
Haber's rule
Encyclopedia
Haber's rule or Haber's law is a mathematical statement of the relationship between the concentration
of a poisonous gas
and how long the gas must be breathed to produce death, or other toxic effect. The rule was formulated by German
chemist
Fritz Haber
in the early 1900s.
Haber's rule states that, for a given poisonous gas,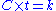 , where
, where  is the concentration of the gas (mass per unit volume),
is the concentration of the gas (mass per unit volume),  is the amount of time necessary to breathe the gas, in order to produce a given toxic effect, and
is the amount of time necessary to breathe the gas, in order to produce a given toxic effect, and 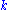 is a constant, depending on both the gas and the effect. Thus, the rule states that doubling the concentration will halve the time, for example.
is a constant, depending on both the gas and the effect. Thus, the rule states that doubling the concentration will halve the time, for example.
It makes equivalent any two groupings of dose concentration
and exposure time that have equivalent mathematical products. For instance, if we assign dose
concentration
the symbol
C, and time
the classic t, then for any two dose schema
, if C1t1=C2t2, then under Haber's rule the two dose schema are equivalent.
Haber's rule is an approximation, useful with certain inhaled poisons under certain conditions, and Haber himself acknowledged that it was not always applicable. If a substance is efficiently eliminated in the host, for example, then Haber's Law breaks down in the limit of t approaching the order
of the half-life
of the drug
, rewriting the equation as the integral ∫Cdt = constant for arbitrary varying C and elapsed time T. It is very convenient, however, because its relationship between and
and  appears as a straight line in a log-log plot.
appears as a straight line in a log-log plot.
In 1940, statistician
C. I. Bliss published a study of toxicity
in insecticide
s in which he proposed more complex models
, for example, expressing the relationship between and
and  as two straight line segments in a log-log plot. However, because of its simplicity, Haber's rule continued to be widely used. Recently, some researchers have argued that it is time to move beyond the simple relationship expressed by Haber's rule and to make regular use of more sophisticated models.
as two straight line segments in a log-log plot. However, because of its simplicity, Haber's rule continued to be widely used. Recently, some researchers have argued that it is time to move beyond the simple relationship expressed by Haber's rule and to make regular use of more sophisticated models.
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
of a poisonous gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
and how long the gas must be breathed to produce death, or other toxic effect. The rule was formulated by German
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
chemist
Chemist
A chemist is a scientist trained in the study of chemistry. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties such as density and acidity. Chemists carefully describe the properties they study in terms of quantities, with detail on the level of molecules and their component atoms...
Fritz Haber
Fritz Haber
Fritz Haber was a German chemist, who received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1918 for his development for synthesizing ammonia, important for fertilizers and explosives. Haber, along with Max Born, proposed the Born–Haber cycle as a method for evaluating the lattice energy of an ionic solid...
in the early 1900s.
Haber's rule states that, for a given poisonous gas,
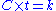 , where
, where  is the concentration of the gas (mass per unit volume),
is the concentration of the gas (mass per unit volume),  is the amount of time necessary to breathe the gas, in order to produce a given toxic effect, and
is the amount of time necessary to breathe the gas, in order to produce a given toxic effect, and 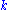 is a constant, depending on both the gas and the effect. Thus, the rule states that doubling the concentration will halve the time, for example.
is a constant, depending on both the gas and the effect. Thus, the rule states that doubling the concentration will halve the time, for example.It makes equivalent any two groupings of dose concentration
Dose concentration
Dose concentration is the measure of the ratio of the mass of the drug to the volume that contains it, often measured in units of moles/m3....
and exposure time that have equivalent mathematical products. For instance, if we assign dose
Dose (biochemistry)
A dose is a quantity of something that may impact an organism biologically; the greater the quantity, the larger the dose. In nutrition, the term is usually applied to how much of a specific nutrient is in a person's diet or in a particular food, meal, or dietary supplement...
concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
the symbol
Symbol
A symbol is something which represents an idea, a physical entity or a process but is distinct from it. The purpose of a symbol is to communicate meaning. For example, a red octagon may be a symbol for "STOP". On a map, a picture of a tent might represent a campsite. Numerals are symbols for...
C, and time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
the classic t, then for any two dose schema
Conceptual model
In the most general sense, a model is anything used in any way to represent anything else. Some models are physical objects, for instance, a toy model which may be assembled, and may even be made to work like the object it represents. They are used to help us know and understand the subject matter...
, if C1t1=C2t2, then under Haber's rule the two dose schema are equivalent.
Haber's rule is an approximation, useful with certain inhaled poisons under certain conditions, and Haber himself acknowledged that it was not always applicable. If a substance is efficiently eliminated in the host, for example, then Haber's Law breaks down in the limit of t approaching the order
Order of reaction
In chemical kinetics, the order of reaction with respect to certain reactant, is defined as the power to which its concentration term in the rate equation is raised .For example, given a chemical reaction 2A + B → C with a rate equation...
of the half-life
Half-life
Half-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to...
of the drug
Drug
A drug, broadly speaking, is any substance that, when absorbed into the body of a living organism, alters normal bodily function. There is no single, precise definition, as there are different meanings in drug control law, government regulations, medicine, and colloquial usage.In pharmacology, a...
, rewriting the equation as the integral ∫Cdt = constant for arbitrary varying C and elapsed time T. It is very convenient, however, because its relationship between
 and
and  appears as a straight line in a log-log plot.
appears as a straight line in a log-log plot.In 1940, statistician
Statistician
A statistician is someone who works with theoretical or applied statistics. The profession exists in both the private and public sectors. The core of that work is to measure, interpret, and describe the world and human activity patterns within it...
C. I. Bliss published a study of toxicity
Toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a substance can damage a living or non-living organisms. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell or an organ , such as the liver...
in insecticide
Insecticide
An insecticide is a pesticide used against insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against the eggs and larvae of insects respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and the household. The use of insecticides is believed to be one of the major factors behind...
s in which he proposed more complex models
Mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used not only in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines A mathematical model is a...
, for example, expressing the relationship between
 and
and  as two straight line segments in a log-log plot. However, because of its simplicity, Haber's rule continued to be widely used. Recently, some researchers have argued that it is time to move beyond the simple relationship expressed by Haber's rule and to make regular use of more sophisticated models.
as two straight line segments in a log-log plot. However, because of its simplicity, Haber's rule continued to be widely used. Recently, some researchers have argued that it is time to move beyond the simple relationship expressed by Haber's rule and to make regular use of more sophisticated models.

