Kolbe electrolysis
Encyclopedia
Kolbe electrolysis or Kolbe reaction is an organic reaction
named after Adolph Wilhelm Hermann Kolbe
. The Kolbe reaction is formally a decarboxylative dimerisation and proceeds by a radical reaction mechanism
. Generally, the reaction can be observed as:
If R1, R2 are different, then alkanes R1-R1 and R2-R2 are also formed.
As an example, electrolysis of acetic acid
yields ethane
and carbon dioxide
:
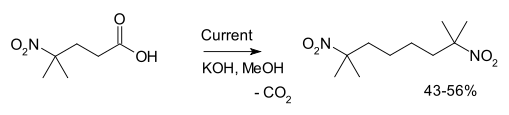
Another example is the synthesis of 2,7-dimethyl-2,7-dinitrooctane from 4-methyl-4-nitrovaleric acid :
Organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis,...
named after Adolph Wilhelm Hermann Kolbe
Adolph Wilhelm Hermann Kolbe
Adolph Wilhelm Hermann Kolbe was a German chemist. He never used the first two of his given names, preferring to be known as Hermann Kolbe.-Life:...
. The Kolbe reaction is formally a decarboxylative dimerisation and proceeds by a radical reaction mechanism
Reaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs.Although only the net chemical change is directly observable for most chemical reactions, experiments can often be designed that suggest the possible sequence of steps in...
. Generally, the reaction can be observed as:
- R1COO− + R2COO− → R1-R2 + 2 CO2
If R1, R2 are different, then alkanes R1-R1 and R2-R2 are also formed.
As an example, electrolysis of acetic acid
Acetic acid
Acetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CO2H . It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar , and has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell...
yields ethane
Ethane
Ethane is a chemical compound with chemical formula C2H6. It is the only two-carbon alkane that is an aliphatic hydrocarbon. At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas....
and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
:
- CH3COOH → CH3COO− → CH3COO· → CH3· + CO2
- 2CH3· → CH3CH3
Another example is the synthesis of 2,7-dimethyl-2,7-dinitrooctane from 4-methyl-4-nitrovaleric acid :