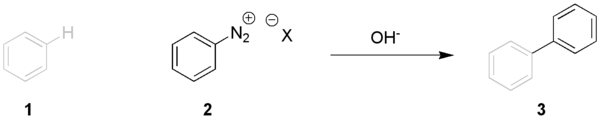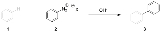
Gomberg-Bachmann reaction
Encyclopedia
The Gomberg–Bachmann reaction, named for the Ukrainian-American chemist Moses Gomberg
and the American chemist Werner Emmanuel Bachmann
, is an aryl
-aryl coupling reaction
via a diazonium salt.
The arene compound 1 (here benzene
) is coupled with base with the diazonium salt 2 to the biaryl 3 through an intermediate aryl radical
. For example, p-bromobiphenyl may be prepared from 4-bromoaniline and benzene
:
The reaction offers a wide scope for both diazonium component and arene component but yields are generally low following the original procedure (less than 40%), given the many side-reactions of diazonium salts. Several improvements have been suggested. One possibility is to employ diazonium tetrafluoroborates in arene solvent together with a phase-transfer catalyst, another is to use 1-aryl-3,3-dialkyltriazenes.
variation which gives better results is the Pschorr reaction:
The group Z can be CH2, CH2CH2, NH and CO (to fluorenone
) to name just a few.
Moses Gomberg
Moses Gomberg was a chemistry professor at the University of Michigan....
and the American chemist Werner Emmanuel Bachmann
Werner Emmanuel Bachmann
Werner Emmanuel Bachmann was a U.S. chemist. Bachmann was born in Detroit, Michigan where he studied chemistry and chemical engineering at Wayne State University and later at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor nearby...
, is an aryl
Aryl
In the context of organic molecules, aryl refers to any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, be it phenyl, naphthyl, thienyl, indolyl, etc....
-aryl coupling reaction
Coupling reaction
A coupling reaction in organic chemistry is a catch-all term for a variety of reactions where two hydrocarbon fragments are coupled with the aid of a metal catalyst...
via a diazonium salt.
The arene compound 1 (here benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
) is coupled with base with the diazonium salt 2 to the biaryl 3 through an intermediate aryl radical
Aryl radical
An Aryl radical in organic chemistry is an reactive intermediate and an arene compound incorporating one free radical carbon atom as part of the ring structure. As such it is the radical counterpart of the Arenium ion. The parent compound is the phenyl radical C6H5....
. For example, p-bromobiphenyl may be prepared from 4-bromoaniline and benzene
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound. It is composed of 6 carbon atoms in a ring, with 1 hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom, with the molecular formula C6H6....
:
- BrC6H4NH2 + C6H6 → BrC6H4−C6H5
The reaction offers a wide scope for both diazonium component and arene component but yields are generally low following the original procedure (less than 40%), given the many side-reactions of diazonium salts. Several improvements have been suggested. One possibility is to employ diazonium tetrafluoroborates in arene solvent together with a phase-transfer catalyst, another is to use 1-aryl-3,3-dialkyltriazenes.
Pschorr reaction
One intramolecularIntramolecular
Intramolecular in chemistry describes a process or characteristic limited within the structure of a single molecule, a property or phenomenon limited to the extent of a single molecule.- Examples :...
variation which gives better results is the Pschorr reaction:
The group Z can be CH2, CH2CH2, NH and CO (to fluorenone
Fluorenone
Fluorenone is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C13H8O. It is used to make antimalaria drugs.It can be produced from fluorene via oxidation ....
) to name just a few.