
Consumption smoothing
Encyclopedia
Consumption smoothing is the economic concept used to express the desire of people for having a stable path of consumption.
Since Milton Friedman
's permanent income theory
(1956) and Modigliani
and Brumberg (1954) life-cycle model
, the idea that agents prefer a stable path of consumption has been widely accepted. This idea came to replace the perception that people had a marginal propensity to consume
and therefore current consumption was tied to current income.
Friedman's theory argues that consumption is linked to the permanent income of agents. Thus for example, when income is affected by transitory shocks, agents' consumption should not change since they can use savings or borrowing to adjust. This theory assumes that agents are able to finance consumption with earning that are not yet generated, thus, it assumes perfect capital markets. Empirical evidence shows that liquidity constraint
is one of the main reasons of why it is so difficult to observe consumption smoothing in the data.
Agent's choose the consumption path that maximize:
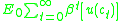
Subject to a sequence of budget constraints:
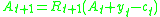
The first order necessary condition in this case will be:

By assuming that we obtain, for the previous
we obtain, for the previous
equation:
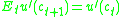
Which, due to the concavity of the utility function, implies:
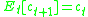
Thus, rational agents would expect to achieve the same consumption in every
period.
Hall also showed that for a quadratic utility function and a stationary
process for income, the optimal consumption is equal to:

This expression shows that agents choose to consume a fraction of their
present discounted value of their human and financial wealth.
. The data used are US National Income and Product Accounts (NIPA) quarterly from 1948 to 1977. For the analysis the author does not consider the consumption of durable goods. Although Hall argues to find some evidence of consumption smoothing it is done for a modified version. Also there is some econometric concerns around his finding.
Wilcox (1989) argue that liquidity constraint is the reason for the consumption smoothing not to hold in the data. Zeldes (1989) follows the same argument and finds that poor household's consumption is correlated with contemporaneous income while rich household is not.
Since Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman was an American economist, statistician, academic, and author who taught at the University of Chicago for more than three decades...
's permanent income theory
Permanent income hypothesis
The permanent income hypothesis is a theory of consumption that was developed by the American economist Milton Friedman. In its simplest form, the hypothesis states that the choices made by consumers regarding their consumption patterns are determined not by current income but by their longer-term...
(1956) and Modigliani
Modigliani
Modigliani may refer to:* Amedeo Modigliani , painter and sculptor** Modigliani, a 2004 biographical film about the painter and sculptor* Elio Modigliani , anthropologist, zoologist, and plant collector...
and Brumberg (1954) life-cycle model
Intertemporal consumption
Economic theories of intertemporal consumption seek to explain people's preferences in relation to consumption and saving over the course of their life...
, the idea that agents prefer a stable path of consumption has been widely accepted. This idea came to replace the perception that people had a marginal propensity to consume
Marginal propensity to consume
In economics, the marginal propensity to consume is an empirical metric that quantifies induced consumption, the concept that the increase in personal consumer spending occurs with an increase in disposable income...
and therefore current consumption was tied to current income.
Friedman's theory argues that consumption is linked to the permanent income of agents. Thus for example, when income is affected by transitory shocks, agents' consumption should not change since they can use savings or borrowing to adjust. This theory assumes that agents are able to finance consumption with earning that are not yet generated, thus, it assumes perfect capital markets. Empirical evidence shows that liquidity constraint
Liquidity constraint
A liquidity constraint in economic theory is a form of imperfection in the capital market. It causes difficulties for models based on intertemporal consumption.Many economic models require individuals to save or borrow money from time to time....
is one of the main reasons of why it is so difficult to observe consumption smoothing in the data.
Model
Robert Hall (1978) formalized Friedman idea. By taking into account the diminishing returns to consumption, and therefore, assuming a concave utility function, he showed that agents optimally would choose to keep a stable path of consumption.Agent's choose the consumption path that maximize:
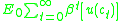
Subject to a sequence of budget constraints:
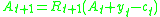
The first order necessary condition in this case will be:

By assuming that
 we obtain, for the previous
we obtain, for the previousequation:
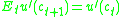
Which, due to the concavity of the utility function, implies:
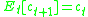
Thus, rational agents would expect to achieve the same consumption in every
period.
Hall also showed that for a quadratic utility function and a stationary
process for income, the optimal consumption is equal to:

This expression shows that agents choose to consume a fraction of their
present discounted value of their human and financial wealth.
Empirical Evidence
Robert Hall (1978) estimated the Euler equation in order to find evidence of a random walk in consumptionRandom walk model of consumption
The random walk model of consumption was introduced by economist Robert Hall This model uses the Euler equation to model consumption. He created his consumption theory in response to the Lucas critique. Using Euler equations to model the random walk of consumption has become the dominant...
. The data used are US National Income and Product Accounts (NIPA) quarterly from 1948 to 1977. For the analysis the author does not consider the consumption of durable goods. Although Hall argues to find some evidence of consumption smoothing it is done for a modified version. Also there is some econometric concerns around his finding.
Wilcox (1989) argue that liquidity constraint is the reason for the consumption smoothing not to hold in the data. Zeldes (1989) follows the same argument and finds that poor household's consumption is correlated with contemporaneous income while rich household is not.

