
Fluid attenuated inversion recovery
Encyclopedia
Fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) is a pulse sequence
used in magnetic resonance imaging
which was invented by Dr. Graeme Bydder. FLAIR can be used with both three dimensional imaging (3D FLAIR) or two dimensional imaging (2D FLAIR).
The pulse sequence is an inversion recovery technique that nulls fluids. For example, it can be used in brain imaging to suppress cerebrospinal fluid
(CSF) effects on the image, so as to bring out the periventricular hyperintense lesions, such as multiple sclerosis
(MS) plaques.
By carefully choosing the inversion time (TI), the signal from any particular tissue can be nulled. The appropriate TI depends on the tissue via the formula:
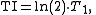
in other words, one should typically use a TI of around 70% of the T1
value. In the case of CSF suppression, one aims for T2
weighted images.
Pulse sequence
In Fourier Transform NMR spectroscopy and imaging, a pulse sequence describes a series of radio frequency pulses applied to the sample, such that the free induction decay is related to the characteristic frequencies of the wanted signals. After applying a Fourier Transform, the signal can be...
used in magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
which was invented by Dr. Graeme Bydder. FLAIR can be used with both three dimensional imaging (3D FLAIR) or two dimensional imaging (2D FLAIR).
The pulse sequence is an inversion recovery technique that nulls fluids. For example, it can be used in brain imaging to suppress cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid , Liquor cerebrospinalis, is a clear, colorless, bodily fluid, that occupies the subarachnoid space and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord...
(CSF) effects on the image, so as to bring out the periventricular hyperintense lesions, such as multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory disease in which the fatty myelin sheaths around the axons of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to demyelination and scarring as well as a broad spectrum of signs and symptoms...
(MS) plaques.
By carefully choosing the inversion time (TI), the signal from any particular tissue can be nulled. The appropriate TI depends on the tissue via the formula:
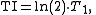
in other words, one should typically use a TI of around 70% of the T1
Spin-lattice relaxation time
Spin–lattice relaxation is the mechanism by which the z component of the magnetization vector comes into thermodynamic equilibrium with its surroundings in nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging. It is characterized by the spin–lattice relaxation time, a time constant known as T1...
value. In the case of CSF suppression, one aims for T2
Spin-spin relaxation time
thumb|right|T2 relaxation curveSpin–spin relaxation is the mechanism by which Mxy, the transverse component of the magnetization vector, exponentially decays towards its equilibrium value of zero, in nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging...
weighted images.
Further reading
- McRobbie D., et al. MRI, From picture to proton. 2003 p.40-42
- Hashemi Ray, et al. MRI, The Basics 2ED. 2004. p.272

