
Isovolumetric contraction
Encyclopedia
Systole (medicine)
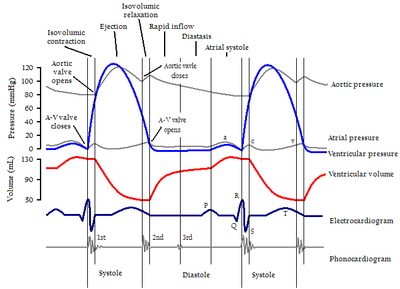
Systole is the contraction of the heart. Used alone, it usually means the contraction of the left ventricle.In all mammals, the heart has 4 chambers. The left and right ventricles pump together. The atria and ventricles pump in sequence...
, during which the ventricles contract with no corresponding volume change.
Description
In a healthy young adult, blood from the venous returnVenous return
Venous return is the rate of blood flow back to the heart. It normally limits cardiac output.Superimposition of the cardiac function curve and venous return curve is used in one hemodynamic model.-Physiology:...
enters the atria and flows to the ventricle
Ventricle (heart)
In the heart, a ventricle is one of two large chambers that collect and expel blood received from an atrium towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The Atria primes the Pump...
s via the opened tricuspid and mitral valves. Atrial contraction rapidly follows, actively pumping about 20% of the returning blood. As diastole
Diastole
Diastole is the period of time when the heart fills with blood after systole . Ventricular diastole is the period during which the ventricles are relaxing, while atrial diastole is the period during which the atria are relaxing...
ends, the ventricles start depolarizing and, while ventricular pressure starts to rise due to contraction, the atrioventricular valves close, so as to prevent back flow to the atria. At this stage, which corresponds to the R peak or the QRS complex seen on an ECG, the aortic and pulmonary valves are also closed. The net result of this situation is that, while contraction causes ventricular pressure to rise sharply, there is no overall change in volume because of the closed valves. The isovolumetric contraction lasts for about 0.03 s, but this short period of time is enough to build up a sufficiently high pressure that will eventually overcome that of the aorta
Aorta
The aorta is the largest artery in the body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it branches off into two smaller arteries...
and the pulmonary trunk upon opening of the semilunar valves, therefore allowing the correct unidirectional flow of blood.
Etymology
The word contains the suffix iso-, derived from the Ancient GreekAncient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
ἴσος (ísos), meaning equal. Therefore, an isovolumetric contraction is one in which the volume of fluid remains constant.

