
Scale analysis (mathematics)
Encyclopedia
Scale analysis is a powerful tool used in the mathematical sciences for the simplification of equation
s with many terms. First the approximate magnitude of individual terms in the equations is determined. Then some negligibly small terms may be ignored.
of the Navier–Stokes equations in the vertical coordinate direction of the atmosphere

where R is Earth
radius, Ω is frequency
of rotation of the Earth, g is gravitational acceleration
, φ is latitude ρ is density
of air and ν is kinematic viscosity
of air (we can neglect turbulence in free atmosphere).
In synoptic scale we can expect horizontal velocities about U = 101 m.s−1 and vertical about W = 10−2 m.s−1. Horizontal scale is L = 106 m and vertical scale is H = 104 m. Typical time scale is T = L/U = 105 s. Pressure differences in troposphere are ΔP = 104 Pa and density of air ρ = 100 kg·m−3. Other physical properties are approximately:
Estimates of the different terms in equation (1) can be made using their scales:
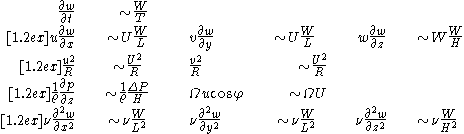
Now we can introduce these scales and their values into equation (1):
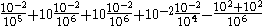

We can see that all terms — except the first and second on the right-hand side — are negligibly small. Thus we can simplify the vertical momentum equation to the hydrostatic equilibrium
equation:

Equation
An equation is a mathematical statement that asserts the equality of two expressions. In modern notation, this is written by placing the expressions on either side of an equals sign , for examplex + 3 = 5\,asserts that x+3 is equal to 5...
s with many terms. First the approximate magnitude of individual terms in the equations is determined. Then some negligibly small terms may be ignored.
Example: vertical momentum in synoptic-scale meteorology
Consider for example the momentum equationPrimitive equations
The primitive equations are a set of nonlinear differential equations that are used to approximate global atmospheric flow and are used in most atmospheric models...
of the Navier–Stokes equations in the vertical coordinate direction of the atmosphere

where R is Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
radius, Ω is frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
of rotation of the Earth, g is gravitational acceleration
Gravitational acceleration
In physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration on an object caused by gravity. Neglecting friction such as air resistance, all small bodies accelerate in a gravitational field at the same rate relative to the center of mass....
, φ is latitude ρ is density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
of air and ν is kinematic viscosity
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
of air (we can neglect turbulence in free atmosphere).
In synoptic scale we can expect horizontal velocities about U = 101 m.s−1 and vertical about W = 10−2 m.s−1. Horizontal scale is L = 106 m and vertical scale is H = 104 m. Typical time scale is T = L/U = 105 s. Pressure differences in troposphere are ΔP = 104 Pa and density of air ρ = 100 kg·m−3. Other physical properties are approximately:
- R = 6.378 × 106 m;
- Ω = 7.292 × 10-5 rad·s−1;
- ν = 1.46 × 10−5 m2·s−1;
- g = 9.81 m·s−2.
Estimates of the different terms in equation (1) can be made using their scales:
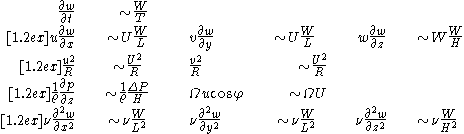
Now we can introduce these scales and their values into equation (1):
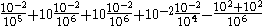

We can see that all terms — except the first and second on the right-hand side — are negligibly small. Thus we can simplify the vertical momentum equation to the hydrostatic equilibrium
Hydrostatic equilibrium
Hydrostatic equilibrium or hydrostatic balance is the condition in fluid mechanics where a volume of a fluid is at rest or at constant velocity. This occurs when compression due to gravity is balanced by a pressure gradient force...
equation:


