
Incomplete markets
Encyclopedia
In economics, incomplete markets refers to markets in which the number of Arrow–Debreu securities is less than the number of states of nature . In contrast with complete market
s, this shortage of securities will likely restrict individuals from transferring the desired level of wealth among states.
An Arrow security purchased or sold at date t is a contract promising to deliver one unit of income in one of the possible contingencies which can occur at date t + 1. If at each date-event there exists a complete set of such contracts, one for each contingency that can occur at the following date, individuals will trade these contracts in order insure against future risks, targeting a desirable and budget feasible level of consumption in each state (i.e. consumption smoothing
). In most set ups when these contracts are not available, optimal risk sharing between agents
will not be possible. For this scenario, agents (homeowners, workers, firms, investors, etc.) will lack the instruments to insure against future risks such as employment status, health, labor income, prices, among others.
environment. Their attitudes toward risk, the production possibility set, and the set of available trades determine the equilibrium quantities and prices of assets that are traded. In an "idealized" representation agents are assumed to have costless contractual enforcement and perfect knowledge of future states and their likelihood. With a complete set of state contingent claims (also known as Arrow–Debreu securities) agents can trade these securities to hedge against undesirable or bad outcomes.
When a market is incomplete, it typically fails to make the optimal allocation of assets. This is, the First Welfare Theorem no longer holds. The competitive equilibrium in an Incomplete Market is generally constrained suboptimal. The notion of constraint suboptimality was formalized by Geanakoplos
and Polemarchakis (1986) .
and insurance
markets, markets remain incomplete. While several contingent claims are traded routinely against many states such as insurance policies, futures
, financial option
s, among others, the set of outcomes is far greater than the set of claims.
In practice the idea of a state contingent security for every possible realization of nature seems unrealistic. For example, if the economy lacks the institutions to guarantee that the contracts are enforced, it is unlikely that agents will either sell or buy these securities.
Another common way to motivate the absence of state contingent securities is asymmetric information
between agents. For example, the realization of labor income for a given individual is private information and it cannot be known without cost by anyone else. If an insurance company cannot verify the individual's labor income, the former would always have the incentive to claim a low realization of income and the market would collapse.
is crucial to explain the counterfactual predictions of the standard Complete Market models. The most notable example is the equity premium puzzle
Mehra and Prescott (1985) , where the Complete Market model failed to explain the historical high equity premium and low risk-free rate.
Along with the Equity premium puzzle other counterfactual implications of the Complete Market model are related to the empirical observations concerning individuals’ consumption, wealth and market transactions. For example, in a Complete Market framework, given that agents can fully insure against idiosyncratic risks, each individual’s consumption must fluctuate as much as anyone else’s, and the relative position in terms wealth distribution of an individual should not vary much over time. The empirical evidence suggests otherwise. Further, the individual consumptions are not highly correlated which each other and wealth holdings are very volatile .
In the first approach, the economic models take as given the institutions and arrangements observed in actual economies. This approach has two advantages. First the structure of the model is similar to that of the Arrow–Debreu model to make it amenable to the powerful techniques of analysis developed for that framework. Second it is easy to compare model allocations with their empirical counterpart. Among the first papers using this approach, Diamond (1967) focused directly on the “realistic” market structure consisting of the stock and bond markets.
The other set of models explicitly account for the frictions that could prevent full insurance, but derive the optimal risk-sharing endogenously. This literature has focused on information frictions. Risk sharing in private information models with asset accumulation and enforcement frictions. The advantage of this approach is that market incompleteness and the available state contingent claims respond to the economic environment, which makes the model appealing for policy experiments since is less vulnerable to the Lucas critique
.
Before the realization of the uncertainty, the two agents can trade the state contingent securities. In equilibrium, the two Arrow-Debreu securities have the same price and the allocation is as follows:
The main outcome in this economy is that both Robinson and Jane will end up with 0.5 units of wealth independently of the state of nature that is realized.
If the market is incomplete, meaning one or both of the securities are not available for trade, the two agents can't trade to hedge against a bad realization of nature and thus remain exposed to the possibility of the undesirable outcome of having zero wealth. In fact, with certainty, one of the agents will be 'rich' and the other 'poor'.
This example is an extreme case of market incompleteness. In practice, agents do have some type of savings or insurance instrument. The main point here is to illustrate the potential welfare losses that can arise if markets are incomplete.
Complete market
In economics, a complete market is one in which the complete set of possible gambles on future states-of-the-world can be constructed with existing assets without friction. Every agent is able to exchange every good, directly or indirectly, with every other agent without transaction costs...
s, this shortage of securities will likely restrict individuals from transferring the desired level of wealth among states.
An Arrow security purchased or sold at date t is a contract promising to deliver one unit of income in one of the possible contingencies which can occur at date t + 1. If at each date-event there exists a complete set of such contracts, one for each contingency that can occur at the following date, individuals will trade these contracts in order insure against future risks, targeting a desirable and budget feasible level of consumption in each state (i.e. consumption smoothing
Consumption smoothing
Consumption smoothing is the economic concept used to express the desire of people for having a stable path of consumption.Since Milton Friedman's permanent income theory and Modigliani and Brumberg life-cycle model, the idea that agents prefer a stable path of consumption has been widely accepted...
). In most set ups when these contracts are not available, optimal risk sharing between agents
Agent (economics)
In economics, an agent is an actor and decision maker in a model. Typically, every agent makes decisions by solving a well or ill defined optimization/choice problem. The term agent can also be seen as equivalent to player in game theory....
will not be possible. For this scenario, agents (homeowners, workers, firms, investors, etc.) will lack the instruments to insure against future risks such as employment status, health, labor income, prices, among others.
Markets, Securities and Market Incompleteness
In a competitive market, each agent makes intertemporal choices in a stochasticStochastic
Stochastic refers to systems whose behaviour is intrinsically non-deterministic. A stochastic process is one whose behavior is non-deterministic, in that a system's subsequent state is determined both by the process's predictable actions and by a random element. However, according to M. Kac and E...
environment. Their attitudes toward risk, the production possibility set, and the set of available trades determine the equilibrium quantities and prices of assets that are traded. In an "idealized" representation agents are assumed to have costless contractual enforcement and perfect knowledge of future states and their likelihood. With a complete set of state contingent claims (also known as Arrow–Debreu securities) agents can trade these securities to hedge against undesirable or bad outcomes.
When a market is incomplete, it typically fails to make the optimal allocation of assets. This is, the First Welfare Theorem no longer holds. The competitive equilibrium in an Incomplete Market is generally constrained suboptimal. The notion of constraint suboptimality was formalized by Geanakoplos
John Geanakoplos
John Geanakoplos is the James Tobin Professor of Economics at Yale University. Before the Late-2000s financial crisis, he was known primarily for his contributions to General equilibrium theory, particularly Incomplete markets general equilibrium theory...
and Polemarchakis (1986) .
Possible Reasons for Market Incompleteness
Despite the latest ongoing innovation in financialFINANCIAL
FINANCIAL is the weekly English-language newspaper with offices in Tbilisi, Georgia and Kiev, Ukraine. Published by Intelligence Group LLC, FINANCIAL is focused on opinion leaders and top business decision-makers; It's about world’s largest companies, investing, careers, and small business. It is...
and insurance
Insurance
In law and economics, insurance is a form of risk management primarily used to hedge against the risk of a contingent, uncertain loss. Insurance is defined as the equitable transfer of the risk of a loss, from one entity to another, in exchange for payment. An insurer is a company selling the...
markets, markets remain incomplete. While several contingent claims are traded routinely against many states such as insurance policies, futures
Futures contract
In finance, a futures contract is a standardized contract between two parties to exchange a specified asset of standardized quantity and quality for a price agreed today with delivery occurring at a specified future date, the delivery date. The contracts are traded on a futures exchange...
, financial option
Option (finance)
In finance, an option is a derivative financial instrument that specifies a contract between two parties for a future transaction on an asset at a reference price. The buyer of the option gains the right, but not the obligation, to engage in that transaction, while the seller incurs the...
s, among others, the set of outcomes is far greater than the set of claims.
In practice the idea of a state contingent security for every possible realization of nature seems unrealistic. For example, if the economy lacks the institutions to guarantee that the contracts are enforced, it is unlikely that agents will either sell or buy these securities.
Another common way to motivate the absence of state contingent securities is asymmetric information
Information asymmetry
In economics and contract theory, information asymmetry deals with the study of decisions in transactions where one party has more or better information than the other. This creates an imbalance of power in transactions which can sometimes cause the transactions to go awry, a kind of market failure...
between agents. For example, the realization of labor income for a given individual is private information and it cannot be known without cost by anyone else. If an insurance company cannot verify the individual's labor income, the former would always have the incentive to claim a low realization of income and the market would collapse.
The Failure of the Standard Complete Markets Model
Many authors have argued that modeling incomplete markets and other sorts of financial frictionsFrictionless market
A Frictionless market is a financial market without transaction costs. Friction is a type of market incompleteness. Every complete market is frictionless, but the converse does not hold. In a frictionless market the solvency cone is the halfspace normal to the unique price vector. The...
is crucial to explain the counterfactual predictions of the standard Complete Market models. The most notable example is the equity premium puzzle
Equity premium puzzle
The equity premium puzzle is a term coined in 1985 by economists Rajnish Mehra and Edward C. Prescott. It is based on the observation that in order to reconcile the much higher returns of stocks compared to government bonds in the United States, individuals must have implausibly high risk aversion...
Mehra and Prescott (1985) , where the Complete Market model failed to explain the historical high equity premium and low risk-free rate.
Along with the Equity premium puzzle other counterfactual implications of the Complete Market model are related to the empirical observations concerning individuals’ consumption, wealth and market transactions. For example, in a Complete Market framework, given that agents can fully insure against idiosyncratic risks, each individual’s consumption must fluctuate as much as anyone else’s, and the relative position in terms wealth distribution of an individual should not vary much over time. The empirical evidence suggests otherwise. Further, the individual consumptions are not highly correlated which each other and wealth holdings are very volatile .
Modeling Market Incompleteness
In the economic and financial literature, a significant effort has been made in recent years to part from the setting of Complete Markets. Market incompleteness is modeled as an exogenous institutional structure or as an endogenous process.In the first approach, the economic models take as given the institutions and arrangements observed in actual economies. This approach has two advantages. First the structure of the model is similar to that of the Arrow–Debreu model to make it amenable to the powerful techniques of analysis developed for that framework. Second it is easy to compare model allocations with their empirical counterpart. Among the first papers using this approach, Diamond (1967) focused directly on the “realistic” market structure consisting of the stock and bond markets.
The other set of models explicitly account for the frictions that could prevent full insurance, but derive the optimal risk-sharing endogenously. This literature has focused on information frictions. Risk sharing in private information models with asset accumulation and enforcement frictions. The advantage of this approach is that market incompleteness and the available state contingent claims respond to the economic environment, which makes the model appealing for policy experiments since is less vulnerable to the Lucas critique
Lucas critique
The Lucas critique, named for Robert Lucas′ work on macroeconomic policymaking, argues that it is naïve to try to predict the effects of a change in economic policy entirely on the basis of relationships observed in historical data, especially highly aggregated historical data.The basic idea...
.
An Example of Complete vs. Incomplete Markets
Suppose there is an economy with two agents (Robinson and Jane) with identical log utility functions. There are two equally likely states of nature. If state 1 is realized, Robinson is endowed with 1 unit of wealth and Jane with 0. In state 2, Robinson gets 0 while Jane receives 1 unit of wealth. With Complete Markets there are two state contingent claims: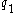 pays 1 unit in state 1 and 0 otherwise.
pays 1 unit in state 1 and 0 otherwise.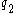 pays 1 unit in state 2 and 0 in state 1.
pays 1 unit in state 2 and 0 in state 1.
Before the realization of the uncertainty, the two agents can trade the state contingent securities. In equilibrium, the two Arrow-Debreu securities have the same price and the allocation is as follows:
- Robinson buys 0.5 of
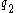 and sells 0.5 of
and sells 0.5 of  .
. - Jane buys 0.5 of
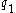 and sells 0.5 of
and sells 0.5 of 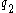 .
.
The main outcome in this economy is that both Robinson and Jane will end up with 0.5 units of wealth independently of the state of nature that is realized.
If the market is incomplete, meaning one or both of the securities are not available for trade, the two agents can't trade to hedge against a bad realization of nature and thus remain exposed to the possibility of the undesirable outcome of having zero wealth. In fact, with certainty, one of the agents will be 'rich' and the other 'poor'.
This example is an extreme case of market incompleteness. In practice, agents do have some type of savings or insurance instrument. The main point here is to illustrate the potential welfare losses that can arise if markets are incomplete.

