
Goldstine theorem
Encyclopedia
In functional analysis
, a branch of mathematics, the Goldstine theorem, named after Herman Goldstine, asserts that the image of the closed unit ball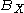 of a Banach space
of a Banach space
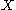 under the canonical imbedding into the closed unit ball
under the canonical imbedding into the closed unit ball 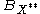 of the bidual space
of the bidual space
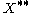 is weakly*
is weakly*
-dense
.
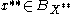 , a tuple
, a tuple 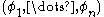 of linearly independent elements of
of linearly independent elements of 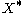 and a
and a 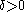 we shall find an
we shall find an 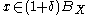 such that
such that 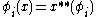 for every
for every 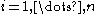 .
.
If the requirement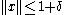 is dropped, the existence of such an
is dropped, the existence of such an  follows from the surjectivity of
follows from the surjectivity of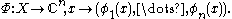
Let now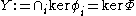 .
.
Every element of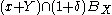 has the required property, so that it suffices to show that the latter set is not empty.
has the required property, so that it suffices to show that the latter set is not empty.
Assume that it is empty. Then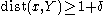 and by the Hahn-Banach theorem there exists a linear form
and by the Hahn-Banach theorem there exists a linear form 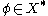 such that
such that 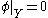 ,
, 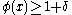 and
and 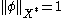 . Then
. Then 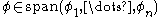 and therefore
and therefore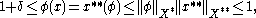
which is a contradiction.
Functional analysis
Functional analysis is a branch of mathematical analysis, the core of which is formed by the study of vector spaces endowed with some kind of limit-related structure and the linear operators acting upon these spaces and respecting these structures in a suitable sense...
, a branch of mathematics, the Goldstine theorem, named after Herman Goldstine, asserts that the image of the closed unit ball
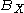 of a Banach space
of a Banach spaceBanach space
In mathematics, Banach spaces is the name for complete normed vector spaces, one of the central objects of study in functional analysis. A complete normed vector space is a vector space V with a norm ||·|| such that every Cauchy sequence in V has a limit in V In mathematics, Banach spaces is the...
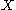 under the canonical imbedding into the closed unit ball
under the canonical imbedding into the closed unit ball 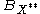 of the bidual space
of the bidual spaceDual space
In mathematics, any vector space, V, has a corresponding dual vector space consisting of all linear functionals on V. Dual vector spaces defined on finite-dimensional vector spaces can be used for defining tensors which are studied in tensor algebra...
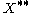 is weakly*
is weakly*Weak topology
In mathematics, weak topology is an alternative term for initial topology. The term is most commonly used for the initial topology of a topological vector space with respect to its continuous dual...
-dense
Dense set
In topology and related areas of mathematics, a subset A of a topological space X is called dense if any point x in X belongs to A or is a limit point of A...
.
Proof
Given an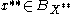 , a tuple
, a tuple 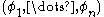 of linearly independent elements of
of linearly independent elements of 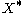 and a
and a 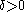 we shall find an
we shall find an 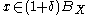 such that
such that 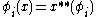 for every
for every 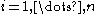 .
.If the requirement
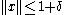 is dropped, the existence of such an
is dropped, the existence of such an  follows from the surjectivity of
follows from the surjectivity of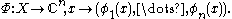
Let now
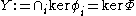 .
.Every element of
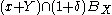 has the required property, so that it suffices to show that the latter set is not empty.
has the required property, so that it suffices to show that the latter set is not empty.Assume that it is empty. Then
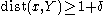 and by the Hahn-Banach theorem there exists a linear form
and by the Hahn-Banach theorem there exists a linear form 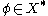 such that
such that 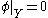 ,
, 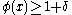 and
and 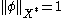 . Then
. Then 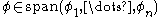 and therefore
and therefore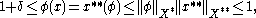
which is a contradiction.

