
Light echo
Encyclopedia
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
. Analogous to an echo
Echo (phenomenon)
In audio signal processing and acoustics, an echo is a reflection of sound, arriving at the listener some time after the direct sound. Typical examples are the echo produced by the bottom of a well, by a building, or by the walls of an enclosed room and an empty room. A true echo is a single...
of sound
Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.-Propagation of...
, a light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
echo is produced when a sudden flash or burst of light, such as that observed in nova
Nova
A nova is a cataclysmic nuclear explosion in a star caused by the accretion of hydrogen on to the surface of a white dwarf star, which ignites and starts nuclear fusion in a runaway manner...
e, is reflected
Reflection (physics)
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two differentmedia so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves...
off a source and arrives at the viewer some time after the initial flash. Because of their geometries
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, light echoes can produce the illusion
Illusion
An illusion is a distortion of the senses, revealing how the brain normally organizes and interprets sensory stimulation. While illusions distort reality, they are generally shared by most people....
of superluminal speeds.
Explanation
Light echoes are produced when the initial flash from a rapidly brightening object such as a novaNova
A nova is a cataclysmic nuclear explosion in a star caused by the accretion of hydrogen on to the surface of a white dwarf star, which ignites and starts nuclear fusion in a runaway manner...
is reflected off intervening interstellar dust which may or may not be associated with the source of the light. Light from the initial flash arrives at the viewer first, while light reflected from dust or other objects between the source and the viewer begins to arrive shortly afterward. Because this light has only traveled forward as well as away from the star, it produces the illusion of an echo expanding faster than the speed of light
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
.
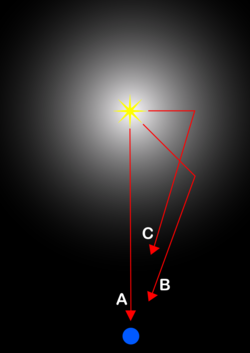
In the illustration to the right, light following path A is emitted from the original source and arrives at the observer first. Light which follows path B is reflected off a part of the gas cloud at a point between the source and the observer, and light following path C is reflected off a part of the gas cloud perpendicular to the direct path. Although light following paths B and C appear to come from the same point in the sky to the observer, B is actually significantly closer. As a result, the echo appears to the observer to expand at a rate faster than the speed of light.
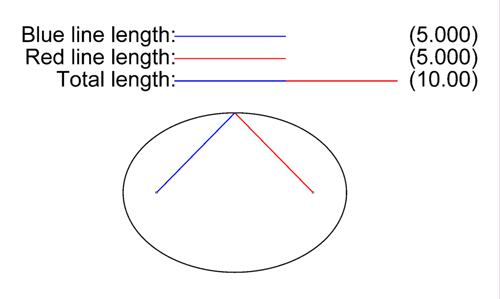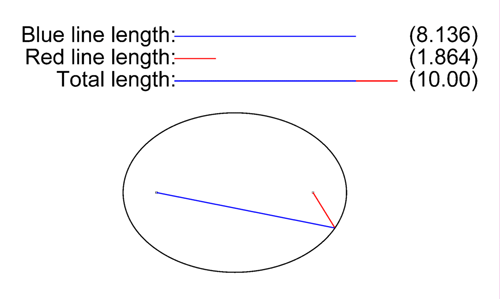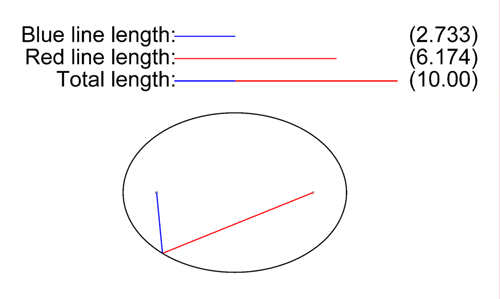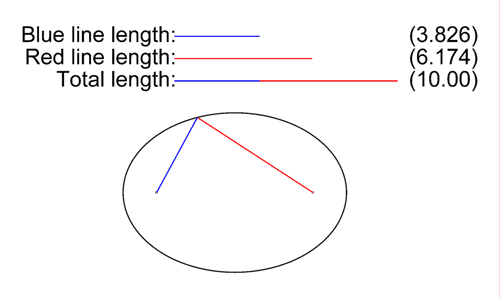
Speed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
is a constant, all light that originates from the same flash must have traveled the same distance. When the ray of light is reflected once, the possible paths between the source and the earth correspond to reflections on an ellipsoid, with the origin of the flash and the earth as its two foci (see animation to the right). This ellipsoid naturally expands over time.
Examples

V838 Monocerotis
V838 Monocerotis is a red variable star in the constellation Monoceros about 20,000 light years from the Sun, and possibly one of the largest known stars. The previously unknown star was observed in early 2002 experiencing a major outburst. Originally believed to be a typical nova eruption, it...
experienced a significant outburst in 2002 as observed by the Hubble Space Telescope
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope is a space telescope that was carried into orbit by a Space Shuttle in 1990 and remains in operation. A 2.4 meter aperture telescope in low Earth orbit, Hubble's four main instruments observe in the near ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared...
. The outburst proved surprising to observers when the object appeared to expand at a rate far exceeding the speed of light as it grew from an apparent visual size of 4 to 7 light years
Light Years
Light Years is the seventh studio album by Australian recording artist Kylie Minogue. It was released on 25 September 2000 by Parlophone and Mushroom Records. The album's style was indicative of her return to "mainstream pop dance tunes"....
in a matter of months. The expansion of the light echo is continuing and is expected to grow until 2010.
Light echos were used to determine the distance to the Cepheid variable
Cepheid variable
A Cepheid is a member of a class of very luminous variable stars. The strong direct relationship between a Cepheid variable's luminosity and pulsation period, secures for Cepheids their status as important standard candles for establishing the Galactic and extragalactic distance scales.Cepheid...
RS Puppis
RS Puppis
RS Puppis is a Cepheid variable star in the constellation of Puppis.Because it is located in a large nebula, astronomers using the ESO's New Technology Telescope at La Silla Observatory, Chile have been able to measure its distance by strictly geometric analysis of light echos from particles in...
to within 1% of its true value. This distance measurement is "the most accurate distance to a Cepheid" according to the lead author of the paper that reported the results.
Light echoes have been observed in connection with supernovae SN 1993J
SN 1993J
SN 1993J is a supernova observed in the galaxy M81. It was discovered on 28 March 1993 by F. Garcia in Spain. At the time, it was the second brightest supernova observed in the twentieth century behind SN 1987A....
and SN 1987A
SN 1987A
SN 1987A was a supernova in the outskirts of the Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a nearby dwarf galaxy. It occurred approximately 51.4 kiloparsecs from Earth, approximately 168,000 light-years, close enough that it was visible to the naked eye. It could be seen from the Southern...
, the closest supernova in modern times. The first recorded instance of a light echo was 1936, but it was not studied in detail.
By calculating the ellipsoid that has the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
and a supernova remnant as its foci and finding places where the ellipsoid intersect with clouds of dust and gas, it is sometimes possible to see the faint reflections of historical supernovae. Using light echoes, astronomer
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist who studies celestial bodies such as planets, stars and galaxies.Historically, astronomy was more concerned with the classification and description of phenomena in the sky, while astrophysics attempted to explain these phenomena and the differences between them using...
s can analyze the spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
of supernovae whose light reached Earth long before the invention of the telescope. Astronomers can compare the explosion with its remnants, centuries or millennia old. One example is the SN 1572
SN 1572
SN 1572 , "B Cassiopeiae" , or 3C 10 was a supernova of Type Ia in the constellation Cassiopeia, one of about eight supernovae visible to the naked eye in historical records...
supernova observed on Earth in 1572, where in 2008, faint light-echos were seen on dust in the northern part of the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
. Light echos can be identified by comparing photos of gas and dust clouds taken months or years apart and spotting changes in the light rippling across the clouds. If the source of the light is unknown, several such observations can be fitted to an ellipsoid to allow astronomer
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist who studies celestial bodies such as planets, stars and galaxies.Historically, astronomy was more concerned with the classification and description of phenomena in the sky, while astrophysics attempted to explain these phenomena and the differences between them using...
s to pinpoint the origin.
Light echoes have been used to study the supernova that produced the supernova remnant
Supernova remnant
A supernova remnant is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar material it sweeps up and shocks along the way.There are two...
Cassiopeia A
Cassiopeia A
Cassiopeia A is a supernova remnant in the constellation Cassiopeia and the brightest astronomical radio source in the sky, with a flux density of 2720 Jy at 1 GHz. The supernova occurred approximately away in the Milky Way. The expanding cloud of material left over from the supernova is now...
. The light from Cassiopeia A would have been visible on Earth around 1660, but went unnoticed, probably because dust obscured the direct view. Reflections from different directions allow astronomers to determine if a supernova was asymmetrical and shone more brightly in some directions than in others. The progenitor of Cassiopeia A has been suspected as being asymmetric, and looking at the light echoes of Cassiopeia A allowed for the first detection of supernova asymmetry in 2010.
External links
- Join the Hunt for Supernova Light Echoes — Animation of the reflection ellipsoid
- SuperMACHO project

