
Isodynamic point
Encyclopedia
Euclidean geometry
Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to the Alexandrian Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry: the Elements. Euclid's method consists in assuming a small set of intuitively appealing axioms, and deducing many other propositions from these...
, every triangle
Triangle
A triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted ....
has two isodynamic points, usually denoted as
 and
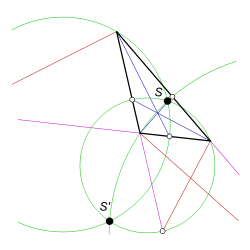
and  . These points are the common intersection points of the three circles of Apollonius
. These points are the common intersection points of the three circles of ApolloniusCircles of Apollonius
The term circle of Apollonius is used to describe several types of circles associated with Apollonius of Perga, a renowned Greek geometer. Most of these circles are found in planar Euclidean geometry, but analogs have been defined on other surfaces; for example, counterparts on the surface of a...
associated with the triangle; hence, the line through these points is the common radical axis
Radical axis
The radical axis of two circles is the locus of points at which tangents drawn to both circles have the same length. For any point P on the radical axis, there is a unique circle centered on P that intersects both circles at right angles ; conversely, the center of any circle that cuts both...
for these circles. The centers of these circles are collinear; they all fall on the Lemoine line
Circles of Apollonius
The term circle of Apollonius is used to describe several types of circles associated with Apollonius of Perga, a renowned Greek geometer. Most of these circles are found in planar Euclidean geometry, but analogs have been defined on other surfaces; for example, counterparts on the surface of a...
, which is perpendicular to the radical axis defined by the isodynamic points.
The isodynamic points have other interesting geometric properties, e.g.,
- Inversion with respect to an isodynamic point transforms the original triangle into an equilateralEquilateralIn geometry, an equilateral polygon is a polygon which has all sides of the same length.For instance, an equilateral triangle is a triangle of equal edge lengths...
triangleTriangleA triangle is one of the basic shapes of geometry: a polygon with three corners or vertices and three sides or edges which are line segments. A triangle with vertices A, B, and C is denoted ....
.
- The pedal trianglePedal triangleIn geometry, a pedal triangle is obtained by projecting a point onto the sides of a triangle.More specifically, consider a triangle ABC, and a point P that is not one of the vertices A, B, C. Drop perpendiculars from P to the three sides of the triangle...
of an isodynamic point is also equilateralEquilateralIn geometry, an equilateral polygon is a polygon which has all sides of the same length.For instance, an equilateral triangle is a triangle of equal edge lengths...
.

