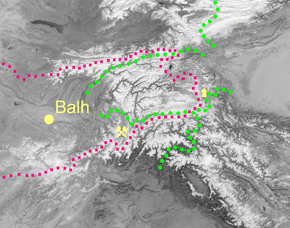
Kingdom of Balhara
Encyclopedia
Fringe theory
A fringe theory is an idea or a collection of ideas that departs significantly from the prevailing or mainstream view in its particular field of study. Examples include ideas that purport to be scientific theories but have little or no scientific support, conspiracy theories, unproven esoteric...
of some Bulgarian scientists (for example: Georgi Bakalov, Petar Dobrev, Ian Mladjov) to have been the earliest known state of the ancient Bulgars
Bulgars
The Bulgars were a semi-nomadic who flourished in the Pontic Steppe and the Volga basin in the 7th century.The Bulgars emerge after the collapse of the Hunnic Empire in the 5th century....
, situated in the upper course of Oxus River (present Amu Darya
Amu Darya
The Amu Darya , also called Oxus and Amu River, is a major river in Central Asia. It is formed by the junction of the Vakhsh and Panj rivers...
), and the foothills and valleys of Hindu Kush
Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range that stretches between central Afghanistan and northern Pakistan. The highest point in the Hindu Kush is Tirich Mir in the Chitral region of Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.It is the westernmost extension of the Pamir Mountains, the Karakoram Range, and is a...
and Pamir Mountains
Pamir Mountains
The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range in Central Asia formed by the junction or knot of the Himalayas, Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, and Hindu Kush ranges. They are among the world’s highest mountains and since Victorian times they have been known as the "Roof of the World" a probable...
(ancient Mount Imeon
Mount Imeon
Mount Imeon is an ancient name for the Central Asian complex of mountain ranges comprising the present Hindu Kush, Pamir and Tian Shan, extending from the Zagros Mountains in the southwest to the Altay Mountains in the northeast, and linked to the Kunlun, Karakoram and Himalayas to the southeast...
). One historian - Dr Peter Dobrev (senior research fellow), places the date of the kingdom around the 12th century BC, while others (from Ashharatsuyts) place the date 7/6th century BC.
Origins of the name
In SanskritSanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
, "Bal" means "strength" and "hara" means "the possessor", thus, "Balhara" means "the possessor of strength" (and so, in that regard also the name of Bulgar could mean "possesor of strength"); another theory is that "Balh" refers to the city of Balkh (Balhara's capital) and that "ar" means "man of", so Bal-hara could mean "man of Balh/Balkh"; consequently "Bulg-ar" could then mean "man of Balkh". The name "Balkan" (mountains) could also come from this connection, instead of the Turkish word for mountain (this is an alternative theory).
History
According to BulgariaBulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
n historian Georgi Bakalov, Bulhi was probably the Armenian name of the ancient Bulgars
Bulgars
The Bulgars were a semi-nomadic who flourished in the Pontic Steppe and the Volga basin in the 7th century.The Bulgars emerge after the collapse of the Hunnic Empire in the 5th century....
. Historiographers in late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages such as Agathias of Myrina
Agathias
Agathias or Agathias Scholasticus , of Myrina , an Aeolian city in western Asia Minor , was a Greek poet and the principal historian of part of the reign of the Roman emperor Justinian I between 552 and 558....
, Theophylact Simocatta
Theophylact Simocatta
Theophylact Simocatta was an early seventh-century Byzantine historiographer, arguably ranking as the last historian of Late Antiquity, writing in the time of Heraclius about the late Emperor Maurice .-Life:His history of the reign of emperor Maurice is in eight books...
, and Michael the Syrian
Michael the Syrian
Michael the Syrian , also known as Michael the Great or Michael Syrus or Michael the Elder, to distinguish him from his nephew, was a patriarch of the Syriac Orthodox Church from 1166 to 1199. He is best known today as the author of the largest medieval Chronicle, which he composed in Syriac...
also identify Mount Imeon as an early homeland of the ancient Bulgars..
A medieval Armenian source that testifies to this is the "Ashharatsuyts" by Anania Shirakatsi.
It was apperently said that the Kingdom was very prosperous and wealthy, trading with other kingdoms and empires (China, Persia, Massegetes), but was conquered and destroyed by a number uncertain forces over the years - probably ancient China, Alexander the Great and various Iranic and Turkic tribes in the vicinity. After the conquest/destruction of the Kingdom of Balhara, the Bulgars (sometime in the 2nd/3rd century AD) migrated west and in the process somehow co-opted into the Hunnic confederacy
Some of them migrated to Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
already BC.
Bakalov cites Byzantine
Byzantine
Byzantine usually refers to the Roman Empire during the Middle Ages.Byzantine may also refer to:* A citizen of the Byzantine Empire, or native Greek during the Middle Ages...
historian Zacharias Rhetor
Zacharias Rhetor
Zacharias of Mytilene , also known as Zacharias Scholasticus or Zacharias Rhetor, was a bishop and ecclesiastical historian....
as saying that the Burgars (presumably also identical to the Bulgars), had towns in the valleys of Northern Caucasus
Caucasus
The Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea...
. They had also the territory along the north coast of Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
east of Axiacus River (Southern Bug)
Southern Bug
The Southern Bug, also called Southern Buh), is a river located in Ukraine. The source of the river is in the west of Ukraine, in the Volyn-Podillia Upland, about 145 km from the Polish border, and flows southeasterly into the Bug Estuary through the southern steppes...
. He concludes that they had migrated to that region from Balhara. In Bakalov's view, the Bulgars established their first state there in 165 AD, a date he arrives at by summing the years of life or reign of all rulers listed in the Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans
Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans
The Nominalia of the Bulgarian khans is a short manuscript containing the names of some early Bulgar rulers, their clans, the year of their ascending to the throne according to the cyclic Bulgar calendar and the length of their rule, including the times of joint rule and civil war...
. The Nominalia claims that the first two rulers lived for 300 and 150 years respectively, which has led earlier historians to ignore these figures. Bakalov, however, is of the opinion that their legendary names should be interpreted as referring to entire dynasties, but the dates themselves are accurate. The Kingdom of Old Great Bulgaria
Old Great Bulgaria
Old Great Bulgaria or Great Bulgaria was а term used by Byzantine historians to refer to Onoguria during the reign of the Bulgar ruler Kubrat in the 7th century north of the Caucasus mountains in the steppe between the Dniester and Lower...
is known to have been established in that area in 632 AD. Among the successors of the latter are the medieval Bulgarian Empire
Bulgarian Empire
Bulgarian Empire is a term used to describe two periods in the medieval history of Bulgaria, during which it acted as a key regional power in Europe in general and in Southeastern Europe in particular, rivalling Byzantium...
and Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria, or Volga–Kama Bolghar, is a historic Bulgar state that existed between the seventh and thirteenth centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama rivers in what is now Russia.-Origin:...
, and present Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
, Tatarstan
Tatarstan
The Republic of Tatarstan is a federal subject of Russia located in the Volga Federal District. Its capital is the city of Kazan, which is one of Russia's largest and most prosperous cities. The republic borders with Kirov, Ulyanovsk, Samara, and Orenburg Oblasts, and with the Mari El, Udmurt,...
, and Chuvashia.
According to the Brockhaus Bilder-Conversations-Lexikon (Band 1. 1837., S. 339-340) - The Bulhi contributed to the ethnogenesis of the present Tajiks in both Afghanistan, Pakistan and Tajikistan[citation needed], and possibly the homonymous ethnic group of Balhara in India.
According to some people, the Armenian geographical atlas ‘Ashharatsuyts’ described the Bulgars as such: The inhabitants of Balhara were called Bulh in the 5th-7th century Armenian geographical atlas ‘Ashharatsuyts’. The atlas describes them as an old settled, artisan and trading nation rather than nomadic tribe, inhabiting the area centered around the ancient major city of Balh
Balkh
Balkh , was an ancient city and centre of Zoroastrianism in what is now northern Afghanistan. Today it is a small town in the province of Balkh, about 20 kilometers northwest of the provincial capital, Mazar-e Sharif, and some south of the Amu Darya. It was one of the major cities of Khorasan...
(Balkh)(which was the capital of Balhara - it was very old - the Arabs called it the "mother of all cities") that comprised roughly present northern Afghanistan and most of Tajikistan. That, though, can't be verified 100%.
Another possible connection between Balhara and the Bulgars is the words by Nasir Khosrow Qubadyani, the famous Persian poet of 11th century, who was born in Qubadyan, a village near Balkh in Afghanistan, says:
Doshvar shavad bange to az khaneh be dehliz
Va asan shavad avaze vey az Balkh be Bulgar
Your voice hardly reaches the corridor from the room
But his song (poem) easily reaches from Balkh to Bulgar
See also
- BulgarsBulgarsThe Bulgars were a semi-nomadic who flourished in the Pontic Steppe and the Volga basin in the 7th century.The Bulgars emerge after the collapse of the Hunnic Empire in the 5th century....
- Old Great BulgariaOld Great BulgariaOld Great Bulgaria or Great Bulgaria was а term used by Byzantine historians to refer to Onoguria during the reign of the Bulgar ruler Kubrat in the 7th century north of the Caucasus mountains in the steppe between the Dniester and Lower...
- Mount ImeonMount ImeonMount Imeon is an ancient name for the Central Asian complex of mountain ranges comprising the present Hindu Kush, Pamir and Tian Shan, extending from the Zagros Mountains in the southwest to the Altay Mountains in the northeast, and linked to the Kunlun, Karakoram and Himalayas to the southeast...
- Bahlikas
- Volga BulgariaVolga BulgariaVolga Bulgaria, or Volga–Kama Bolghar, is a historic Bulgar state that existed between the seventh and thirteenth centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama rivers in what is now Russia.-Origin:...
- First Bulgarian EmpireFirst Bulgarian EmpireThe First Bulgarian Empire was a medieval Bulgarian state founded in the north-eastern Balkans in c. 680 by the Bulgars, uniting with seven South Slavic tribes...
- BalharaBalharaBalhara is a gotra of Jats found in Haryana, Delhi, Punjab and Rajasthan in India. The Balhara gotra exists among both Sikhs and Hindus.-Origin:...
- BulgariaBulgariaBulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...

