Isoptic
Encyclopedia
In the geometry
of curve
s, an isoptic is the set of points for which two tangent
s of a given curve meet at a given angle
. The orthoptic is the isoptic whose given angle is a right angle.
Without an invertible Gauss map
, an explicit general form is impossible because of the difficulty knowing which points on the given curve pair up.
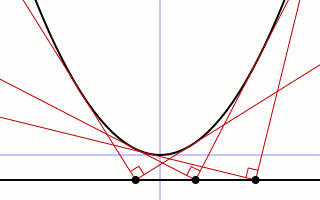
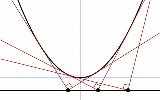
Take as given the parabola
(t,t²) and angle 90°. Find, first, τ such that the tangents at t and τ are orthogonal: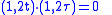
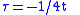
Then find (x,y) such that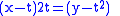 and
and 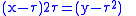
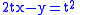 and
and 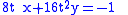
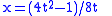 and
and 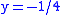
so the orthoptic of a parabola is its directrix.
The orthoptic of an ellipse is the director circle
.
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
of curve
Curve
In mathematics, a curve is, generally speaking, an object similar to a line but which is not required to be straight...
s, an isoptic is the set of points for which two tangent
Tangent
In geometry, the tangent line to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. More precisely, a straight line is said to be a tangent of a curve at a point on the curve if the line passes through the point on the curve and has slope where f...
s of a given curve meet at a given angle
Angle
In geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle.Angles are usually presumed to be in a Euclidean plane with the circle taken for standard with regard to direction. In fact, an angle is frequently viewed as a measure of an circular arc...
. The orthoptic is the isoptic whose given angle is a right angle.
Without an invertible Gauss map
Gauss map
In differential geometry, the Gauss map maps a surface in Euclidean space R3 to the unit sphere S2. Namely, given a surface X lying in R3, the Gauss map is a continuous map N: X → S2 such that N is a unit vector orthogonal to X at p, namely the normal vector to X at p.The Gauss map can be defined...
, an explicit general form is impossible because of the difficulty knowing which points on the given curve pair up.
Example

Take as given the parabola
Parabola
In mathematics, the parabola is a conic section, the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to a generating straight line of that surface...
(t,t²) and angle 90°. Find, first, τ such that the tangents at t and τ are orthogonal:
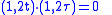
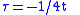
Then find (x,y) such that
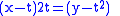 and
and 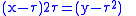
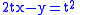 and
and 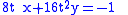
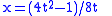 and
and 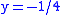
so the orthoptic of a parabola is its directrix.
The orthoptic of an ellipse is the director circle
Director circle
In geometry, the director circle of an ellipse or hyperbola is a circle formed by the points where two perpendicular tangent lines to the curve cross....
.

