
Hydrogen difluoride
Encyclopedia
The bifluoride, or hydrogen(difluoride) ion is the species HF2−. This centrosymmetric triatomic anion features the strongest known hydrogen bond
, with an F
−H
length of 114 pm and a bond strength of >155 kJ mol−1. A molecular orbital diagram reveals the atoms to be held together by a 3-center 4-electron bond. Hydrogen(difluoride) is written as one word because it is an anion. Hydrogen difluoride would imply an electrically neutral compound, HF2, which does not exist. It is isoelectronic with the hypothetical compound helium
difluoride, HeF2, which also does not exist, and the fluoroheliate anion, FHeO−, whose existence is suspected.
, and [NH4][HF2]. Many salts claimed to be anhydrous sources of fluoride (e.g. tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride
) can decompose yielding bifluoride.
, which autodissociates
in a manner similar to the self-ionization of water
. This equilibrium
can be denoted as
However, both the H+ and F− ions are solvated
by HF, so a better descriptive equation is
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine, that comes from another molecule or chemical group. The hydrogen must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom to create the bond...
, with an F
Fluorine
Fluorine is the chemical element with atomic number 9, represented by the symbol F. It is the lightest element of the halogen column of the periodic table and has a single stable isotope, fluorine-19. At standard pressure and temperature, fluorine is a pale yellow gas composed of diatomic...
−H
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
length of 114 pm and a bond strength of >155 kJ mol−1. A molecular orbital diagram reveals the atoms to be held together by a 3-center 4-electron bond. Hydrogen(difluoride) is written as one word because it is an anion. Hydrogen difluoride would imply an electrically neutral compound, HF2, which does not exist. It is isoelectronic with the hypothetical compound helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
difluoride, HeF2, which also does not exist, and the fluoroheliate anion, FHeO−, whose existence is suspected.
Salts
Some HF2− salts are common, examples include potassium hydrogen fluoride, KHF2Potassium bifluoride
Potassium bifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula KHF2. This colourless salt consists of the potassium cation and the bifluoride anion. The salt is used in etchant for glass...
, and [NH4][HF2]. Many salts claimed to be anhydrous sources of fluoride (e.g. tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride
Tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride
Tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride or TBAF is a quaternary ammonium salt with the chemical formula 4N+F-. It is commercially available as the trihydrate and as a solution in tetrahydrofuran....
) can decompose yielding bifluoride.
Autodissociation of pure HF
The bifluoride ion also contributes to the unusually high auto-protolysis constant of liquid anhydrous hydrogen fluorideHydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula HF. This colorless gas is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often in the aqueous form as hydrofluoric acid, and thus is the precursor to many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers . HF is widely used in the...
, which autodissociates
Dissociation (chemistry)
Dissociation in chemistry and biochemistry is a general process in which ionic compounds separate or split into smaller particles, ions, or radicals, usually in a reversible manner...
in a manner similar to the self-ionization of water
Self-ionization of water
The self-ionization of water is the chemical reaction in which a proton is transferred from one water molecule to another, in pure water or an aqueous solution, to create the two ions, hydronium, H3O+ and hydroxide, OH−...
. This equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products have not yet changed with time. It occurs only in reversible reactions, and not in irreversible reactions. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same...
can be denoted as
- HF
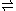 H+ + F−
H+ + F−
However, both the H+ and F− ions are solvated
Solvation
Solvation, also sometimes called dissolution, is the process of attraction and association of molecules of a solvent with molecules or ions of a solute...
by HF, so a better descriptive equation is
- 3HF
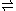 H2F+(HF) + HF2−(HF)
H2F+(HF) + HF2−(HF)

