
Keulegan–Carpenter number
Encyclopedia
 |
 |
| The Keulegan–Carpenter number is important for the computation of the wave Ocean surface wave In fluid dynamics, wind waves or, more precisely, wind-generated waves are surface waves that occur on the free surface of oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, and canals or even on small puddles and ponds. They usually result from the wind blowing over a vast enough stretch of fluid surface. Waves in the... forces on offshore platforms Oil platform An oil platform, also referred to as an offshore platform or, somewhat incorrectly, oil rig, is a lаrge structure with facilities to drill wells, to extract and process oil and natural gas, and to temporarily store product until it can be brought to shore for refining and marketing... . |
In fluid dynamics
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
, the Keulegan–Carpenter number, also called the period number, is a dimensionless quantity
Dimensionless quantity
In dimensional analysis, a dimensionless quantity or quantity of dimension one is a quantity without an associated physical dimension. It is thus a "pure" number, and as such always has a dimension of 1. Dimensionless quantities are widely used in mathematics, physics, engineering, economics, and...
describing the relative importance of the drag forces over inertia
Inertia
Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to a change in its state of motion or rest, or the tendency of an object to resist any change in its motion. It is proportional to an object's mass. The principle of inertia is one of the fundamental principles of classical physics which are used to...
forces for bluff objects in an oscillatory
Oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value or between two or more different states. Familiar examples include a swinging pendulum and AC power. The term vibration is sometimes used more narrowly to mean a mechanical oscillation but sometimes...
fluid flow. Or similarly, for objects that oscillate in a fluid at rest. For small Keulegan–Carpenter number inertia dominates, while for large numbers the (turbulence
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...
) drag forces are important.
The Keulegan–Carpenter number KC is defined as:
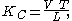
where:
- V is the amplitudeAmplitudeAmplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
of the flow velocityFlow velocityIn fluid dynamics the flow velocity, or velocity field, of a fluid is a vector field which is used to mathematically describe the motion of a fluid...
oscillation (or the amplitude of the object's velocity, in case of an oscillating object), - T is the periodPeriodic functionIn mathematics, a periodic function is a function that repeats its values in regular intervals or periods. The most important examples are the trigonometric functions, which repeat over intervals of length 2π radians. Periodic functions are used throughout science to describe oscillations,...
of the oscillation, and - L is a characteristic length scale of the object, for instance the diameterDiameterIn geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints are on the circle. The diameters are the longest chords of the circle...
for a cylinderCylinder (geometry)A cylinder is one of the most basic curvilinear geometric shapes, the surface formed by the points at a fixed distance from a given line segment, the axis of the cylinder. The solid enclosed by this surface and by two planes perpendicular to the axis is also called a cylinder...
under wave loadingWave loadingWave loading is most commonly the application of a pulsed or wavelike load to a material or object. This is most commonly used in the analysis of piping, ships, or building structures which experience wind, water, or seismic disturbances....
.
A closely related parameter, also often used for sediment transport
Sediment transport
Sediment transport is the movement of solid particles , typically due to a combination of the force of gravity acting on the sediment, and/or the movement of the fluid in which the sediment is entrained...
under water waves, is the displacement parameter δ:
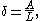
with A the excursion amplitude of fluid particles in oscillatory flow. For sinusoidal motion of the fluid, A is related to V and T as A = VT/(2π), and:
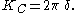
The Keulegan–Carpenter number can be directly related to the Navier–Stokes equations, by looking at characteristic scales
Scale analysis (mathematics)
Scale analysis is a powerful tool used in the mathematical sciences for the simplification of equations with many terms. First the approximate magnitude of individual terms in the equations is determined...
for the acceleration
Acceleration
In physics, acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time. In one dimension, acceleration is the rate at which something speeds up or slows down. However, since velocity is a vector, acceleration describes the rate of change of both the magnitude and the direction of velocity. ...
terms:
- convective acceleration:
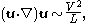
- local acceleration:
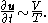
Dividing these two acceleration scales gives the Keulegan–Carpenter number.
A somewhat similar parameter is the Strouhal number
Strouhal number
In dimensional analysis, the Strouhal number is a dimensionless number describing oscillating flow mechanisms. The parameter is named after Vincenc Strouhal, a Czech physicist who experimented in 1878 with wires experiencing vortex shedding and singing in the wind...
, in form equal to the reciprocal of the Keulegan–Carpenter number. The Strouhal number gives the vortex shedding
Vortex shedding
Vortex shedding is an unsteady flow that takes place in special flow velocities . In this flow, vortices are created at the back of the body and detach periodically from either side of the body. See Von Kármán vortex street.Vortex shedding is caused when a fluid flows past a blunt object...
frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
resulting from placing an object in a steady flow, so it describes the flow unsteadiness as a result of an instability of the flow downstream of the object. While the Keulegan–Carpenter number is related to the oscillation frequency of an unsteady flow, into which the object is placed.

