
Lindemann index
Encyclopedia
The Lindemann index is a simple measure of thermally driven disorder
in atoms or molecules. The local Lindemann index is defined as:
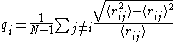
Where angle brackets indicate a time average. The global Lindemann index is a system average of this quantity.
In condensed matter
physics
: a departure from linearity in the behaviour of the global Lindemann index or an increase above a threshold value related to the spacing between atom
s (or micelle
s, particles, globules, etc.) is often taken as the indication that a solid-liquid phase transition
has taken place. See Lindemann melting criterion.
In Biomolecules : biomolecule
s often possess separate regions with different order characteristics. In order to quantify or illustrate local disorder, the local Lindemann index can be used.
Care must be taken if the molecule possesses globally defined dynamics, such as about a hinge or pivot, because these motions will obscure the local motions which the Lindemann index is designed to quantify. An appropriate tactic in this circumstance is to sum the rij only over a small number of neighbouring atoms to arrive at each qi. A further variety of such modifications to the Lindemann index are available and have different merits, e.g. for the study of glassy vs crystalline materials.
Entropy
Entropy is a thermodynamic property that can be used to determine the energy available for useful work in a thermodynamic process, such as in energy conversion devices, engines, or machines. Such devices can only be driven by convertible energy, and have a theoretical maximum efficiency when...
in atoms or molecules. The local Lindemann index is defined as:
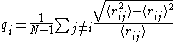
Where angle brackets indicate a time average. The global Lindemann index is a system average of this quantity.
In condensed matter
Condensed Matter
Condensed matter may refer to several things*Condensed matter physics, the study of the physical properties of condensed phases of matter*European Physical Journal B: Condensed Matter and Complex Systems, a scientific journal published by EDP sciences...
physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
: a departure from linearity in the behaviour of the global Lindemann index or an increase above a threshold value related to the spacing between atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
s (or micelle
Micelle
A micelle is an aggregate of surfactant molecules dispersed in a liquid colloid. A typical micelle in aqueous solution forms an aggregate with the hydrophilic "head" regions in contact with surrounding solvent, sequestering the hydrophobic single tail regions in the micelle centre. This phase is...
s, particles, globules, etc.) is often taken as the indication that a solid-liquid phase transition
Phase transition
A phase transition is the transformation of a thermodynamic system from one phase or state of matter to another.A phase of a thermodynamic system and the states of matter have uniform physical properties....
has taken place. See Lindemann melting criterion.
In Biomolecules : biomolecule
Biomolecule
A biomolecule is any molecule that is produced by a living organism, including large polymeric molecules such as proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, and nucleic acids as well as small molecules such as primary metabolites, secondary metabolites, and natural products...
s often possess separate regions with different order characteristics. In order to quantify or illustrate local disorder, the local Lindemann index can be used.
Care must be taken if the molecule possesses globally defined dynamics, such as about a hinge or pivot, because these motions will obscure the local motions which the Lindemann index is designed to quantify. An appropriate tactic in this circumstance is to sum the rij only over a small number of neighbouring atoms to arrive at each qi. A further variety of such modifications to the Lindemann index are available and have different merits, e.g. for the study of glassy vs crystalline materials.

