
Least squares inference in phylogeny
Encyclopedia
Least squares inference in phylogeny generates a
phylogenetic tree
based on an
observed matrix of pairwise genetic distance
s and
optionally a weight
matrix. The goal is to find a tree which satisfies the distance constraints as
best as possible.
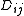
and the distances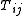 over a phylogenetic tree (i.e. the sum
over a phylogenetic tree (i.e. the sum
of the branch lengths in the path from leaf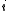 to leaf
to leaf
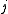 ) is measured by
) is measured by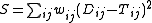
where the weights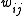 depend on the least squares method used.
depend on the least squares method used.
Least squares
distance tree construction aims to find the tree (topology and branch lengths)
with minimal S. This is a non-trivial problem. It involves searching the
discrete space of unrooted binary tree topologies whose size is exponential in
the number of leaves. For n leaves there are
1 • 3 • 5 • ... • (2n-3)
different topologies. Enumerating them is not feasible already for a small
number of leaves. Heuristic search methods are used to find a reasonably
good topology. The evaluation of S for a given topology (which includes the
computation of the branch lengths) is a linear least squares
problem.
There are several ways to weight the squared errors
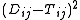 ,
,
depending on the knowledge and assumptions about the variances of the observed
distances. When nothing is known about the errors, or if they are assumed to be
independently distributed and equal for all observed distances, then all the
weights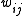 are set to one. This leads to an ordinary least
are set to one. This leads to an ordinary least
squares estimate.
In the weighted least squares case the errors are assumed to be independent
(or their correlations are not known). Given independent errors, a particular
weight should ideally be set to the inverse of the variance of the corresponding distance
estimate. Sometimes the variances may not be known, but they
can be modeled as a function of the distance estimates. In the Fitch and
Margoliash method
for instance it is assumed that the variances are proportional to the squared
distances.
assume independent distance estimates. If the distances
are derived from genomic data their estimates covary, because evolutionary
events on internal
branches (of the true tree) can push several distances up or down at
the same time. The resulting covariances can be taken into account using the
method of generalized least squares, i.e. minimizing the following quantity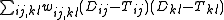
where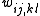 are the entries of the inverse of the covariance matrix
are the entries of the inverse of the covariance matrix
of the distance estimates.
problem . However, for a given tree, the optimal branch lengths can be determined in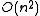 time for ordinary least squares,
time for ordinary least squares, 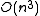 time for weighted least squares, and
time for weighted least squares, and 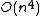 time for generalised least squares (given the inverse of the covariance matrix
time for generalised least squares (given the inverse of the covariance matrix
).
phylogenetic tree
Phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree or evolutionary tree is a branching diagram or "tree" showing the inferred evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical and/or genetic characteristics...
based on an
observed matrix of pairwise genetic distance
Genetic distance
Genetic distance refers to the genetic divergence between species or between populations within a species. It is measured by a variety of parameters. Smaller genetic distances indicate a close genetic relationship whereas large genetic distances indicate a more distant genetic relationship...
s and
optionally a weight
matrix. The goal is to find a tree which satisfies the distance constraints as
best as possible.
Ordinary and weighted least squares
The discrepancy between the observed pairwise distances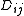
and the distances
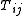 over a phylogenetic tree (i.e. the sum
over a phylogenetic tree (i.e. the sumof the branch lengths in the path from leaf
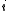 to leaf
to leaf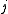 ) is measured by
) is measured by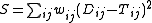
where the weights
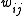 depend on the least squares method used.
depend on the least squares method used.Least squares
distance tree construction aims to find the tree (topology and branch lengths)
with minimal S. This is a non-trivial problem. It involves searching the
discrete space of unrooted binary tree topologies whose size is exponential in
the number of leaves. For n leaves there are
1 • 3 • 5 • ... • (2n-3)
different topologies. Enumerating them is not feasible already for a small
number of leaves. Heuristic search methods are used to find a reasonably
good topology. The evaluation of S for a given topology (which includes the
computation of the branch lengths) is a linear least squares
Linear least squares
In statistics and mathematics, linear least squares is an approach to fitting a mathematical or statistical model to data in cases where the idealized value provided by the model for any data point is expressed linearly in terms of the unknown parameters of the model...
problem.
There are several ways to weight the squared errors
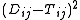 ,
,depending on the knowledge and assumptions about the variances of the observed
distances. When nothing is known about the errors, or if they are assumed to be
independently distributed and equal for all observed distances, then all the
weights
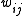 are set to one. This leads to an ordinary least
are set to one. This leads to an ordinary leastsquares estimate.
In the weighted least squares case the errors are assumed to be independent
(or their correlations are not known). Given independent errors, a particular
weight should ideally be set to the inverse of the variance of the corresponding distance
estimate. Sometimes the variances may not be known, but they
can be modeled as a function of the distance estimates. In the Fitch and
Margoliash method
for instance it is assumed that the variances are proportional to the squared
distances.
Generalized least squares
The ordinary and weighted least squares methods described aboveassume independent distance estimates. If the distances
are derived from genomic data their estimates covary, because evolutionary
events on internal
branches (of the true tree) can push several distances up or down at
the same time. The resulting covariances can be taken into account using the
method of generalized least squares, i.e. minimizing the following quantity
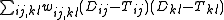
where
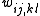 are the entries of the inverse of the covariance matrix
are the entries of the inverse of the covariance matrixCovariance matrix
In probability theory and statistics, a covariance matrix is a matrix whose element in the i, j position is the covariance between the i th and j th elements of a random vector...
of the distance estimates.
Computational Complexity
Finding the tree and branch lengths minimizing the least squares residual is an NP-completeNP-complete
In computational complexity theory, the complexity class NP-complete is a class of decision problems. A decision problem L is NP-complete if it is in the set of NP problems so that any given solution to the decision problem can be verified in polynomial time, and also in the set of NP-hard...
problem . However, for a given tree, the optimal branch lengths can be determined in
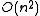 time for ordinary least squares,
time for ordinary least squares, 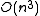 time for weighted least squares, and
time for weighted least squares, and 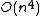 time for generalised least squares (given the inverse of the covariance matrix
time for generalised least squares (given the inverse of the covariance matrixCovariance matrix
In probability theory and statistics, a covariance matrix is a matrix whose element in the i, j position is the covariance between the i th and j th elements of a random vector...
).

