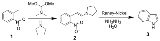
Leimgruber-Batcho indole synthesis
Encyclopedia
The Leimgruber–Batcho indole synthesis is a series of organic reaction
s that produce indole
s from o-nitrotoluene
s 1. The first step is the formation of an enamine
2 using N,N-dimethylformamide dimethyl acetal and pyrrolidine
. The desired indole 3 is then formed in a second step by reductive
cyclisation.
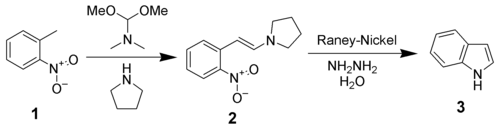 In the above scheme, the reductive cyclisation is effected by Raney nickel
In the above scheme, the reductive cyclisation is effected by Raney nickel
and hydrazine
. Palladium-on-carbon
and hydrogen
, stannous chloride, sodium dithionite
, or iron
in acetic acid
are also effective reducing agent
s.
(a gas) is displaced by pyrrolidine
from the dimethylformamide dimethylacetal, producing a more reactive reagent
. The mildly acidic hydrogens of the methyl group in the nitrotoluene can be deprotonated
under the basic conditions, and the resultant carbanion
attacks to produce the enamine
shown, with loss of methanol
. The sequence can be also be performed without the pyrrolidine, via the N,N-dimethyl enamine, though reaction times may be much longer in some cases. In the second step the nitro group
is reduced to -NH2 using hydrogen
and a Raney nickel
catalyst, followed by cyclisation then elimination
of the pyrrolidine. The hydrogen is often generated in situ
by the spontaneous decomposition of hydrazine
hydrate to H2
and N2
in the presence of the nickel.
The reaction is a good example of a reaction that was widely used in industry before any procedures were published in the mainstream scientific literature. Many indoles are pharmacalogically active
, so a good indole synthesis is important for the pharmaceutical industry. The process has become a popular alternative to the Fischer indole synthesis
because many starting ortho-nitrotoluenes are commercially available or easily made. In addition, the reactions proceed in high chemical yield under mild conditions.
The intermediate enamines are electronically related to push–pull olefins, having an electron-withdrawing
nitro group conjugated
to an electron-donating group. The extended conjugation means that these compounds are usually an intense red colour.
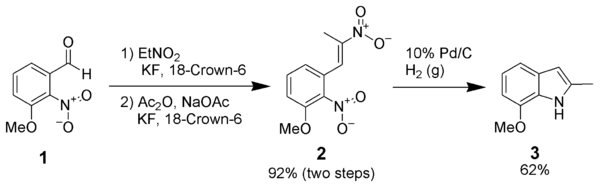 Most of the standard reduction methods listed above are successful with this reaction.
Most of the standard reduction methods listed above are successful with this reaction.
Organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis,...
s that produce indole
Indole
Indole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered nitrogen-containing pyrrole ring. Indole is a popular component of fragrances and the precursor to many pharmaceuticals. Compounds that contain an...
s from o-nitrotoluene
Toluene
Toluene, formerly known as toluol, is a clear, water-insoluble liquid with the typical smell of paint thinners. It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, i.e., one in which a single hydrogen atom from the benzene molecule has been replaced by a univalent group, in this case CH3.It is an aromatic...
s 1. The first step is the formation of an enamine
Enamine
An enamine is an unsaturated compound derived by the reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a secondary amine followed by loss of H2O.The word "enamine" is derived from the affix en-, used as the suffix of alkene, and the root amine. This can be compared with enol, which is a functional group...
2 using N,N-dimethylformamide dimethyl acetal and pyrrolidine
Pyrrolidine
Pyrrolidine, also known as tetrahydropyrrole, is an organic compound with the molecular formula C4H9N. It is a cyclic secondary amine with a five-membered heterocycle containing four carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom...
. The desired indole 3 is then formed in a second step by reductive
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
cyclisation.

Raney nickel
Raney nickel is a solid catalyst composed of fine grains of a nickel-aluminium alloy, used in many industrial processes. It was developed in 1926 by American]] engineer Murray Raney as an alternative catalyst for the hydrogenation of vegetable oils in industrial processes...
and hydrazine
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the formula N2H4. It is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Hydrazine is highly toxic and dangerously unstable unless handled in solution. Approximately 260,000 tons are manufactured annually...
. Palladium-on-carbon
Palladium on carbon
Palladium on carbon, often referred to as Pd/C, is a form of palladium used for catalysis. It is usually used for catalytic hydrogenations in organic chemistry...
and hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
, stannous chloride, sodium dithionite
Sodium dithionite
Sodium dithionite is a white crystalline powder with a weak sulfurous odor. It is a sodium salt of dithionous acid. Although it is stable under most conditions, it will decompose in hot water and in acid solutions...
, or iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
in acetic acid
Acetic acid
Acetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CO2H . It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar , and has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell...
are also effective reducing agent
Reducing agent
A reducing agent is the element or compound in a reduction-oxidation reaction that donates an electron to another species; however, since the reducer loses an electron we say it is "oxidized"...
s.
Reaction mechanism
In the initial enamine formation, dimethylamineDimethylamine
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula 2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable liquified gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is generally encountered as a solution in water at concentrations up to around 40%...
(a gas) is displaced by pyrrolidine
Pyrrolidine
Pyrrolidine, also known as tetrahydropyrrole, is an organic compound with the molecular formula C4H9N. It is a cyclic secondary amine with a five-membered heterocycle containing four carbon atoms and one nitrogen atom...
from the dimethylformamide dimethylacetal, producing a more reactive reagent
Reagent
A reagent is a "substance or compound that is added to a system in order to bring about a chemical reaction, or added to see if a reaction occurs." Although the terms reactant and reagent are often used interchangeably, a reactant is less specifically a "substance that is consumed in the course of...
. The mildly acidic hydrogens of the methyl group in the nitrotoluene can be deprotonated
Deprotonation
Deprotonation is the removal of a proton from a molecule, forming the conjugate base.The relative ability of a molecule to give up a proton is measured by its pKa value. A low pKa value indicates that the compound is acidic and will easily give up its proton to a base...
under the basic conditions, and the resultant carbanion
Carbanion
A carbanion is an anion in which carbon has an unshared pair of electrons and bears a negative charge usually with three substituents for a total of eight valence electrons. The carbanion exists in a trigonal pyramidal geometry. Formally a carbanion is the conjugate base of a carbon acid.where B...
attacks to produce the enamine
Enamine
An enamine is an unsaturated compound derived by the reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a secondary amine followed by loss of H2O.The word "enamine" is derived from the affix en-, used as the suffix of alkene, and the root amine. This can be compared with enol, which is a functional group...
shown, with loss of methanol
Methanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol...
. The sequence can be also be performed without the pyrrolidine, via the N,N-dimethyl enamine, though reaction times may be much longer in some cases. In the second step the nitro group
Nitro compound
Nitro compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more nitro functional groups . They are often highly explosive, especially when the compound contains more than one nitro group and is impure. The nitro group is one of the most common explosophores used globally...
is reduced to -NH2 using hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
and a Raney nickel
Raney nickel
Raney nickel is a solid catalyst composed of fine grains of a nickel-aluminium alloy, used in many industrial processes. It was developed in 1926 by American]] engineer Murray Raney as an alternative catalyst for the hydrogenation of vegetable oils in industrial processes...
catalyst, followed by cyclisation then elimination
Elimination reaction
An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one or two-step mechanism...
of the pyrrolidine. The hydrogen is often generated in situ
In situ
In situ is a Latin phrase which translated literally as 'In position'. It is used in many different contexts.-Aerospace:In the aerospace industry, equipment on board aircraft must be tested in situ, or in place, to confirm everything functions properly as a system. Individually, each piece may...
by the spontaneous decomposition of hydrazine
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the formula N2H4. It is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Hydrazine is highly toxic and dangerously unstable unless handled in solution. Approximately 260,000 tons are manufactured annually...
hydrate to H2
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
and N2
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
in the presence of the nickel.
The reaction is a good example of a reaction that was widely used in industry before any procedures were published in the mainstream scientific literature. Many indoles are pharmacalogically active
Pharmacology
Pharmacology is the branch of medicine and biology concerned with the study of drug action. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur between a living organism and chemicals that affect normal or abnormal biochemical function...
, so a good indole synthesis is important for the pharmaceutical industry. The process has become a popular alternative to the Fischer indole synthesis
Fischer indole synthesis
The Fischer indole synthesis isa chemical reaction that produces the aromatic heterocycle indole from a phenylhydrazine and an aldehyde or ketone under acidic conditions. The reaction was discovered in 1883 by Hermann Emil Fischer. Today antimigraine drugs of the triptan class are often...
because many starting ortho-nitrotoluenes are commercially available or easily made. In addition, the reactions proceed in high chemical yield under mild conditions.
The intermediate enamines are electronically related to push–pull olefins, having an electron-withdrawing
Polar effect
The Polar effect or electronic effect in chemistry is the effect exerted by a substituent on modifying electrostatic forces operating on a nearby reaction center...
nitro group conjugated
Conjugated system
In chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in compounds with alternating single and multiple bonds, which in general may lower the overall energy of the molecule and increase stability. Lone pairs, radicals or carbenium ions may be part of the...
to an electron-donating group. The extended conjugation means that these compounds are usually an intense red colour.
Dinitrostyrene reductive cyclization
The reductive cyclization of dinitrostyrenes (1) has proven itself effective when other more common methods have failed.
See also
- Bartoli indole synthesisBartoli indole synthesisThe Bartoli indole synthesis is the chemical reaction of ortho-substituted nitroarenes with vinyl grignard reagents to form substituted indoles....
- Fischer indole synthesisFischer indole synthesisThe Fischer indole synthesis isa chemical reaction that produces the aromatic heterocycle indole from a phenylhydrazine and an aldehyde or ketone under acidic conditions. The reaction was discovered in 1883 by Hermann Emil Fischer. Today antimigraine drugs of the triptan class are often...
- Reissert indole synthesisReissert indole synthesisThe Reissert indole synthesis is a series of chemical reactions designed to synthesize indole or substituted-indoles from ortho-nitrotoluene 1 and diethyl oxalate 2....

