Immunodeficiency, centromere instability and facial anomalies syndrome
Encyclopedia
ICF syndrome is a very rare autosomal
recessive immune disorder
.
immunoglobulin levels which cause most ICF patients to succumb to infectious disease
s before adulthood. ICF syndrome patients exhibit facial anomalies which include hypertelorism
, low-set ears
, epicanthal fold
s and macroglossia
.

ICF syndrome can be caused by a mutation
in the DNA-methyltransferase-3b (Dnmt3b
) gene
, located on chromosome
20q11.2
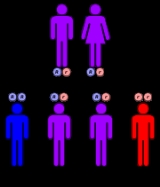
. The disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome
(chromosome 20 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry
one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
recessive immune disorder
Immune disorder
An immune disorder is a dysfunction of the immune system. These disorders can be characterized in several different ways:* By the component of the immune system affected* By whether the immune system is overactive or underactive...
.
Characteristics
It is characterized by variable reductions in serumBlood plasma
Blood plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which the blood cells in whole blood are normally suspended. It makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid...
immunoglobulin levels which cause most ICF patients to succumb to infectious disease
Infectious disease
Infectious diseases, also known as communicable diseases, contagious diseases or transmissible diseases comprise clinically evident illness resulting from the infection, presence and growth of pathogenic biological agents in an individual host organism...
s before adulthood. ICF syndrome patients exhibit facial anomalies which include hypertelorism
Hypertelorism
Hypertelorism is an abnormally increased distance between two organs or bodily parts, usually referring to an increased distance between the orbits . In this condition the distance between the inner eye corners as well as the distance between the pupils is greater than normal...
, low-set ears
Low-set ears
Low-set ears is a term used to describe a depressed positioning of the pinna two or more standard deviations below the population average.It can be associated with conditions such as:* Down's syndrome and Turner Syndrome* Noonan syndrome* Patau syndrome...
, epicanthal fold
Epicanthal fold
An epicanthic fold, epicanthal fold, or epicanthus is a skin fold of the upper eyelid, covering the inner corner of the eye....
s and macroglossia
Macroglossia
Macroglossia is the medical term for unusual enlargement of the tongue. Severe enlargement of the tongue can cause cosmetic and functional difficulties including in speaking, eating, swallowing and sleeping.- Amyloid Disorders :...
.
Genetics

ICF syndrome can be caused by a mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
in the DNA-methyltransferase-3b (Dnmt3b
DNMT3B
DNA -methyltransferase 3 beta, also known as DNMT3B, is a protein associated with immunodeficiency, centromere instability and facial anomalies syndrome.-Interactions:...
) gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
, located on chromosome
Chromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
20q11.2
Chromosome 20 (human)
Chromosome 20 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 20 spans around 63 million base pairs and represents between 2 and 2.5 percent of the total DNA in cells...
. The disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
(chromosome 20 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry
Genetic carrier
A genetic carrier , is a person or other organism that has inherited a genetic trait or mutation, but who does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. They are, however, able to pass the gene onto their offspring, who may then express the gene...
one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
External links
- Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases link to ICF syndrome http://www.ojrd.com/content/1/1/2

