
Hyperintensity
Encyclopedia
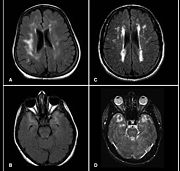
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
(MRI) scans of the human brain
Human brain
The human brain has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times larger than the brain of a typical mammal with an equivalent body size. Estimates for the number of neurons in the human brain range from 80 to 120 billion...
. These small regions of high intensity are observed on T2
Spin-spin relaxation time
thumb|right|T2 relaxation curveSpin–spin relaxation is the mechanism by which Mxy, the transverse component of the magnetization vector, exponentially decays towards its equilibrium value of zero, in nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging...
weighted MRI images (typically created using 3D FLAIR
Fluid attenuated inversion recovery
Fluid attenuated inversion recovery is a pulse sequence used in magnetic resonance imaging which was invented by Dr. Graeme Bydder. FLAIR can be used with both three dimensional imaging or two dimensional imaging ....
) within cerebral white matter
White matter
White matter is one of the two components of the central nervous system and consists mostly of myelinated axons. White matter tissue of the freshly cut brain appears pinkish white to the naked eye because myelin is composed largely of lipid tissue veined with capillaries. Its white color is due to...
(white matter hyperintensities or WMH) or subcortical gray matter (gray matter hyperintensities or GMH). They are usually seen in normal aging but also in a number of neurological disorders and psychiatric illnesses. For example deep white matter hyperintensites are 2.5 to 3 times more likely to occur in bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder or bipolar affective disorder, historically known as manic–depressive disorder, is a psychiatric diagnosis that describes a category of mood disorders defined by the presence of one or more episodes of abnormally elevated energy levels, cognition, and mood with or without one or...
and major depressive disorder than control subjects. WMH volume, calculated as a potential diagnostic measure, has been shown to correlate to certain cognitive factors.Hyperintensities appear as "bright signals" (bright areas) on an MRI image and the term "bright signal" is occasionally used as a synonym for a hyperintensity.
Hyperintensities are commonly divided into 3 types depending on the region of the brain where they are found. Deep white matter hyperintensites occur deep within white matter, periventricular white matter hyperintensities occur adjacent to the lateral ventricles
Lateral ventricles
The lateral ventricles are part of the ventricular system of the brain. Classified as part of the telencephalon, they are the largest of the ventricles....
and subcortical hyperintensities occur in the basal ganglia
Basal ganglia
The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei of varied origin in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit. They are situated at the base of the forebrain and are strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other brain areas...
.
Postmortem studies combined with MRI suggest that hyperintensities are dilated perivascular spaces
Virchow-Robin spaces
Virchow-Robin spaces are perivascular, fluid-filled canals that surround perforating arteries and veins in the parenchyma of the brain. These spaces are separated from the subarachnoid space by a thin pia layer. VRS are extremely small and can usually only be seen on MR images when dilated...
, or demyelination
Demyelinating disease
A demyelinating disease is any disease of the nervous system in which the myelin sheath of neurons is damaged. This impairs the conduction of signals in the affected nerves, causing impairment in sensation, movement, cognition, or other functions depending on which nerves are involved.The term...
caused by reduced local blood flow.
See also
- Hypertensive leukoencephalopathyHypertensive leukoencephalopathyHypertensive leukoencephalopathy refers to a degeneration of the white matter of the brain following a sudden increase in blood pressure. -Presentation:...
- Virchow-Robin spacesVirchow-Robin spacesVirchow-Robin spaces are perivascular, fluid-filled canals that surround perforating arteries and veins in the parenchyma of the brain. These spaces are separated from the subarachnoid space by a thin pia layer. VRS are extremely small and can usually only be seen on MR images when dilated...
- Subcortical ischemic depressionSubcortical ischemic depressionSubcortical ischemic depression, also known as vascular depression is a medical condition most commonly seen in elderly depressed patients. Late onset depression is increasingly seen as a distinct variety of depression, and is commonly detected with an MRI...

