
Ion cyclotron resonance
Encyclopedia
Ion cyclotron resonance is a phenomenon related to the movement of ions in a magnetic field
. It is used for accelerating ions in a cyclotron
, and for measuring the masses of an ionized analyte in mass spectrometry
, particularly with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance
mass spectrometers. It can also be used to follow the kinetics of chemical reactions
in a dilute gas mixture, provided these involve charged species.
. The circular motion may be superimposed with a uniform axial motion, resulting in a helix
, or with a uniform motion perpendicular to the field, e.g., in the presence of an electrical or gravitational field, resulting in a cycloid
. The angular frequency
(ω = 2π f
) of this cyclotron motion for a given magnetic field strength B is given (in SI
units) by
 .
.
where z is the algebraic number of positive or negative charges of the ion, e is the elementary charge
and m is the mass of the ion.
The formula above means that an electric excitation signal having a frequency f will resonate with ions having a mass-to-charge ratio m/z given by:
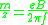 .
.
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
. It is used for accelerating ions in a cyclotron
Cyclotron
In technology, a cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator. In physics, the cyclotron frequency or gyrofrequency is the frequency of a charged particle moving perpendicularly to the direction of a uniform magnetic field, i.e. a magnetic field of constant magnitude and direction...
, and for measuring the masses of an ionized analyte in mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
, particularly with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance
Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance
Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry, also known as Fourier transform mass spectrometry, is a type of mass analyzer for determining the mass-to-charge ratio of ions based on the cyclotron frequency of the ions in a fixed magnetic field...
mass spectrometers. It can also be used to follow the kinetics of chemical reactions
Chemical kinetics
Chemical kinetics, also known as reaction kinetics, is the study of rates of chemical processes. Chemical kinetics includes investigations of how different experimental conditions can influence the speed of a chemical reaction and yield information about the reaction's mechanism and transition...
in a dilute gas mixture, provided these involve charged species.
Definition of the resonant frequency
An ion in a static and uniform magnetic field will move in a circle due to the Lorentz forceLorentz force
In physics, the Lorentz force is the force on a point charge due to electromagnetic fields. It is given by the following equation in terms of the electric and magnetic fields:...
. The circular motion may be superimposed with a uniform axial motion, resulting in a helix
Helix
A helix is a type of smooth space curve, i.e. a curve in three-dimensional space. It has the property that the tangent line at any point makes a constant angle with a fixed line called the axis. Examples of helixes are coil springs and the handrails of spiral staircases. A "filled-in" helix – for...
, or with a uniform motion perpendicular to the field, e.g., in the presence of an electrical or gravitational field, resulting in a cycloid
Cycloid
A cycloid is the curve traced by a point on the rim of a circular wheel as the wheel rolls along a straight line.It is an example of a roulette, a curve generated by a curve rolling on another curve....
. The angular frequency
Angular frequency
In physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity...
(ω = 2π f
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
) of this cyclotron motion for a given magnetic field strength B is given (in SI
Si
Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
units) by
 .
.where z is the algebraic number of positive or negative charges of the ion, e is the elementary charge
Elementary charge
The elementary charge, usually denoted as e, is the electric charge carried by a single proton, or equivalently, the absolute value of the electric charge carried by a single electron. This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constant. To avoid confusion over its sign, e is sometimes called...
and m is the mass of the ion.
The formula above means that an electric excitation signal having a frequency f will resonate with ions having a mass-to-charge ratio m/z given by:
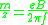 .
.See also
- Electron cyclotron resonanceElectron cyclotron resonanceElectron cyclotron resonance is a phenomenon observed both in plasma physics and condensed matter physics. An electron in a static and uniform magnetic field will move in a circle due to the Lorentz force...
- CyclotronCyclotronIn technology, a cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator. In physics, the cyclotron frequency or gyrofrequency is the frequency of a charged particle moving perpendicularly to the direction of a uniform magnetic field, i.e. a magnetic field of constant magnitude and direction...
- Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonanceFourier transform ion cyclotron resonanceFourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry, also known as Fourier transform mass spectrometry, is a type of mass analyzer for determining the mass-to-charge ratio of ions based on the cyclotron frequency of the ions in a fixed magnetic field...

