
Iminium
Encyclopedia
Salt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
or cation in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
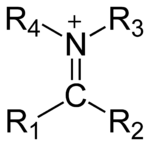
has the general structure [R1R2C=NR3R4]+ and is as such a protonated
Protonation
In chemistry, protonation is the addition of a proton to an atom, molecule, or ion. Some classic examples include*the protonation of water by sulfuric acid:*the protonation of isobutene in the formation of a carbocation:2C=CH2 + HBF4 → 3C+ + BF4−*the protonation of ammonia in the...
or substituted
Substitution reaction
In a substitution reaction, a functional group in a particular chemical compound is replaced by another group. In organic chemistry, the electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution reactions are of prime importance...
imine
Imine
An imine is a functional group or chemical compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond, with the nitrogen attached to a hydrogen atom or an organic group. If this group is not a hydrogen atom, then the compound is known as a Schiff base...
. It is an intermediate in many organic reaction
Organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis,...
s such as the Beckmann rearrangement
Beckmann rearrangement
The Beckmann rearrangement, named after the German chemist Ernst Otto Beckmann , is an acid-catalyzed rearrangement of an oxime to an amide...
, Vilsmeier-Haack reaction
Vilsmeier-Haack reaction
The Vilsmeier–Haack reaction is the chemical reaction of a substituted amide with phosphorus oxychloride and an electron-rich arene to produce an aryl aldehyde or ketone . The reaction is named after Anton Vilsmeier and Albrecht Haack...
, Stephen reaction or the Duff reaction
Duff reaction
The Duff reaction or hexamine aromatic formylation is a formylation reaction used in organic chemistry for the synthesis of benzaldehydes with hexamine as the formyl carbon source...
. The use of the alternative names imonium compounds and immonium compounds is discouraged.
Reactions involving iminium salts
- Beckmann rearrangementBeckmann rearrangementThe Beckmann rearrangement, named after the German chemist Ernst Otto Beckmann , is an acid-catalyzed rearrangement of an oxime to an amide...
- Eschenmoser's saltEschenmoser's saltEschenmoser's salt, dimethylmethylideneammonium iodide, is a strong dimethylaminomethylating agent, used to prepare derivatives of the type RCH2N2. Enolates, enolsilylethers, and even more acidic ketones undergo efficient dimethylaminomethylation...
- Duff reactionDuff reactionThe Duff reaction or hexamine aromatic formylation is a formylation reaction used in organic chemistry for the synthesis of benzaldehydes with hexamine as the formyl carbon source...
- Stephen reactionStephen aldehyde synthesisStephen aldehyde synthesis, a named reaction in chemistry, was invented by Henry Stephen . This reaction involves the preparation of aldehydes from nitriles using tin chloride , hydrochloric acid and quenching the resulting iminium salt with water .Overall, the reaction scheme is as...
- Vilsmeier-Haack reactionVilsmeier-Haack reactionThe Vilsmeier–Haack reaction is the chemical reaction of a substituted amide with phosphorus oxychloride and an electron-rich arene to produce an aryl aldehyde or ketone . The reaction is named after Anton Vilsmeier and Albrecht Haack...
- Pictet-Spengler
Iminylium ions
Iminylium ions have the general structure R2C=N+. They form a subclass of nitrenium ionNitrenium ion
A nitrenium ion in organic chemistry is a reactive intermediate based on nitrogen with both an electron lone pair and a positive charge and with two substituents . Nitrenium ions are isoelectronic to carbenes, and can exist in either a singlet or a triplet state...
s.

