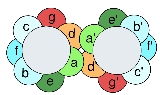
Leucine zipper
Overview
Structural motif
In a chain-like biological molecule, such as a protein or nucleic acid, a structural motif is a supersecondary structure, which appears also in a variety of other molecules...
in proteins. These motifs are usually found as part of a DNA-binding domain in various transcription factors, and are therefore involved in regulating gene expression. Leucine zippers are found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic regulatory proteins, but are mainly a feature of eukaryotes.
The leucine zipper is a super-secondary structure that functions as a dimer
Protein dimer
In biochemistry, a dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two, usually non-covalently bound, macromolecules like proteins or nucleic acids...
ization domain, and its presence generates adhesion forces in parallel
Parallel (geometry)
Parallelism is a term in geometry and in everyday life that refers to a property in Euclidean space of two or more lines or planes, or a combination of these. The assumed existence and properties of parallel lines are the basis of Euclid's parallel postulate. Two lines in a plane that do not...
alpha helices.
Unanswered Questions

