
Linked Data
Encyclopedia
In computing
, linked data describes a method of publishing structured data so that it can be interlinked and become more useful. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP
and URIs
, but rather than using them to serve web pages for human readers, it extends them to share information in a way that can be read automatically by computers. This enables data from different sources to be connected and queried.
Tim Berners-Lee
, director of the World Wide Web Consortium
, coined the term in a design note discussing issues around the Semantic Web
project. However, the idea is very old and is closely related to concepts such as the network model (database), citations between scholarly articles, and authority control
in libraries.
outlined four principles of linked data in his Design Issues: Linked Data note, paraphrased along the following lines:
Tim Berners-Lee gave a presentation on linked data at the TED
2009 conference. In it, he restated the linked data principles as three "extremely simple" rules:
Note that although the second rule mentions "standard formats", it does not require any specific standard, such as RDF/XML.
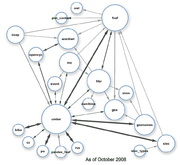 The goal of the W3C Semantic Web Education and Outreach group's Linking Open Data community project is to extend the Web with a data commons by publishing various open datasets as RDF on the Web and by setting RDF links between data items from different data sources. In October 2007, datasets consisted of over two billion RDF triples, which were interlinked by over two million RDF links. By September 2011 this had grown to 31 billion RDF triples, interlinked by around 504 million RDF links. There is also an interactive visualization of the linked data sets to browse through the cloud.
The goal of the W3C Semantic Web Education and Outreach group's Linking Open Data community project is to extend the Web with a data commons by publishing various open datasets as RDF on the Web and by setting RDF links between data items from different data sources. In October 2007, datasets consisted of over two billion RDF triples, which were interlinked by over two million RDF links. By September 2011 this had grown to 31 billion RDF triples, interlinked by around 504 million RDF links. There is also an interactive visualization of the linked data sets to browse through the cloud.
has provided a support action grant as part of the 7th Framework Programme to support the publishing and consumption of linked open data http://latc-project.eu/.
The goals are:
-funded network of excellence which is concerned with bringing together European researchers in the area of large-scale data management which includes Semantic Web (RDF) data published adhering to Linked Data principles.
Planet Data is unique in its approach to having open calls for bringing in additional partners during the project duration via the PlanetData Programs http://planet-data.eu/about.
's 7th Framework Programme a €6.5m grant has been given to the LOD2 project, to continue the work of the Linking Open Data project. Started in September 2010 and due to run until 2014, this project states its aims as "Creating Knowledge out of Interlinked Data" by developing:
Computing
Computing is usually defined as the activity of using and improving computer hardware and software. It is the computer-specific part of information technology...
, linked data describes a method of publishing structured data so that it can be interlinked and become more useful. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol is a networking protocol for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web....
and URIs
Uniform Resource Identifier
In computing, a uniform resource identifier is a string of characters used to identify a name or a resource on the Internet. Such identification enables interaction with representations of the resource over a network using specific protocols...
, but rather than using them to serve web pages for human readers, it extends them to share information in a way that can be read automatically by computers. This enables data from different sources to be connected and queried.
Tim Berners-Lee
Tim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John "Tim" Berners-Lee, , also known as "TimBL", is a British computer scientist, MIT professor and the inventor of the World Wide Web...
, director of the World Wide Web Consortium
World Wide Web Consortium
The World Wide Web Consortium is the main international standards organization for the World Wide Web .Founded and headed by Tim Berners-Lee, the consortium is made up of member organizations which maintain full-time staff for the purpose of working together in the development of standards for the...
, coined the term in a design note discussing issues around the Semantic Web
Semantic Web
The Semantic Web is a collaborative movement led by the World Wide Web Consortium that promotes common formats for data on the World Wide Web. By encouraging the inclusion of semantic content in web pages, the Semantic Web aims at converting the current web of unstructured documents into a "web of...
project. However, the idea is very old and is closely related to concepts such as the network model (database), citations between scholarly articles, and authority control
Authority control
Authority control is the practice of creating and maintaining index terms for bibliographic material in a catalog in library and information science. Authority control fulfills two important functions. First, it enables catalogers to disambiguate items with similar or identical headings...
in libraries.
Principles
Tim Berners-LeeTim Berners-Lee
Sir Timothy John "Tim" Berners-Lee, , also known as "TimBL", is a British computer scientist, MIT professor and the inventor of the World Wide Web...
outlined four principles of linked data in his Design Issues: Linked Data note, paraphrased along the following lines:
- Use URIs
Uniform Resource IdentifierIn computing, a uniform resource identifier is a string of characters used to identify a name or a resource on the Internet. Such identification enables interaction with representations of the resource over a network using specific protocols...
to identify things.- Use HTTP
Hypertext Transfer ProtocolThe Hypertext Transfer Protocol is a networking protocol for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web....
URIs so that these things can be referred to and looked up ("dereferencedDereferenceable Uniform Resource IdentifierA dereferenceable Uniform Resource Identifier or dereferenceable URI is a resource retrieval mechanism that uses any of the internet protocols A dereferenceable Uniform Resource Identifier or dereferenceable URI is a resource retrieval mechanism that uses any of the internet protocols A...
") by people and user agents.- Provide useful information about the thing when its URI is dereferenced, using standard formats such as RDF/XML
RDF/XMLRDF/XML is a syntax, defined by the W3C, to express an RDF graph as an XML document. According to the W3C, "RDF/XML is the normative syntax for writing RDF"....
.- Include links to other, related URIs in the exposed data to improve discovery of other related information on the Web.
Tim Berners-Lee gave a presentation on linked data at the TED
TED (conference)
TED is a global set of conferences owned by the private non-profit Sapling Foundation, formed to disseminate "ideas worth spreading"....
2009 conference. In it, he restated the linked data principles as three "extremely simple" rules:
- All kinds of conceptual things, they have names now that start with HTTP.
- I get important information back. I will get back some data in a standard format which is kind of useful data that somebody might like to know about that thing, about that event.
- I get back that information it's not just got somebody's height and weight and when they were born, it's got relationships. And when it has relationships, whenever it expresses a relationship then the other thing that it's related to is given one of those names that starts with HTTP.
Note that although the second rule mentions "standard formats", it does not require any specific standard, such as RDF/XML.
Components
- URIsUniform Resource IdentifierIn computing, a uniform resource identifier is a string of characters used to identify a name or a resource on the Internet. Such identification enables interaction with representations of the resource over a network using specific protocols...
(specifically, of the dereferenceable variety) - HTTPHypertext Transfer ProtocolThe Hypertext Transfer Protocol is a networking protocol for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web....
- Resource Description FrameworkResource Description FrameworkThe Resource Description Framework is a family of World Wide Web Consortium specifications originally designed as a metadata data model...
(RDF) - SerializationSerializationIn computer science, in the context of data storage and transmission, serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object state into a format that can be stored and "resurrected" later in the same or another computer environment...
formats (RDFaRDFaRDFa is a W3C Recommendation that adds a set of attribute-level extensions to XHTML for embedding rich metadata within Web documents...
, RDF/XMLRDF/XMLRDF/XML is a syntax, defined by the W3C, to express an RDF graph as an XML document. According to the W3C, "RDF/XML is the normative syntax for writing RDF"....
, N3Notation 3Notation3, or N3 as it is more commonly known, is a shorthand non-XML serialization of Resource Description Framework models, designed with human-readability in mind: N3 is much more compact and readable than XML RDF notation...
, TurtleTurtle (syntax)Turtle is a serialization format for Resource Description Framework graphs. A subset of Tim Berners-Lee and Dan Connolly's Notation3 language, it was defined by Dave Beckett, and is a superset of the minimal N-Triples format. Unlike full N3, Turtle doesn't go beyond RDF's graph model...
, and others)
Linking open-data community project

Dataset instance and class relationships
Clickable diagrams that show the individual datasets and their relationships within the DBpedia-spawned LOD cloud, as shown by the figures to the right, are:Linked open data around the clock (LATC) – EU project
The European CommissionEuropean Commission
The European Commission is the executive body of the European Union. The body is responsible for proposing legislation, implementing decisions, upholding the Union's treaties and the general day-to-day running of the Union....
has provided a support action grant as part of the 7th Framework Programme to support the publishing and consumption of linked open data http://latc-project.eu/.
The goals are:
- improve a round-the-clock infrastructure to monitor the usage and improve the quality of linked open data
- provide low barrier access for data publishers and consumers
- develop a library of open source data processing tools
- maintain a test-bed for processing linked data in combination with European Union data
- support the community with tutorials and best practices
PlanetData – EU project
The PlanetData project is an European CommissionEuropean Commission
The European Commission is the executive body of the European Union. The body is responsible for proposing legislation, implementing decisions, upholding the Union's treaties and the general day-to-day running of the Union....
-funded network of excellence which is concerned with bringing together European researchers in the area of large-scale data management which includes Semantic Web (RDF) data published adhering to Linked Data principles.
Planet Data is unique in its approach to having open calls for bringing in additional partners during the project duration via the PlanetData Programs http://planet-data.eu/about.
Linking Open Data 2 – EU project
As part of the European CommissionEuropean Commission
The European Commission is the executive body of the European Union. The body is responsible for proposing legislation, implementing decisions, upholding the Union's treaties and the general day-to-day running of the Union....
's 7th Framework Programme a €6.5m grant has been given to the LOD2 project, to continue the work of the Linking Open Data project. Started in September 2010 and due to run until 2014, this project states its aims as "Creating Knowledge out of Interlinked Data" by developing:
- enterprise-ready tools and methodologies for exposing and managing very large amounts of structured information on the Data Web,
- a testbed and bootstrap network of high-quality multi-domain, multi-lingual ontologies from sources such as Wikipedia and OpenStreetMap.
- algorithms based on machine learning for automatically interlinking and fusing data from the Web.
- standards and methods for reliably tracking provenance, ensuring privacy and data security as well as for assessing the quality of information.
- adaptive tools for searching, browsing, and authoring of linked data.
Datasets
- CKANCKANThe Comprehensive Knowledge Archive Network is a web-based system for the storage and distribution of data, such as spreadsheets and the contents of databases supported by the Open Knowledge Foundation...
– registry of open data and content packages provided by the Open Knowledge FoundationOpen Knowledge FoundationThe Open Knowledge Foundation is a not-for-profit organization that promotes open knowledge, including open content and open data. It was founded 24 May 2004 in Cambridge, UK... - DBpediaDBpediaDBpedia is a project aiming to extract structured content from the information created as part of the Wikipedia project. This structured information is then made available on the World Wide Web. DBpedia allows users to query relationships and properties associated with Wikipedia resources,...
– a dataset containing extracted data from WikipediaWikipediaWikipedia is a free, web-based, collaborative, multilingual encyclopedia project supported by the non-profit Wikimedia Foundation. Its 20 million articles have been written collaboratively by volunteers around the world. Almost all of its articles can be edited by anyone with access to the site,...
; it contains about 3.4 million concepts described by 1 billion triples, including abstracts in 11 different languages - DBLP Bibliography – provides bibliographic information about scientific papers; it contains about 800,000 articles, 400,000 authors, and approx. 15 million triples
- GeoNamesGeoNamesGeoNames is a geographical database available and accessible through various Web services, under a Creative Commons attribution license.- Database and web services :...
provides RDF descriptions of more than 7,500,000 geographical features worldwide. - Revyu – a Review service consumes and publishes linked data, primarily from DBpedia.
- riese – serving statistical data about 500 million Europeans (the first linked dataset deployed with XHTML+RDFaRDFaRDFa is a W3C Recommendation that adds a set of attribute-level extensions to XHTML for embedding rich metadata within Web documents...
) - UMBELUMBELUMBEL, short for Upper Mapping and Binding Exchange Layer, is an extracted subset of OpenCyc, providing the Cyc data in an RDF ontology based on SKOS and OWL 2...
– a lightweight reference structure of 20,000 subject concept classes and their relationships derived from OpenCyc, which can act as binding classes to external data; also has links to 1.5 million named entities from DBpedia and YAGOYAGO (Ontology)YAGO is a huge semantic knowledge base. Currently, YAGO knows over two million entities such as persons, organizations and cities and about twenty million facts about these entities. A web interface allows users to pose questions to YAGO in the form of queries on the YAGO homepage... - Sensorpedia – A scientific initiative at Oak Ridge National LaboratoryOak Ridge National LaboratoryOak Ridge National Laboratory is a multiprogram science and technology national laboratory managed for the United States Department of Energy by UT-Battelle. ORNL is the DOE's largest science and energy laboratory. ORNL is located in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, near Knoxville...
using a RESTful web architecture to link to sensor data and related sensing systems. - FOAFFOAF (software)FOAF is a machine-readable ontology describing persons, their activities and their relations to other people and objects. Anyone can use FOAF to describe him or herself...
– a dataset describing persons, their properties and relationships - OpenPSI for the OpenPSI project a community effort to create UK government linked data service that supports research
- VIAF (Virtual International Authority File) – an aggregation of authority files (author names) from national libraries from around the world.
Use case demos
See also
- Entity-attribute-value modelEntity-Attribute-Value modelEntity–attribute–value model is a data model to describe entities where the number of attributes that can be used to describe them is potentially vast, but the number that will actually apply to a given entity is relatively modest. In mathematics, this model is known as a sparse matrix...
- Open dataOpen DataOpen data is the idea that certain data should be freely available to everyone to use and republish as they wish, without restrictions from copyright, patents or other mechanisms of control. The goals of the open data movement are similar to those of other "Open" movements such as open source, open...
- Record linkageRecord linkageRecord linkage refers to the task of finding records in a data set that refer to the same entity across different data sources...
- Identity resolutionIdentity resolutionIdentity resolution is an operational intelligence process, typically powered by an identity resolution engine or middleware stack, whereby organizations can connect disparate data sources with a view to understanding possible identity matches and non-obvious relationships across multiple data silos...
- Data deduplicationData deduplicationIn computing, data deduplication is a specialized data compression technique for eliminating coarse-grained redundant data. The technique is used to improve storage utilization and can also be applied to network data transfers to reduce the number of bytes that must be sent across a link...
Further reading
- Linked data web architecture note by Tim Berners-LeeTim Berners-LeeSir Timothy John "Tim" Berners-Lee, , also known as "TimBL", is a British computer scientist, MIT professor and the inventor of the World Wide Web...
- Linked Data: Evolving the Web into a Global Data Space (2011) by Tom Heath and Christian Bizer, Synthesis Lectures on the Semantic Web: Theory and Technology, Morgan & Claypool
- The Web Turns 20: Linked Data Gives People Power, part 1 of 4, by Mark Fischetti, Scientific AmericanScientific AmericanScientific American is a popular science magazine. It is notable for its long history of presenting science monthly to an educated but not necessarily scientific public, through its careful attention to the clarity of its text as well as the quality of its specially commissioned color graphics...
2010 October 23 - Linked Data Is Merely More Data – Prateek Jain, Pascal Hitzler, Peter Z. Yeh, Kunal Verma, and Amit P. Sheth. In: Dan Brickley, Vinay K. Chaudhri, Harry Halpin, and Deborah McGuinness: Linked Data Meets Artificial Intelligence. Technical Report SS-10-07, AAAI Press, Menlo Park, California, 2010, pp. 82–86.
- Linked Data – The Story So Far (2009) by Christian Bizer, Tom Heath, Tim Berners-LeeTim Berners-LeeSir Timothy John "Tim" Berners-Lee, , also known as "TimBL", is a British computer scientist, MIT professor and the inventor of the World Wide Web...
, International Journal on Semantic Web and Information Systems (IJSWIS), 5(3): 1–22. DOI: 10.4018/jswis.2009081901 - LinkedData at the W3C Wiki
- LinkedData.org
- OpenLink Software white papers
- Linked Data on the Web – Chris Bizer, Tom Heath, Kingsley Uyi Idehen, Tim Berners-LeeTim Berners-LeeSir Timothy John "Tim" Berners-Lee, , also known as "TimBL", is a British computer scientist, MIT professor and the inventor of the World Wide Web...
. In Proceedings WWW2008, Beijing, China - Interlinking Open Data on the Web – Chris Bizer, Tom Heath, Danny Ayers, Yves Raimond. In Proceedings Poster Track, ESWC2007, Innsbruck, Austria
- Ontology Alignment for Linked Open Data – Prateek Jain, Pascal Hitzler, Amit Sheth, Kunal Verma, Peter Z. Yeh. In proceedings of the 9th International Semantic Web Conference, ISWC 2010, Shanghai, China
- Interview with Sören Auer, head of the LOD2 project about the continuation of LOD2 in 2011, June 2011
Browsers
- Explorator – a browser for exploring Sparql endpoints.
- Sig.ma – Browser for Linked data and embeddable mashup generator.
- razorbase – Faceted browser for LOD cloud data.
- The Tabulator – Generic data browser and editor.
- OpenLink Data Explorer (ODE)
- Zitgist DataViewer – linked data viewer
- Disco – Hyperdata Browser – A simple browser for navigating the semantic web.
- LENA – a Fresnel LEns based RDF/Linked data navigator with SPARQL selector support.
- RelFinder – Visual relationship discovery and exploration.
- Sheaflight – visual linked data browser.
- VisiNav – Visual Data Navigation.
- Wandora – information mashup creator with numerous information extractors.
- Ontology Browser – An online OWL ontology and LOD browser.
- Falcons Explorer – Tabular and relational end-user programming for the web of data.
- MyView – Querying linked data by navigation.
Presentations
- Tim Berners Lee : The next Web of open, linked data at TED
- Linked Data Tutorial – Michael Hausenblas
- Sir Tim Berners Lee: Linked Open Data at LinkedData Planet
- Linked Data: Principles and State of the Art – Chris Bizer, Tom Heath, Tim Berners-LeeTim Berners-LeeSir Timothy John "Tim" Berners-Lee, , also known as "TimBL", is a British computer scientist, MIT professor and the inventor of the World Wide Web...
at WWW2008 - The Linking Open Data Project – Bootstrapping the Web of Data – Tom Heath
- Creating, Deploying and Exploiting Linked Data – Keynote by Kingsley Uyi Idehen at Linked Data Planet, 2008
- Deploying Linked Data using OpenLink VirtuosoVirtuoso Universal ServerVirtuoso Universal Server is a middleware and database engine hybrid that combines the functionality of a traditional RDBMS, ORDBMS, virtual database, RDF, XML, free-text, web application server and file server functionality in a single system...
- Native to a Web of Data – Tom CoatesTom CoatesTom Coates is a technologist and early weblogger based in San Francisco, California who has been writing plasticbag.org since 1999...
- How To Make Linked Data More than Data – Prateek Jain, Pascal Hitzler, Amit Sheth, Peter Yeh, Kunal Verma – Presented by Amit ShethAmit ShethDr. Amit Sheth is a computer scientist at Wright State University in Dayton, Ohio. He is the Lexis Nexis Ohio Eminent Scholar for Advanced Data Management and Analysis....
at Semantic Technology Conference 2010
Events
- Workshop on Consuming Linked Data (COLD2011) at ISWC 2011
- Workshop on Linked Data on the Web (LDOW2011) at WWW2011
- Workshop on Consuming Linked Data (COLD2010) at ISWC 2010
- Workshop on Linked Data on the Web (LDOW2010) at WWW2010
- Workshop on Linked Data on the Web (LDOW2009) at WWW2009
- Workshop on Linked Data on the Web (LDOW2008) at WWW2008
- LinkedData Planet 2008 conference in New York City

