
Kifu
Encyclopedia
Kifu is the Japanese
term for a game
record for a game of Go or shogi
. Kifu is traditionally used to record games on a grid diagram, marking the plays on the points by numbers.
This term is originally from China. In China, people named this kind of record "Ch'i-p'u" (Traditional Chinese: 棋譜, Simplified Chinese: 棋谱). The earliest surviving kifu is collected by the ancient book "I Chi" (The Principle of the Go, 弈旨), written by Pan Ku
.
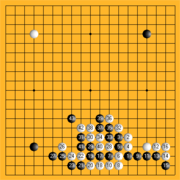 A large corpus
A large corpus
— many thousands of games — of kifu records from the Edo period
has survived. Quite a low proportion was published in book form; strong players used to make their own copies by hand of games to study. This accounts for one feature of the records passed down: they often omit much of the endgame, since for a strong player reconstructing the smaller endgame plays is routine. This explains the survival of some games in different versions, and possible discrepancies in the final margin.
The early Western Go players found the kifu inconvenient, probably because as chess players they were more familiar with algebraic notation
, and because as new players they found it difficult to locate moves. But they quickly discovered the advantages of kifu-style notation—as much as an entire game can be visually displayed in one diagram—and now virtually all Go books and magazines use some modification of the kifu to display games, variations and problems. While a typical piece of chess literature is in algebraic notation punctuated by occasional diagrams, Go literature mostly consists of diagrams with a sequence of plays marked, and prose commentary.
The pioneering European player Oskar Korschelt disliked kifu because nineteenth century kifu always used Chinese numerals, which are indeed difficult to read unless one is familiar with them. Numbering in that style continued until 1945, having been popular in the 1930s on the basis of nationalist feeling in Japan. (Hindu-Arabic numeral
s were also used.) In Japanese Go books, when unoccupied points of the board are mentioned in the commentary, they are usually labelled by hiragana
(in iroha
order) to this day.
The playing-through on a Go board of a game record given as a kifu on a single diagram is still a little taxing for a beginner player, because the next move has to be found. An amateur dan
player would expect to play through a game of normal length in around 20 minutes. A player of professional level would take ten minutes, and could easily sight-read a professional game from the kifu. Stronger players can locate plays more easily because they often know where the next move is likely to be found.
In most games, a small number of plays are at intersections that were previously occupied (this happens, for example, during a ko
fight). Annotations by the side of the kifu give this information, usually in the form '57 at 51' or something comparable. Game records are usually completed by information on the players' ranks, the date and competition data, location, winning player and margin of victory.
Many of the most important games are now available in machine-readable form, using one of a small number of Go file format
s. This has great advantages in terms of ease of playing through games, and lends itself well to database
storage and archival. The common opinion is that playing games through on a board (rather than computer monitor) from a printed record is a qualitatively different experience.
for Go. There are several methods in use, including
Since the Go board is symmetrical with no particular sides, it makes no difference which corner is used as the reference point from which to count coordinates.
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
term for a game
Game
A game is structured playing, usually undertaken for enjoyment and sometimes used as an educational tool. Games are distinct from work, which is usually carried out for remuneration, and from art, which is more often an expression of aesthetic or ideological elements...
record for a game of Go or shogi
Shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a two-player board game in the same family as Western chess, chaturanga, and Chinese Xiangqi, and is the most popular of a family of chess variants native to Japan...
. Kifu is traditionally used to record games on a grid diagram, marking the plays on the points by numbers.
This term is originally from China. In China, people named this kind of record "Ch'i-p'u" (Traditional Chinese: 棋譜, Simplified Chinese: 棋谱). The earliest surviving kifu is collected by the ancient book "I Chi" (The Principle of the Go, 弈旨), written by Pan Ku
Ban Gu
Ban Gu , courtesy name Mengjian , was a 1st century Chinese historian and poet best known for his part in compiling the Book of Han. He also wrote in the main poetic genre of the Han era, a kind of poetry interspersed with prose called fu. Some are anthologized by Xiao Tong in his Selections of...
.

Text corpus
In linguistics, a corpus or text corpus is a large and structured set of texts...
— many thousands of games — of kifu records from the Edo period
Edo period
The , or , is a division of Japanese history which was ruled by the shoguns of the Tokugawa family, running from 1603 to 1868. The political entity of this period was the Tokugawa shogunate....
has survived. Quite a low proportion was published in book form; strong players used to make their own copies by hand of games to study. This accounts for one feature of the records passed down: they often omit much of the endgame, since for a strong player reconstructing the smaller endgame plays is routine. This explains the survival of some games in different versions, and possible discrepancies in the final margin.
The early Western Go players found the kifu inconvenient, probably because as chess players they were more familiar with algebraic notation
Algebraic chess notation
Algebraic notation is a method for recording and describing the moves in a game of chess. It is now standard among all chess organizations and most books, magazines, and newspapers...
, and because as new players they found it difficult to locate moves. But they quickly discovered the advantages of kifu-style notation—as much as an entire game can be visually displayed in one diagram—and now virtually all Go books and magazines use some modification of the kifu to display games, variations and problems. While a typical piece of chess literature is in algebraic notation punctuated by occasional diagrams, Go literature mostly consists of diagrams with a sequence of plays marked, and prose commentary.
The pioneering European player Oskar Korschelt disliked kifu because nineteenth century kifu always used Chinese numerals, which are indeed difficult to read unless one is familiar with them. Numbering in that style continued until 1945, having been popular in the 1930s on the basis of nationalist feeling in Japan. (Hindu-Arabic numeral
Hindu-Arabic numeral system
The Hindu–Arabic numeral system or Hindu numeral system is a positional decimal numeral system developed between the 1st and 5th centuries by Indian mathematicians, adopted by Persian and Arab mathematicians , and spread to the western world...
s were also used.) In Japanese Go books, when unoccupied points of the board are mentioned in the commentary, they are usually labelled by hiragana
Hiragana
is a Japanese syllabary, one basic component of the Japanese writing system, along with katakana, kanji, and the Latin alphabet . Hiragana and katakana are both kana systems, in which each character represents one mora...
(in iroha
Iroha
The is a Japanese poem, probably written in the Heian era . Originally the poem was attributed to the founder of the Shingon Esoteric sect of Buddhism in Japan, Kūkai, but more modern research has found the date of composition to be later in the Heian Period. The first record of its existence...
order) to this day.
The playing-through on a Go board of a game record given as a kifu on a single diagram is still a little taxing for a beginner player, because the next move has to be found. An amateur dan
Go ranks and ratings
Skill in the traditional board game Go is measured by a number of different national, regional and online ranking and rating systems. Traditionally, go rankings have been measured using a system of dan and kyu ranks...
player would expect to play through a game of normal length in around 20 minutes. A player of professional level would take ten minutes, and could easily sight-read a professional game from the kifu. Stronger players can locate plays more easily because they often know where the next move is likely to be found.
In most games, a small number of plays are at intersections that were previously occupied (this happens, for example, during a ko
Rules of Go
This is an in-depth discussion of the rules of go.There has been a certain amount of variation in the rules of go over time, and from place to place. This article discusses those sets of rules broadly similar to the ones currently in use in East Asia. Even among these, there is a degree of...
fight). Annotations by the side of the kifu give this information, usually in the form '57 at 51' or something comparable. Game records are usually completed by information on the players' ranks, the date and competition data, location, winning player and margin of victory.
Many of the most important games are now available in machine-readable form, using one of a small number of Go file format
Go file format
Go file formats are used to record the moves in a game of Go or for demonstrations, game reviews, and tsumego . The most popular file format is SGF. Many Go programs can read, edit, and write this format....
s. This has great advantages in terms of ease of playing through games, and lends itself well to database
Database
A database is an organized collection of data for one or more purposes, usually in digital form. The data are typically organized to model relevant aspects of reality , in a way that supports processes requiring this information...
storage and archival. The common opinion is that playing games through on a board (rather than computer monitor) from a printed record is a qualitatively different experience.
Other notations
There is no other universally-recognised notation comparable to algebraic chess notationAlgebraic chess notation
Algebraic notation is a method for recording and describing the moves in a game of chess. It is now standard among all chess organizations and most books, magazines, and newspapers...
for Go. There are several methods in use, including
- Using chess-like notation so on a 19x19 board points are a-t (j is excluded) for one axis, and 1-19 for the other.
- A similar system using Japanese numeralsJapanese numeralsThe system of Japanese numerals is the system of number names used in the Japanese language. The Japanese numerals in writing are entirely based on the Chinese numerals and the grouping of large numbers follow the Chinese tradition of grouping by 10,000...
instead of letters. - Using numbers for both axes, e.g. 3-4 is on the third row and fourth column from a corner.
- Dmitry Andreev in the 1970s suggested a system where each point is identified from its position relative to all four corners.
Since the Go board is symmetrical with no particular sides, it makes no difference which corner is used as the reference point from which to count coordinates.

