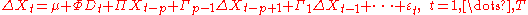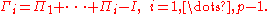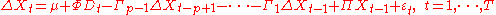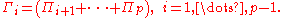Johansen test
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, the Johansen test, named after Søren Johansen, is a procedure for testing cointegration
of several I(1) time series
. This test permits more than one cointegrating relationship so is more generally applicable than the Engle–Granger test which is based on the Dickey–Fuller (or the augmented) test for unit root
s in the residuals from a single (estimated) cointegrating relationship.
There are two types of Johansen test, either with trace or with eigenvalue, and the inferences might be a little bit different. The null hypothesis for the trace test is the number of cointegration vectors r ≤ ?, the null hypothesis for the eigenvalue test is r = ?.
Just like a unit root test, there can be a constant term, a trend term, both, or neither in the model. For a general VAR
(p) model:

There are two possible specifications for error correction: that is, two VECM (vector error correction model
s):
1. The longrun VECM:
2. The transitory VECM:
Be aware that the two are the same. In both VECM,
Inferences are drawn on Π, and they will be the same, so is the explanatory power.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, the Johansen test, named after Søren Johansen, is a procedure for testing cointegration
Cointegration
Cointegration is a statistical property of time series variables. Two or more time series are cointegrated if they share a common stochastic drift.-Introduction:...
of several I(1) time series
Time series
In statistics, signal processing, econometrics and mathematical finance, a time series is a sequence of data points, measured typically at successive times spaced at uniform time intervals. Examples of time series are the daily closing value of the Dow Jones index or the annual flow volume of the...
. This test permits more than one cointegrating relationship so is more generally applicable than the Engle–Granger test which is based on the Dickey–Fuller (or the augmented) test for unit root
Unit root
In time series models in econometrics , a unit root is a feature of processes that evolve through time that can cause problems in statistical inference if it is not adequately dealt with....
s in the residuals from a single (estimated) cointegrating relationship.
There are two types of Johansen test, either with trace or with eigenvalue, and the inferences might be a little bit different. The null hypothesis for the trace test is the number of cointegration vectors r ≤ ?, the null hypothesis for the eigenvalue test is r = ?.
Just like a unit root test, there can be a constant term, a trend term, both, or neither in the model. For a general VAR
Vector autoregression
Vector autoregression is a statistical model used to capture the linear interdependencies among multiple time series. VAR models generalize the univariate autoregression models. All the variables in a VAR are treated symmetrically; each variable has an equation explaining its evolution based on...
(p) model:

There are two possible specifications for error correction: that is, two VECM (vector error correction model
Error correction model
An error correction model is a dynamical system with the characteristics that the deviation of the current state from its long-run relationship will be fed into its short-run dynamics....
s):
1. The longrun VECM:
-
- where
2. The transitory VECM:
-
- where
Be aware that the two are the same. In both VECM,
Inferences are drawn on Π, and they will be the same, so is the explanatory power.