
Hydrogenase (acceptor)
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a hydrogenase (acceptor) is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are H2
and A, whereas its product
is AH2.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductase
s, specifically those acting on hydrogen as donor with other acceptors. The systematic name of this enzyme class is hydrogen:acceptor oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include H2 producing hydrogenase[ambiguous], hydrogen-lyase[ambiguous], hydrogenlyase[ambiguous], uptake hydrogenase[ambiguous], and hydrogen:(acceptor) oxidoreductase.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- H2 + A
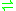 AH2
AH2
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are H2
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
and A, whereas its product
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
is AH2.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductase
Oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule to another...
s, specifically those acting on hydrogen as donor with other acceptors. The systematic name of this enzyme class is hydrogen:acceptor oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include H2 producing hydrogenase[ambiguous], hydrogen-lyase[ambiguous], hydrogenlyase[ambiguous], uptake hydrogenase[ambiguous], and hydrogen:(acceptor) oxidoreductase.

