
Interferon type I
Encyclopedia
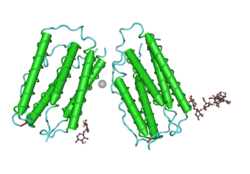
Interferon
Interferons are proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of pathogens—such as viruses, bacteria, or parasites—or tumor cells. They allow communication between cells to trigger the protective defenses of the immune system that eradicate pathogens or tumors.IFNs belong to...
s comprise a vast and growing group of IFN proteins.
All type I IFNs bind to a specific cell surface receptor complex known as the IFN-α receptor (IFNAR
Interferon-alpha/beta receptor
The interferon-α/β receptor is a receptor which binds type I interferons including interferon-α and -β. It is a heteromeric receptor composed of one chain with two subunits referred to as IFNAR1 and IFNAR2. It is a cell surface receptor. Binding of cytokine follows a JAK-STAT signaling pathway...
) that consists of IFNAR1
IFNAR1
Interferon-alpha/beta receptor alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNAR1 gene.-Interactions:IFNAR1 has been shown to interact with STAT2, Tyrosine kinase 2 and PRMT1.-Further reading:...
and IFNAR2
IFNAR2
Interferon-alpha/beta receptor beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNAR2 gene.-Interactions:IFNAR2 has been shown to interact with STAT2, STAT1, GNB2L1 and IFNA2.-Further reading:...
chains.
Homologous molecules to type I IFNs are found in many species, including all mammals, and some have been identified in birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish species.
Mammalian types
The mammalian types are designated IFN-α (alpha), IFN-β (beta), IFN-κ (kappa), IFN-δ (delta), IFN-ε (epsilon), IFN-τ (tau), IFN-ω (omega), and IFN-ζ (zeta, also known as limitin).IFN-α
The IFN-α proteins are produced by leukocytes. They are mainly involved in innate immune response against viral infection. They come in 14 subtypes that are called IFNA1IFNA1
Interferon alpha-1/13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNA1 gene.-Further reading:...
, IFNA2
IFNA2
Interferon alpha-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNA2 gene.-Further reading:...
, IFNA4
IFNA4
Interferon alpha-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNA4 gene.-Further reading:...
, IFNA5
IFNA5
Interferon alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNA5 gene.-Further reading:...
, IFNA6
IFNA6
Interferon alpha-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNA6 gene.-Further reading:...
, IFNA7
IFNA7
Interferon alpha-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNA7 gene.-Further reading:...
, IFNA8
IFNA8
Interferon alpha-8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNA8 gene.-Further reading:...
, IFNA10
IFNA10
Interferon alpha-10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNA10 gene.-Further reading:...
, IFNA13
IFNA13
Interferon alpha-1/13, also known as IFN-alpha-1/13, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNA1 and IFNA13 genes.-Further reading:IFNA13 is an interferon gene....
, IFNA14
IFNA14
Interferon alpha-14 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNA14 gene.-Further reading:...
, IFNA16
IFNA16
Interferon alpha-16, also known as IFN-alpha-16, is a protein that in humans is encoded by theIFNA16 gene....
, IFNA17
IFNA17
Interferon alpha-17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNA17 gene.-Further reading:...
, IFNA21
IFNA21
Interferon alpha-21 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNA21 gene.-Further reading:...
. These genes for these IFN-α molecules are found together in a cluster on chromosome 9.
IFN-α is also made synthetically as medication
Medication
A pharmaceutical drug, also referred to as medicine, medication or medicament, can be loosely defined as any chemical substance intended for use in the medical diagnosis, cure, treatment, or prevention of disease.- Classification :...
. Types are:
- Pegylated interferon alfa-2a
- Pegylated interferon alfa-2b
IFN-β
The IFN-β proteins are produced in large quantities by fibroblasts. They have antiviral activity which is mainly involved in innate immune response. Two types of IFN-β have been described, IFN-β1 (IFNB1IFNB1
Interferon beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNB1 gene.-Further reading:...
) and IFN-β3 (IFNB3) (a gene designated IFN-β2 is actually IL-6). IFN-β1 is used as a treatment for multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory disease in which the fatty myelin sheaths around the axons of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to demyelination and scarring as well as a broad spectrum of signs and symptoms...
as it reduces the relapse rate.
IFN-ε, –κ, -τ, -δ, and –ζ
IFN-ε, –κ, -τ, and –ζ appear, at this time, to come in a single isoform in humans, IFNKIFNK
Interferon kappa, also known as IFN-kappa, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNK gene.- Function :IFN-kappa is a member of the type I interferon family. Type I interferons are a group of related glycoproteins that play an important role in host defenses against viral infections...
. Only ruminants encode IFN-τ, a variant of IFN-ω. So far, IFN-ζ is found only in mice, while a structural homolog, IFN-δ is found in a diverse array of non-primate and non-rodent placental mammals. Most but not all placental mammals encode functional IFN-ε and IFN-κ genes.
IFN-ω
IFN-ω, although having only one functional form described to date (IFNW1IFNW1
Interferon omega-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFNW1 gene.-Further reading:...
), has several pseudogenes: , , , , , , and in humans. Many non-primate placental mammals express multiple IFN-ω subtypes
IFN-ν
This subtype of Type I IFN was recently described as a pseudogene in human, but potentially functional in the domestic cat genome. In all other genomes of non-feline placental mammals, IFN-ν is a pseudogene; in some species, the pseudogene is well preserved, while in others, it is badly mutilated or is undetectable. Moreover, in the cat genome, the IFN-ν promoter is deleteriously mutated. It is likely that the IFN-ν gene family was rendered useless prior to mammalian diversification. Its presence on the edge of the Type I IFN locus in mammals may have shielded it from obliteration, allowing its detection.Sources and functions
IFN-α and IFN-β are secreted by many cell types including lymphocytes (NK cells, B-cells and T-cells), macrophages, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, osteoblasts and others. They stimulate both macrophageMacrophage
Macrophages are cells produced by the differentiation of monocytes in tissues. Human macrophages are about in diameter. Monocytes and macrophages are phagocytes. Macrophages function in both non-specific defense as well as help initiate specific defense mechanisms of vertebrate animals...
s and NK cells to elicit an anti-viral response, and are also active against tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
s. Recently, plasmacytoid dendritic cells have been identified as being the most potent producers of type I IFNs in response to antigen, and have thus been coined natural IFN producing cells.
IFN-ω is released by leukocytes at the site of viral infection or tumors.
IFN-α acts as a pyrogenic factor by altering the activity of thermosensitive neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
s in the hypothalamus
Hypothalamus
The Hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions...
thus causing fever. It does this by binding to opioid receptor
Opioid receptor
Opioid receptors are a group of G protein-coupled receptors with opioids as ligands. The endogenous opioids are dynorphins, enkephalins, endorphins, endomorphins and nociceptin. The opioid receptors are ~40% identical to somatostatin receptors...
s and eliciting the release of prostaglandin
Prostaglandin
A prostaglandin is any member of a group of lipid compounds that are derived enzymatically from fatty acids and have important functions in the animal body. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring....
-E2 (PGE2).
A similar mechanism is used by IFN-α to reduce pain; IFN-α interacts with the μ-opioid receptor to act as an analgesic
Analgesic
An analgesic is any member of the group of drugs used to relieve pain . The word analgesic derives from Greek an- and algos ....
.
Non-mammalian types
Avian Type I IFNs have been characterized and preliminarily assigned to subtypes (IFN I, IFN II, and IFN III), but their classification into subtypes should await a more extensive characterization of avian genomes.Functional lizard Type I IFNs can be found in lizard genome databases.
Turtle Type I IFNs have been purified (references from 1970s needed). They resemble mammalian homologs.
The existence of amphibian Type I IFNs have been inferred by the discovery of the genes encoding their receptor chains. They have not yet been purified, or their genes cloned.
Piscine (bony fish) Type I IFN has been cloned in several teleost species. With few exceptions, and in stark contrast to avian and especially mammalian IFNs, they are present as single genes (multiple genes are however seen in polyploid fish genomes, possibly arising from whole-genome duplication). Unlike amniote IFN genes, piscine Type I IFN genes contain introns, in similar positions as do their orthologs, certain interleukins.

