
Kohn-Sham equations
Encyclopedia
In quantum chemistry
, specifically density functional theory
, the Kohn–Sham equation is the Schrödinger equation
of a fictitious system (the "Kohn–Sham system") of non-interacting particles (typically electrons) that generate the same density
as any given system of interacting particles. The Kohn–Sham equation is defined by a local effective (fictitious) external potential in which the non-interacting particles move, typically denoted as vs(r) or veff(r), called the Kohn–Sham potential. As the particles in the Kohn–Sham system are non-interacting fermions, the Kohn–Sham wavefunction is a single Slater determinant
constructed from a set of orbital
s that are the lowest energy solutions to
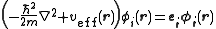
This eigenvalue equation is the typical representation of the Kohn–Sham equations. Here, εi is the orbital energy of the corresponding Kohn–Sham orbital, φi, and the density for an N-particle system is
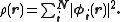
The Kohn–Sham equations are named after Walter Kohn
and Lu Jeu Sham, who introduced the concept at the University of California, San Diego
in 1965.
, the total energy of a system is expressed as a functional
of the charge density as
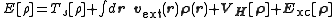
where Ts is the Kohn–Sham kinetic energy
which is expressed in terms of the Kohn–Sham orbitals as
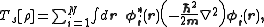
vext is the external potential
acting on the interacting system (at minimum, for a molecular system, the electron-nuclei interaction), VH is the Hartree (or Coulomb) energy,
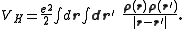
and Exc is the exchange-correlation energy. The Kohn–Sham equations are found by varying the total energy expression with respect to a set of orbitals to yield the Kohn–Sham potential as
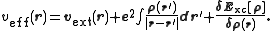
where the last term
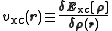
is the exchange-correlation potential. This term, and the corresponding energy expression, are the only unknowns in the Kohn–Sham approach to density functional theory. An approximation that does not vary the orbitals is Harris functional
theory.
The Kohn–Sham orbital energies εi, in general, have little physical meaning (see Koopmans' theorem
). The sum of the orbital energies is related to the total energy as
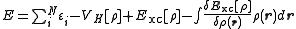
Because the orbital energies are non-unique in the more general restricted open-shell case, this equation only holds true for specific choices of orbital energies (see Koopmans' theorem
).
Quantum chemistry
Quantum chemistry is a branch of chemistry whose primary focus is the application of quantum mechanics in physical models and experiments of chemical systems...
, specifically density functional theory
Density functional theory
Density functional theory is a quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics and chemistry to investigate the electronic structure of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. With this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can be determined by...
, the Kohn–Sham equation is the Schrödinger equation
Schrödinger equation
The Schrödinger equation was formulated in 1926 by Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger. Used in physics , it is an equation that describes how the quantum state of a physical system changes in time....
of a fictitious system (the "Kohn–Sham system") of non-interacting particles (typically electrons) that generate the same density
Electronic density
In quantum mechanics, and in particular quantum chemistry, the electronic density is a measure of the probability of an electron occupying an infinitesimal element of space surrounding any given point. It is a scalar quantity depending upon three spatial variables and is typically denoted as either...
as any given system of interacting particles. The Kohn–Sham equation is defined by a local effective (fictitious) external potential in which the non-interacting particles move, typically denoted as vs(r) or veff(r), called the Kohn–Sham potential. As the particles in the Kohn–Sham system are non-interacting fermions, the Kohn–Sham wavefunction is a single Slater determinant
Slater determinant
In quantum mechanics, a Slater determinant is an expression that describes the wavefunction of a multi-fermionic system that satisfies anti-symmetry requirements and consequently the Pauli exclusion principle by changing sign upon exchange of fermions . It is named for its discoverer, John C...
constructed from a set of orbital
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus...
s that are the lowest energy solutions to
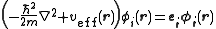
This eigenvalue equation is the typical representation of the Kohn–Sham equations. Here, εi is the orbital energy of the corresponding Kohn–Sham orbital, φi, and the density for an N-particle system is
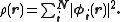
The Kohn–Sham equations are named after Walter Kohn
Walter Kohn
Walter Kohn is an Austrian-born American theoretical physicist.He was awarded, with John Pople, the Nobel Prize in chemistry in 1998. The award recognized their contributions to the understandings of the electronic properties of materials...
and Lu Jeu Sham, who introduced the concept at the University of California, San Diego
University of California, San Diego
The University of California, San Diego, commonly known as UCSD or UC San Diego, is a public research university located in the La Jolla neighborhood of San Diego, California, United States...
in 1965.
Kohn–Sham potential
In density functional theoryDensity functional theory
Density functional theory is a quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics and chemistry to investigate the electronic structure of many-body systems, in particular atoms, molecules, and the condensed phases. With this theory, the properties of a many-electron system can be determined by...
, the total energy of a system is expressed as a functional
Functional (mathematics)
In mathematics, and particularly in functional analysis, a functional is a map from a vector space into its underlying scalar field. In other words, it is a function that takes a vector as its input argument, and returns a scalar...
of the charge density as
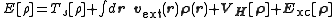
where Ts is the Kohn–Sham kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
which is expressed in terms of the Kohn–Sham orbitals as
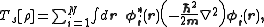
vext is the external potential
Potential energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy stored in a body or in a system due to its position in a force field or due to its configuration. The SI unit of measure for energy and work is the Joule...
acting on the interacting system (at minimum, for a molecular system, the electron-nuclei interaction), VH is the Hartree (or Coulomb) energy,
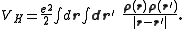
and Exc is the exchange-correlation energy. The Kohn–Sham equations are found by varying the total energy expression with respect to a set of orbitals to yield the Kohn–Sham potential as
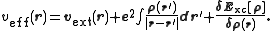
where the last term
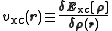
is the exchange-correlation potential. This term, and the corresponding energy expression, are the only unknowns in the Kohn–Sham approach to density functional theory. An approximation that does not vary the orbitals is Harris functional
Harris functional
In computational condensed-matter physics, the Harris energy functional is a non-self-consistent approximation to Kohn-Sham density functional theory...
theory.
The Kohn–Sham orbital energies εi, in general, have little physical meaning (see Koopmans' theorem
Koopmans' theorem
Koopmans' theorem states that in closed-shell Hartree-Fock theory, the first ionization energy of a molecular system is equal to the negative of the orbital energy of the highest occupied molecular orbital...
). The sum of the orbital energies is related to the total energy as
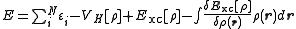
Because the orbital energies are non-unique in the more general restricted open-shell case, this equation only holds true for specific choices of orbital energies (see Koopmans' theorem
Koopmans' theorem
Koopmans' theorem states that in closed-shell Hartree-Fock theory, the first ionization energy of a molecular system is equal to the negative of the orbital energy of the highest occupied molecular orbital...
).

