
Graded-index fiber
Encyclopedia
In fiber optics, a graded-index or gradient-index fiber is an optical fiber
whose core has a refractive index
that decreases with increasing radial distance from the fiber axis (the imaginary central axis running down the length of the fiber).
Because parts of the core closer to the fiber axis have a higher refractive index than the parts near the cladding, light rays follow sinusoidal paths down the fiber.
The advantage of the graded-index fiber compared to multimode step-index fiber
is the considerable decrease in modal dispersion
.
The most common refractive index profile for a graded-index fiber is very nearly parabolic. The parabolic profile
results in continual refocusing of the rays in the core, and minimizes modal dispersion.
This type of fiber is normalized by the International Telecommunications Union ITU-T at recommendation G.651.1.
Pulse dispersion in a graded index optical fiber is given by

where
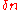 is the difference in refractive indices of core and cladding,
is the difference in refractive indices of core and cladding,
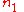 is the refractive index of the cladding,
is the refractive index of the cladding,
 is the length of the fiber taken for observing the pulse dispersion,
is the length of the fiber taken for observing the pulse dispersion,
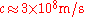 is the speed of light
is the speed of light
, and
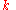 is the constant of graded index profile.
is the constant of graded index profile.
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
whose core has a refractive index
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
that decreases with increasing radial distance from the fiber axis (the imaginary central axis running down the length of the fiber).
Because parts of the core closer to the fiber axis have a higher refractive index than the parts near the cladding, light rays follow sinusoidal paths down the fiber.
The advantage of the graded-index fiber compared to multimode step-index fiber
Multi-mode optical fiber
Multi-mode optical fiber is a type of optical fiber mostly used for communication over short distances, such as within a building or on a campus...
is the considerable decrease in modal dispersion
Modal dispersion
Modal dispersion is a distortion mechanism occurring in multimode fibers and other waveguides, in which the signal is spread in time because the propagation velocity of the optical signal is not the same for all modes...
.
The most common refractive index profile for a graded-index fiber is very nearly parabolic. The parabolic profile
Parabola
In mathematics, the parabola is a conic section, the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to a generating straight line of that surface...
results in continual refocusing of the rays in the core, and minimizes modal dispersion.
This type of fiber is normalized by the International Telecommunications Union ITU-T at recommendation G.651.1.
Pulse dispersion in a graded index optical fiber is given by

where
 is the difference in refractive indices of core and cladding,
is the difference in refractive indices of core and cladding,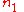 is the refractive index of the cladding,
is the refractive index of the cladding, is the length of the fiber taken for observing the pulse dispersion,
is the length of the fiber taken for observing the pulse dispersion,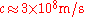 is the speed of light
is the speed of lightSpeed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
, and
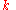 is the constant of graded index profile.
is the constant of graded index profile.See also
- Step-index profileStep-index profileFor an optical fiber, a step-index profile is a refractive index profile characterized by a uniform refractive index within the core and a sharp decrease in refractive index at the core-cladding interface so that the cladding is of a lower refractive index. The step-index profile corresponds to a...
- Power-law index profile
- Gradient index opticsGradient index opticsGradient-index optics is the branch of optics covering optical effects produced by a gradual variation of the refractive index of a material. Such variations can be used to produce lenses with flat surfaces, or lenses that do not have the aberrations typical of traditional spherical lenses...
- Multi-mode optical fiberMulti-mode optical fiberMulti-mode optical fiber is a type of optical fiber mostly used for communication over short distances, such as within a building or on a campus...
- Single-mode optical fiberSingle-mode optical fiberIn fiber-optic communication, a single-mode optical fiber is an optical fiber designed to carry only a single ray of light . Modes are the possible solutions of the Helmholtz equation for waves, which is obtained by combining Maxwell's equations and the boundary conditions...

