colors of the exclusive EGA palette and the CGA 16-color palette looks like:
By selecting any 16 of the 64 possible colors available, the text modes were also affected (that is, text modes in the EGA are not restricted to the 16 CGA colors only).
Also, monochrome "analog" monitors existed for EGA. The colors are then mapped internally to the correspondent luminance gray (the sum of the 30% of the red signal, the 59% of the green and the 11% of the blue), giving a 16-shades from a 64-grayscale palette. "Positive" class monitors inverts the signal, providing that the default EGA colors for text modes (black background and white foreground) displays reversed (white background and black foreground), as if were a printed document.
(VGA) used a 6-bits per channel, 64 levels Digital-to-Analog Converter
(DAC) to give an 18-bit RGB palette (262,144 colors), from which can be selected any two (in MCGA 640×480 graphic mode), 16 (in VGA 320×200, 640×200, 640×350 and 640×480 graphic modes) or 256 (in MCGA 320×200 graphic mode) at a time. They both provided full compatibility with CGA
modes, while VGA included all the EGA
modes as well as the MCGA modes.
The output of the sample image with the 256- and 16-colors modes with the MCGA/VGA palette and color monitors looks like:
By selecting any 16 of the 262,144 possible colors available, the text modes were also affected (that is, text modes in the VGA, as in the case of the EGA, are not restricted to the 16 CGA colors only).
When connected to analog monochrome monitors, they can offer 64 levels of grey. Some of the first portable PCs
featured a flat red monochrome plasma display
with a VGA. Then all possible colors are output as a shade of red.
The eXtended Graphics Array (XGA) supports all 8514/A modes plus a 800×600 16-bit RGB Highcolor mode, with 65,536 simultaneous colors on screen.
In the 1990s, most manufacturers adhered to the VESA BIOS Extensions
(VBE), used for enabling standard support for advanced video modes (at high resolutions and color depths).
They are the direct predecessors, not the IBM 8514/A nor XGA, of actual graphic display PC hardware.
Palette (computing)
In computer graphics, a palette is either a given, finite set of colors for the management of digital images , or a small on-screen graphical element for choosing from a limited set of choices, not necessarily colors .Depending on the context In computer graphics, a palette is either a given,...
of some of the most popular 16-bit
16-bit
-16-bit architecture:The HP BPC, introduced in 1975, was the world's first 16-bit microprocessor. Prominent 16-bit processors include the PDP-11, Intel 8086, Intel 80286 and the WDC 65C816. The Intel 8088 was program-compatible with the Intel 8086, and was 16-bit in that its registers were 16...
personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s, roughly those manufactured from 1985 to 1995. All of them are based on RGB palettes; although some output in composite video
Composite video
Composite video is the format of an analog television signal before it is combined with a sound signal and modulated onto an RF carrier. In contrast to component video it contains all required video information, including colors in a single line-level signal...
, the internal logic to produce colors is always RGB. Also, the list does not include obscure palettes, such as those available only through special adjustment and/or CPU assisted techniques (flickering, palette swapping, etc.), except where noted.
For color palettes of early 8-bit
8-bit
The first widely adopted 8-bit microprocessor was the Intel 8080, being used in many hobbyist computers of the late 1970s and early 1980s, often running the CP/M operating system. The Zilog Z80 and the Motorola 6800 were also used in similar computers...
personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s, see the List of 8-bit computer hardware palettes article.
For current RGB display systems for 32-bit
32-bit
The range of integer values that can be stored in 32 bits is 0 through 4,294,967,295. Hence, a processor with 32-bit memory addresses can directly access 4 GB of byte-addressable memory....
and better PCs
IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are those generally similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT. Such computers used to be referred to as PC clones, or IBM clones since they almost exactly duplicated all the significant features of the PC architecture, facilitated by various manufacturers' ability to...
(Super VGA, etc.), see the 16-bit RGB for HighColor (thousands) and 24-bit RGB for TrueColor (millions of colors) modes.
This n-bit distinction is not intended as a true strict categorization of such machines, due to mixed architectures also existing (16-bit processors
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
with 8-bit data bus or 32-bit processors with 16-bit data bus, among others). The distinction is more related with a broad 16-bit computer age or generation (around 1985-1995) and its associated state of the art
State of the art
The state of the art is the highest level of development, as of a device, technique, or scientific field, achieved at a particular time. It also refers to the level of development reached at any particular time as a result of the latest methodologies employed.- Origin :The earliest use of the term...
in color display capabilities.
For various software arrangements and sorts of colors, see the List of software palettes article.
For video game console
Video game console
A video game console is an interactive entertainment computer or customized computer system that produces a video display signal which can be used with a display device to display a video game...
s, see the List of videogame consoles palettes article.
For a more complete and technical description of the computer's hardware video capabilities, see the List of home computers by video hardware.
They are listed the original model of every system, which implies that enhanced versions, clones and compatibles also supports the original's one palette.
For every model, their main different graphical color modes are listed based exclusively in the way they handle colors on screen, not all their possible different screen modes (text modes or resolution modes that shares the same color schemes).
Every palette has technical details about how the colors are produced and/or used by the computer's display video subsystem.
Due to all palettes being RGB based, color charts already exist in other articles, and they are not shown here. Links to their corresponding RGB palette color charts are available.
Simulations of how the parrot sample image would render in different graphic modes are provided. These simulations are always up to the maximum vertical resolution of the given graphic mode or up to 200 scan lines, if vertical resolution is greater. So any of them could be properly padded, transcoded and dumped into the original hardware and/or software emulators without any other changes. See the summary of every simulated image to obtain technical details about conversion to the original machine's format.
The simulated images only try to show how a certain system is able to handle to an image in terms of color without improvements nor additional clever tricks of design like anti-aliasing
Anti-aliasing
In digital signal processing, spatial anti-aliasing is the technique of minimizing the distortion artifacts known as aliasing when representing a high-resolution image at a lower resolution...
or dithering. Doubtlessly a human artist is able to improve enormously the look of the simulated images to approximate them to the original one, but that is not the goal of this article.
Note: please do not change the compression scheme of every image by a lossy compression scheme (i.e. JPEG
JPEG
In computing, JPEG . The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality....
) in order to improve their file size, nor change the thumbnail size of the images, nor gamma-correct them. They are didactical material AS IS, and they have been already optimized for this purpose.
ST series
The Atari STAtari ST
The Atari ST is a home/personal computer that was released by Atari Corporation in 1985 and commercially available from that summer into the early 1990s. The "ST" officially stands for "Sixteen/Thirty-two", which referred to the Motorola 68000's 16-bit external bus and 32-bit internals...
series has a Digital-to-Analog Converter
Digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal . An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation...
of 3-bits, eight levels per RGB channel, featuring a 9-bit RGB palette (512 colors).
The STE series has a Digital-to-Analog Converter
Digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal . An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation...
of 4-bits, sixteen levels per RGB channel, featuring a 12-bit RGB palette (4096 colors).
Depending on the (proprietary) monitor type attached, it displays one of the 320×200, 16-colors and 640×200, 4-colors modes with the color monitor, or the high resolution 640×400 black and white mode with the monochrome monitor.
The output of the sample image with the 16-, 4-colors and the monochrome modes with the Atari ST video hardware looks like:
Amiga OCS
The Original Chip Set (OCS) of the Commodore Amiga features a 12-bit RGB, 4,096-color palette.The graphic surface is divided in a series of bit planes
Bit-plane
A bit plane of a digital discrete signal is a set of bits having the same position in the respective binary numbers.For example, for 16-bit data representation there are 16 bit-planes: the first bit-plane contains the set of the most significant bit and the 16th contains the least significant...
, from 1 up to 6, no matter how many horizontal (320 or 640) or vertical resolution (200 NTSC
NTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
compatible, 256 PAL
PAL
PAL, short for Phase Alternating Line, is an analogue television colour encoding system used in broadcast television systems in many countries. Other common analogue television systems are NTSC and SECAM. This page primarily discusses the PAL colour encoding system...
compatible, both interlaced or not) it has in a given graphic mode. The color lookup table
CLUT
A colour look-up table is a mechanism used to transform a range of input colours into another range of colours. It can be a hardware device built into an imaging system or a software function built into an image processing application...
has up to 32 entries. So the different indexed color modes are from 1 to 5 bits pixel depth, 2-, 4-, 8-, 16- or 32-color out of 4,096.
When the sixth bit-plane is used, two extra color modes can be set: Extra Half-Brite (EHB) and Hold-And-Modify
Hold-and-Modify
Hold-And-Modify, usually abbreviated as HAM, is a display mode of the Commodore Amiga computer. It uses a highly unusual technique to express the color of pixels, allowing many more colors to appear on screen than would otherwise be possible....
(HAM). The EHB mode 6-bits pixel points to one of the 32 colors in the palette with their lower 5-bits, and if the 6th bit is on, the bright of the color is halved (hence the name of this mode). So there are a total of 64 visible colors: the user chooses light versions of the first 32 colors and the system already provides their darker versions.
In the HAM mode, the two higher bits of the 6-bits pixels are used as a four state command. Three of the states changes only the red, green or blue component of the pixel respect of the precedent in the scan line, and hold the other two RGB components. The new value for the modified color component is in the four lower bits. The remaining command state forces the pixel value to be one of the 16 first values of the palette, whose indice is in the four lower bits of the pixel. So it is very important to have a well selected palette, or the color will spread easily among consecutive pixels in the scan line of the image. This mode can display all of the 4,096 colors simultaneously.
Here are the simulated images for the EHB and the HAM modes:
Apple IIgs
Apple IIgsApple IIGS
The Apple , the fifth and most powerful model in the Apple II series of personal computers produced by Apple Computer. The "GS" in the name stands for Graphics and Sound, referring to its enhanced graphics and sound capabilities, both of which greatly surpassed previous models of the line...
, along with full compatible graphic modes with the Apple II
Apple II
The Apple II is an 8-bit home computer, one of the first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products, designed primarily by Steve Wozniak, manufactured by Apple Computer and introduced in 1977...
, features a custom Video Graphics Chip (VGC) which supports a 12-bit RGB, 4,096-color palette. It has an extended set of 320×200 and 640×200 graphic modes (called Super High-Res modes by Apple), with different (and a bit complex) color modes:
- 320×200 with 16 palettes of 16 selected colors out of 4,096 each. Every single scan line can be assigned to one of the sixteen palettes, so it can have up to 16×16=256 different simultaneous colors (although some common colors like black and white are usually shared among the different palettes, giving less than 256 total different colors). The most simple way to use this mode is having a unique 16-color selection for the entire screen and assign it to all scan lines. Here are shown the sample image both using a single shared palette and using all the 16 palettes (in this case, by dividing the image into 16 strips):


- 640×200 with 16 palettes of 8 selected colors out of 4,096 each. Every single scan line can be assigned to one of the sixteen palettes, so it can be have up to 8×16=128 different simultaneous colors (usually less due to shared colors). In a single scan line, even column pixels can have one of the first four colors of the line's assigned palette, and odd column pixels one of the last four colors of the eight. The most simple way to use this mode is having a unique 8-color selection for the entire screen with four duplicate colors (the same to both even and odd pixel columns) and assign it to all scan lines. Here are shown the sample image both with a single shared custom 4-color palette and with a single 8-color palette (black, blue, yellow, white, black again, red, green, white again) to produce 13 dithered-by-hardware colors ("dark blue", "dark yellow", "gray", "dark red", "magenta", "orange", "light red", "dark green", "cyan", "lime green", "light green", "light blue" and "light yellow") plus pure black and white. The last was the Apple IIgs Finder default mode and palette.
Also, along with the one of 16 palettes, to each scan line the Apple IIgs VGC is able to assign individual 320 or 640 horizontal resolution independently.
IBM PC-AT and compatible systems
- For the palettes of previous original IBM PCIBM PCThe IBM Personal Computer, commonly known as the IBM PC, is the original version and progenitor of the IBM PC compatible hardware platform. It is IBM model number 5150, and was introduced on August 12, 1981...
, IBM XT and IBM PCjrIBM PCjrThe IBM PCjr was IBM's first attempt to enter the home computer market. The PCjr, IBM model number 4860, retained the IBM PC's 8088 CPU and BIOS interface for compatibility, but various design and implementation decisions led the PCjr to be a commercial failure.- Features :Announced November 1,...
/Tandy 1000Tandy 1000The Tandy 1000 was the first in a line of more-or-less IBM PC compatible home computer systems produced by the Tandy Corporation for sale in its Radio Shack chain of stores.-Overview:...
series hardware displays, please visit IBM PC/XT and compatible systems in the List of 8-bit computer hardware palettes article.
EGA
The Enhanced Graphics AdapterEnhanced Graphics Adapter
The Enhanced Graphics Adapter is the IBM PC computer display standard specification which is between CGA and VGA in terms of color and space resolution. Introduced in October 1984 by IBM shortly after its new PC/AT, EGA produces a display of 16 simultaneous colors from a palette of 64 at a...
(EGA) supports all CGA modes and add three more: two 320×200 and 640×200 graphic modes, both with the full CGA 16-color palette (intended to be used with the same "digital RGB" CGA color monitor of 200 scan lines) and an extra 640×350 graphic mode with 16 colors chosen from a 6-bit RGB (64 colors) palette for what IBM then called an "analog RGB" type monitor.
The word analog
Analog signal
An analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.e., analogous to another time varying signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the signal which are...
means here that the RGB signals can have more than the bare two possible levels 0 and 1 (as the so called —by IBM— "digital RGB" CGA monitor type has); despite of its name, colors are produced digitally, so there exists binary (quantized) steps for every primary RGB signal (two bits, four levels per primary, in this case). Thus, the EGA signal from the computer to this kind of monitor had two wires for each primary red, green and blue. Later, true analog connectors were developed by IBM for the more advanced MCGA and VGA display adapters and monitors (see the next section), which are unrelated to (and incompatible with) the EGA "analog" monitors.
Some early EGA cards shipped only 64 KiB of video memory (the nominal was 128KiB, up to a maximum of 256 KiB to allow more screen pages in memory), so the 640×350 graphic mode provides only four colors. This was never a proper mode by itself, and therefore was not popular.
The output of the sample image with 16 colors of the exclusive EGA palette and the CGA 16-color palette looks like:
By selecting any 16 of the 64 possible colors available, the text modes were also affected (that is, text modes in the EGA are not restricted to the 16 CGA colors only).
Also, monochrome "analog" monitors existed for EGA. The colors are then mapped internally to the correspondent luminance gray (the sum of the 30% of the red signal, the 59% of the green and the 11% of the blue), giving a 16-shades from a 64-grayscale palette. "Positive" class monitors inverts the signal, providing that the default EGA colors for text modes (black background and white foreground) displays reversed (white background and black foreground), as if were a printed document.
MCGA and VGA
The Multicolor Graphics Array (MCGA) and Video Graphics ArrayVideo Graphics Array
Video Graphics Array refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector or the 640×480 resolution...
(VGA) used a 6-bits per channel, 64 levels Digital-to-Analog Converter
Digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal . An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation...
(DAC) to give an 18-bit RGB palette (262,144 colors), from which can be selected any two (in MCGA 640×480 graphic mode), 16 (in VGA 320×200, 640×200, 640×350 and 640×480 graphic modes) or 256 (in MCGA 320×200 graphic mode) at a time. They both provided full compatibility with CGA
Color Graphics Adapter
The Color Graphics Adapter , originally also called the Color/Graphics Adapter or IBM Color/Graphics Monitor Adapter, introduced in 1981, was IBM's first color graphics card, and the first color computer display standard for the IBM PC....
modes, while VGA included all the EGA
Enhanced Graphics Adapter
The Enhanced Graphics Adapter is the IBM PC computer display standard specification which is between CGA and VGA in terms of color and space resolution. Introduced in October 1984 by IBM shortly after its new PC/AT, EGA produces a display of 16 simultaneous colors from a palette of 64 at a...
modes as well as the MCGA modes.
The output of the sample image with the 256- and 16-colors modes with the MCGA/VGA palette and color monitors looks like:
By selecting any 16 of the 262,144 possible colors available, the text modes were also affected (that is, text modes in the VGA, as in the case of the EGA, are not restricted to the 16 CGA colors only).
When connected to analog monochrome monitors, they can offer 64 levels of grey. Some of the first portable PCs
Portable computer
A portable computer is a computer that is designed to be moved from one place to another and includes a display and keyboard. Portable computers, by their nature, are generally microcomputers. Portable computers, because of their size, are also commonly known as 'Lunchbox' or 'Luggable' computers...
featured a flat red monochrome plasma display
Plasma display
A plasma display panel is a type of flat panel display common to large TV displays or larger. They are called "plasma" displays because the technology utilizes small cells containing electrically charged ionized gases, or what are in essence chambers more commonly known as fluorescent...
with a VGA. Then all possible colors are output as a shade of red.
8514/A and XGA
The IBM 8514/A uses the 18-bit RGB palette from which the user could select any 256 at a time in both 640×480 and 1024×768 graphic modes. It does not support compatibility with VGA modes, but a VGA card are usually already installed and bridged to the 8514/A to provide a single output cable for a single monitor which can display any of all VGA and 8514/A possible modes.The eXtended Graphics Array (XGA) supports all 8514/A modes plus a 800×600 16-bit RGB Highcolor mode, with 65,536 simultaneous colors on screen.
Super VGA (SVGA)
Enhanced clones of the IBM VGA, known as Super VGA (SVGA), support 256 simultaneous colors in 640×480 and higher pixel resolutions (800×600, 1024×768) in both 16 and 256 picked colors from the VGA 18-bit RGB palette, depending on the model and the manufacturer. Also, some SVGA cards support 15- and 16-bit RGB Highcolor modes, with 32,768 or 65,536 simultaneous colors on screen in 640×480 and higher resolutions. Some later models reach the 24-bit RGB True color modes.In the 1990s, most manufacturers adhered to the VESA BIOS Extensions
VESA BIOS Extensions
VESA BIOS Extensions is a VESA standard, currently at version 3, that defines the interface that can be used by software to access compliant video boards at high resolutions and bit depths...
(VBE), used for enabling standard support for advanced video modes (at high resolutions and color depths).
They are the direct predecessors, not the IBM 8514/A nor XGA, of actual graphic display PC hardware.
See also
- Palette (computing)Palette (computing)In computer graphics, a palette is either a given, finite set of colors for the management of digital images , or a small on-screen graphical element for choosing from a limited set of choices, not necessarily colors .Depending on the context In computer graphics, a palette is either a given,...
- Indexed colorIndexed colorIn computing, indexed color is a technique to manage digital images' colors in a limited fashion, in order to save computer memory and file storage, while speeding up display refresh and file transfers...
- Color Lookup TableCLUTA colour look-up table is a mechanism used to transform a range of input colours into another range of colours. It can be a hardware device built into an imaging system or a software function built into an image processing application...
- Color depthColor depthIn computer graphics, color depth or bit depth is the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer. This concept is also known as bits per pixel , particularly when specified along with the number of bits used...
- Computer displayComputer displayA monitor or display is an electronic visual display for computers. The monitor comprises the display device, circuitry, and an enclosure...
- List of home computers by video hardware