
Heath-Jarrow-Morton framework
Encyclopedia
The Heath–Jarrow–Morton framework is a general framework to model the evolution of interest rate
curve – instantaneous forward rate curve in particular (as opposed to simple forward rate
s). When the volatility and drift of the instantaneous forward rate are assumed to be deterministic, this is known as the Gaussian Heath–Jarrow–Morton (HJM) Model of forward rates . For direct modeling of simple forward rates please see the Brace–Gatarek–Musiela Model
as an example.
The HJM framework originates from the work of David Heath, Robert A. Jarrow
and Andrew Morton in the late 1980s, especially Bond pricing and the term structure of interest rates: a new methodology (1987) – working paper, Cornell University
, and Bond pricing and the term structure of interest rates: a new methodology (1989) – working paper (revised ed.), Cornell University.
evolution of certain variables can be expressed as functions of their volatilities and the correlations among themselves. In other words, no drift estimation is needed.
Models developed according to the HJM framework are different from the so called short-rate models in the sense that HJM-type models capture the full dynamics of the entire forward rate curve, while the short-rate models only capture the dynamics of a point on the curve (the short rate).
However, models developed according to the general HJM framework are often non-Markovian and can even have infinite dimensions. A number of researchers have made great contributions to tackle this problem. They show that if the volatility structure of the forward rates satisfy certain conditions, then an HJM model can be expressed entirely by a finite state Markovian system, making it computationally feasible. Examples include a one-factor, two state model (O. Cheyette, "Term Structure Dynamics and Mortgage Valuation", Journal of Fixed Income, 1, 1992; P. Ritchken and L. Sankarasubramanian in "Volatility Structures of Forward Rates and the Dynamics of Term Structure", Mathematical Finance, 5, No. 1, Jan 1995), and later multi-factor versions.
The instantaneous forward rate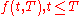 is the continuous compounding rate available at time
is the continuous compounding rate available at time 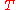 as seen from time
as seen from time  . It is defined by:
. It is defined by:
The basic relation between the rates and the bond prices is given by:
Consequently, the bank account grows according to:
grows according to:
since the spot rate at time is
is 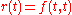 .
.
The assumption of the HJM model is that the forward rates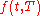 satisfy for any
satisfy for any 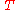 :
:
where the processes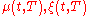 are continuous and adapted.
are continuous and adapted.
For this assumption to be compatible with the assumption of the existence of martingale measures we need the following relation to hold:
We find the return on the bond in the HJM model and compare it (5) to obtain models that do not allow for arbitrage.
Let
Then
Using Leibniz's rule
for differentiating under the integral sign we have that:
where

By Itō's lemma
,
It follows from (5) and (9), we must have that
Rearranging the terms we get that
Differentiating both sides by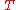 , we have that
, we have that
Equation (13) is known as the no-arbitrage condition in the HJM model. Under the martingale probability measure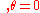 and the equation for the forward rates becomes:
and the equation for the forward rates becomes:
This equation is used in pricing of bonds and its derivatives.
Interest rate
An interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by a borrower for the use of money that they borrow from a lender. For example, a small company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for their business, and in return the lender receives interest at a predetermined interest rate for...
curve – instantaneous forward rate curve in particular (as opposed to simple forward rate
Forward rate
The forward rate is the future yield on a bond. It is calculated using the yield curve. For example, the yield on a three-month Treasury bill six months from now is a forward rate.-Forward rate calculation:...
s). When the volatility and drift of the instantaneous forward rate are assumed to be deterministic, this is known as the Gaussian Heath–Jarrow–Morton (HJM) Model of forward rates . For direct modeling of simple forward rates please see the Brace–Gatarek–Musiela Model
LIBOR Market Model
The LIBOR market model, also known as the BGM Model , is a financial model of interest rates...
as an example.
The HJM framework originates from the work of David Heath, Robert A. Jarrow
Robert A. Jarrow
Robert Alan Jarrow is the Ronald P. and Susan E. Lynch Professor of Investment Management at the Johnson Graduate School of Management, Cornell University...
and Andrew Morton in the late 1980s, especially Bond pricing and the term structure of interest rates: a new methodology (1987) – working paper, Cornell University
Cornell University
Cornell University is an Ivy League university located in Ithaca, New York, United States. It is a private land-grant university, receiving annual funding from the State of New York for certain educational missions...
, and Bond pricing and the term structure of interest rates: a new methodology (1989) – working paper (revised ed.), Cornell University.
Framework
The key to these techniques is the recognition that the drifts of the no-arbitrageRational pricing
Rational pricing is the assumption in financial economics that asset prices will reflect the arbitrage-free price of the asset as any deviation from this price will be "arbitraged away"...
evolution of certain variables can be expressed as functions of their volatilities and the correlations among themselves. In other words, no drift estimation is needed.
Models developed according to the HJM framework are different from the so called short-rate models in the sense that HJM-type models capture the full dynamics of the entire forward rate curve, while the short-rate models only capture the dynamics of a point on the curve (the short rate).
However, models developed according to the general HJM framework are often non-Markovian and can even have infinite dimensions. A number of researchers have made great contributions to tackle this problem. They show that if the volatility structure of the forward rates satisfy certain conditions, then an HJM model can be expressed entirely by a finite state Markovian system, making it computationally feasible. Examples include a one-factor, two state model (O. Cheyette, "Term Structure Dynamics and Mortgage Valuation", Journal of Fixed Income, 1, 1992; P. Ritchken and L. Sankarasubramanian in "Volatility Structures of Forward Rates and the Dynamics of Term Structure", Mathematical Finance, 5, No. 1, Jan 1995), and later multi-factor versions.
Mathematical formulation
The class of models developed by Heath, Jarrow and Morton (1992) is based on modeling the forward rates, yet it does not capture all of the complexities of an evolving term structure.The instantaneous forward rate
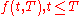 is the continuous compounding rate available at time
is the continuous compounding rate available at time 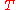 as seen from time
as seen from time  . It is defined by:
. It is defined by:The basic relation between the rates and the bond prices is given by:
Consequently, the bank account
 grows according to:
grows according to:since the spot rate at time
 is
is 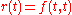 .
.The assumption of the HJM model is that the forward rates
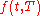 satisfy for any
satisfy for any 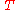 :
:where the processes
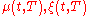 are continuous and adapted.
are continuous and adapted.For this assumption to be compatible with the assumption of the existence of martingale measures we need the following relation to hold:
We find the return on the bond in the HJM model and compare it (5) to obtain models that do not allow for arbitrage.
Let
Then
Using Leibniz's rule
Leibniz integral rule
In mathematics, Leibniz's rule for differentiation under the integral sign, named after Gottfried Leibniz, tells us that if we have an integral of the formthen for x \in the derivative of this integral is thus expressible...
for differentiating under the integral sign we have that:
where

By Itō's lemma
Ito's lemma
In mathematics, Itō's lemma is used in Itō stochastic calculus to find the differential of a function of a particular type of stochastic process. It is named after its discoverer, Kiyoshi Itō...
,
It follows from (5) and (9), we must have that
Rearranging the terms we get that
Differentiating both sides by
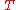 , we have that
, we have thatEquation (13) is known as the no-arbitrage condition in the HJM model. Under the martingale probability measure
 and the equation for the forward rates becomes:
and the equation for the forward rates becomes:This equation is used in pricing of bonds and its derivatives.
See also
- Ho–Lee model
- Hull–White model
- Black–Derman–Toy model
- Chen modelChen modelIn finance, the Chen model is a mathematical model describing the evolution of interest rates. It is a type of "three-factor model" as it describes interest rate movements as driven by three sources of market risk...
- Brace–Gatarek–Musiela ModelLIBOR Market ModelThe LIBOR market model, also known as the BGM Model , is a financial model of interest rates...
External links and references
- Bond Pricing and the Term Structure of Interest Rates: A New Methodology for Contingent Claims Valuation. David Heath, Robert A. Jarrow and Andrew Morton, EconometricaEconometricaEconometrica is a peer-reviewed academic journal of economics, publishing articles not only in econometrics but in many areas of economics. It is published by the Econometric Society and distributed by Wiley-Blackwell. Econometrica is one of the most highly ranked economics journals in the world...
, 1992, vol. 60, issue 1, pages 77–105 - Heath–Jarrow–Morton model and its application, Vladimir I Pozdynyakov, University of PennsylvaniaUniversity of PennsylvaniaThe University of Pennsylvania is a private, Ivy League university located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. Penn is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States,Penn is the fourth-oldest using the founding dates claimed by each institution...
- An Empirical Study of the Convergence Properties of the Non-recombining HJM Forward Rate Tree in Pricing Interest Rate Derivatives, A.R. Radhakrishnan New York UniversityNew York UniversityNew York University is a private, nonsectarian research university based in New York City. NYU's main campus is situated in the Greenwich Village section of Manhattan...

